![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hormones
|
chemical messengers, secreted by endocrine glands directly into the blood which carries them to target cells
|
|
|
types of hormones
|
1. Steroids e.g. estrogen, progesterone, testosterone
2. Peptides e.g. Insulin, ADH, FSH, LH 3. Tyrosine derivatives e.g. thyroxin |
|
|
Mode of action of peptide hormones
|
- do not enter cells
- bind to receptors on the plasma membrane of the target cells - release of a secondary messenger inside cells - change to the activities of the cell, usually by activating and inhibiting enzymes |
|
|
Mode of action of steroid hormones
|
- pass through the plasma membrane of the target cell
- form a Hormone-receptor-complex (regulator of gene transcription by binding to specific genes) - transcription of some genes is promoted and other genes are inhibited |
|
|
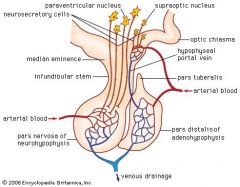
Draw the structure of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland
|
|
|
|
Hypothalamus
|
small part of the brain that links the nervous and endocrine systems
|
|
|
anterior pituitary
|
- neurosecretory cells secrete hormonones into capillaries in the Hypothalamus which are then carried by the portal vein to the anterior pituitary gland
--> releasing hormones stimulate the anterior pituitary to secrete hormones e.g. GnRH stimulates the release of FSH and LH |
|
|
posterior pituitary
|
- neurosecretory cells synthesize hormones
- passed via axons to nerve endings in the pituitary gland e.g. secretion of ADH is controlled in this way |
|
|
Control of ADH secretion
|
1. neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus synthesize ADH, transport it down their axons and store it in nerve endings in the posterior pituitary gland
2. osmoreceptors in the Hypothalamus monitor the concentration of the blood Plasma 3. ADH causes a reduction in the concentration of the blood plasma by stimulating the kidney to produce hypertonic urine 4. low blood concentration: release of ADH is not stimulated high blood concentration: release of ADH stimulated |
|
|
examples of exocrine glands
|
salivary glands, pancreas
|
|
|
digestion
|
chemical breakdown of large molecules into their components and Absorption
|
|
|
exocrine glands
|
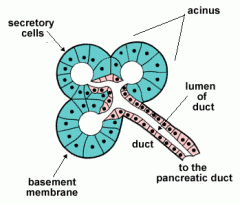
- secretory cells in a layer that is one cell tick
- digestive juices released by exocytosis - travels along ducts |
|
|
acinus
|
one group os secretory cells clustered around the end of a duct
|
|
|
feature of exocrine gland cells
|
1. one or two prominent nucleoli inside the Nucleus for production of ribosome subunits
2. extensive area for the RER 3. Golgi apparatus for processing Proteins 4. many large vesicles (secretory granules) 5. mitochondria |
|
|
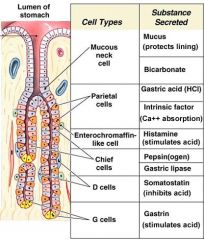
control of gastric juice secretion
|
- nervous and hormonal control
- sight and smell of food stimulates the brain to send nerve impulses to exocrine glands in the cell wall of the stomach, starts to secrete gastric juices - food detected by touch receptors in the stomach, by chemoreceptors and by stretch receptors, impulses send to brain which send more impulses to exocrine gland cells - secretion of a hormone called gastrin: stimulates the increase of the secretion of hydrochloric acid |
|
|
membrane-bound digestive enzymes
|
- produced by the cell wall of the small intestine, but are not secreted
- remain on the surface of the villi |
|
|
Digestive Juices/source and content
|
saliva/salivary glands/ salivary amylase, mucks
gastric Juice/glands in stomach wall/pepsinogen, hydrochloric acid, mucus pancreatic Juice/pancreas/pancreatic amylase, lipase, phospholipase, trypsinogen, carboxypeptidase |
|
|
Pepsin
|
pepsinogen + hydrochloric acid
|
|
|
trypsin
|
Trypsinogen + enterokinase
|
|
|
draw the structure of the stomach wall!
|
|
|
|
bile salts
|
- natural detergents
- hydrophobic end and hydrophilic end |
|
|
emulsification
|
process in which bile salts coat lipid droplets, causing them to break into smaller droplets
|
|
|
bile
|
- contains bile salts
- secreted by the liver - stored in the gall bladder - emulsifies lipids which speeds up their digestion |
|
|
Helicobacter pylori
|
acid-tolerant bacterium that infects the lining of the stomach, causes several diseases
|
|
|
stomach ulcers
|
- areas of damage to the lining of the stomach
- caused by H.pylori - proteases abd other enzymes that are released by H.pylori damage the stomach lining |
|
|
stomach cancer
|
- growth of tumours in the walls of the stomach
- caused by H.pylori - reduced vitamin C concentration in gastric juice - increase the chance of a tumour forming |

