![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Speed of light |
c = vh v = frequency h = wavelength C = 3x10^10 cm/s |
|
|
Energy of a photon |
E = hv h = Planks constant = 6.6x10^34 v = frequency of light wave |
|
|
Shorter wavelengths = ________ energy and refract _______. |
more and more Blue Bends More |
|
|
Critical angle (total internal reflection) |
sin(critical angle) = n'/n n air = 1 n water = 1.33 |
|
|
Vergence formula |
U + D = V U = object vergence D = Lens power V = Image vergence |
|
|
Lens power |
D = 1/f f = focal length (meters) |
|
|
Snell's Law |
nsin(i) = n'sin(r) n = refractive index i = angle of incidence r = angle of refraction |
|
|
Prismatic power |
/\ = (image deflection cm)/meters /\ = 100tan(B) B = angle of deviation |
|
|
Prentice's Rule |
/\ = hD h = distance from optical axis (cm) D = lens power |
|
|
Reduced schematic of the eye |
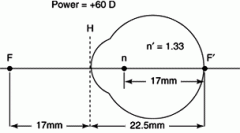
|
|
|
Calculation of retinal image size |
I/17mm = O/X I = Retina image size O = Object size X = Distance to object Set up like triangles |
|
|
Spherical equivalent |
SE = sphere + (cyl/2) |
|
|
Refracting power of a spherical surface |
Ds = (n' - n)/r n = refractive index to left n' = refractive index to right r = radius of curvature of surface (m) (+ is convex, - is concave) |
|
|
Reflecting power of a spherical mirror |
Dr = (-1/f) = (-2/r) f = focal length = (r/2) r = radius of curvature (- is convex, + is concave) |
|
|
Power of thin lens immersed in fluid |
Dair/Daqueous = (niol - nair)/(niol - naqueous) |
|
|
Power of lens at new vertex distance |
D2 = D1 + S(D1)^2 D1 = original power of lens D2 = new power of lens S = change in vertex distance (m) **S is + or - (V1 - V2) |
|
|
Linear Magnification |
ML = I/O I = image distance or height O = object distance or height |
|
|
Axial Magnification |
Max = (ML)^2 ML = linear magnification |
|
|
Angular Magnification |
Ma = xD x = distance D = power of lens |
|
|
Simple Magnifier (+ sphere lens) |
M+ = D/4 D = power of a simple plus lens ex. 1x magnifier = +4 lens; 2x = +8 lens |
|
|
Telescope Magnification |
Mtele = -De/Do De = eyepiece power Do = objective power |
|
|
Total accommodatoin through telescope |
Atotal = An(Mtele)^2 An = normal accommodation required Mtele = magnification of telescope |
|
|
SRK IOL power formula |
P = A - 2.5L - 0.9K A = constant for type of IOL L = axial length of eye K = average keratometry value |
|
|
Antireflective coating on glass |
Is 1/4 wavelength thick --> causes the reflecting light to be out of phase by 1/2 wavelength --> negative interference |
|
|
Convex lens is a _____ lens and gives _____ vergence |
plus and plus |
|
|
Concave lens is a ______ lens and gives _______ vergence |
minus and minus |
|
|
Cylindrical lenses power is ______ (@ or x) axis is ______ (@ or x) |
power is @ axis is x Power is @ 90 degrees from axis x |
|
|
How to convert from plus cyl to minus cyl notation |
1. add cylinder to sphere 2. switch the sign of cylinder 3. change axis of cylinder by 90 degrees |
|
|
What is the power cross for the following Rx: -4.00 + 3.00 x 180 |
-1.00 | ----------- -4.00 | |
|
|
Real image vs virtual image for a lens |
Real Image Virtual Image - Right of lens - Left of lens |
|
|
Image characteristics of plus (converging) Lens |
Image is Real & Inverted most of time. Exception: object distance < or = focal length will produce a virtual and upright image |
|
|
Image characteristics of a minus (diverging) lens |
Image is always virtual and upright Image is always smaller than the object |
|
|
Real image vs virtual image for a mirror |
Real Image Virtual Image - Left of mirror - Right of mirror opposite of lenses |
|
|
Image characteristics of convex (-) mirror |
Always - Virtual (right) - Upright - Minified |
|
|
Image characteristics of concave (+) mirror |
1. Object outside focal point - Real (left), Inverted, Mag/Min or same size 2. Object on focal point - No image 3. Object inside focal point - Virtual, Upright, Magnified |
|
|
Total magnification of a lens system |
Mtotal = M1xM2xM3.... |
|
|
Prism diopter = |
= cm of image displacement over a reference of 100 cm |
|
|
Galilean Telescope |
Eye piece: minus (high D) Object piece: plus (low D) Separation = subtract the two focal lengths Upright image |
|
|
Keplarian Telescope |
Eye piece: plus (high D) Object piece: plus (low D) Separation = add the two focal lengths Inverted image |
|
|
Which bifocal lens would you add to a + lens? |
Round top - minimizes displacement - still has jump |
|
|
Which bifocal lens would you add to a - lens? |
Flat top or executive - minimized both displacement and jump (always minimizes jump in both hyperopes and myopes) |
|
|
Spectacle lenses: Image size changes ____% for each 1D change in Rx |
2% + magnify - minify |
|
|
Prism: Image is displaced in which direction? |
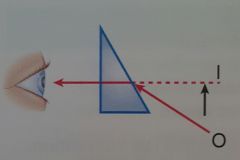
|
|
|
Age 40 has _____ D of accommadation |
6D |
|
|
Up to age 40, accommodation decreases by _____D every ____ years. |
decreases by 1 D every 4 years |
|
|
Between age 40 to 48, accommodation decreases by ____ D every ____ years? |
decreases by 1.5D every 4 years |
|
|
Above age 48, accommodation decreases by _____ D for every _____ years? |
decreases by 0.5D every 4 years |
|
|
Snellen denominator = _____ arcmins at that distance |
5 arcmins Ex. 20/60 >> letter subtends 5 arcmins at 60ft. So, at 20 feet it is bigger by 3x (60'/20') 3 x 5 arcmins = 15 arcmins on the retina |
|
|
Good soft contact lens has _____ fit? |
3-point touch Lightly touches apex and limbus on both sides |
|
|
Define aniseikonia |
Unequal magnification (size) of images projected on the retina due to difference in spectacle correction between eyes. Can tolerate up to 7-8% difference in image size. This is approximately 3D difference between each eye. |
|
|
List the methods to reduce cylinder-induced asthenopia and distortion |
1. Use minus cylinder form 2. Minimize the vertex distance 3. Decrease cyl power while keeping the proper spherical equivalent 4. Rotate the axis of the correcting cyl towards 90 or 180 |
|
|
When performing retinoscopy, as neutralization is approached, the light beam becomes _______, _________ & __________. |
brighter, wider & faster
|
|
|
AC/A ratio by Gradient Method formula |
AC/A = (deviation c lens - deviation s lens) / (lens power) |
|
|
Power of a thick lens |
Pfront + Pback - [(t/n) x (Pfront x Pback)] t = thickness of lens in meters n = refractive index of lens |
|
|
Zero order aberrations: |
Piston |
|
|
First order aberrations: |
Prism |
|
|
Second order aberrations: |
Myopia (positive defocus) Hyperopia (negative defocus) Regular astigmatism |
|
|
Third order aberrations: |
look these up |
|
|
Fourth order aberrations: |
look these up |

