![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
sclera
|
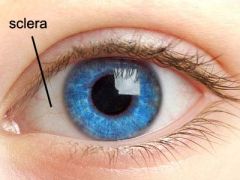
white, outermost layer of eye
|
|
|
uvea
|
beneath sclera, made of iris, ciliary body and choroid
|
|
|
iris
|
colored portion of eye
|
|
|
lens
|
portion of eye that helps light refract
|
|
|
conjunctiva
|
covers inner surface of eyelid & sclera
highly vascularized |
|
|
cornea
|
crystal clear portion of eye surface (allows light to enter)
|
|
|
macula
|
area of acute central vision
|
|
|
retina
|
nerve tissue
contains the rods & cones of eye |
|
|
choroid
|
vascular layer between retina & sclera
|
|
|
aqueous humor
|
fluid in front of eyes
|
|
|
vitreous humor
|
fluid-like gel behind the lens of the eye
(also present in front of eye) |
|
|
blood-retinal barrier
|
restricts drug transport to retina
not affected by inflammation |
|
|
blood-aqueous barrier
|
barrier within eye that acts like blood-brain barrier
inflammation causes breakdown |
|
|
mydriatics
|
agents that cause contraction of muscles to enlarge pupils
|
|
|
cycloplegics
|
agents that relax muscles in the eye to make pupils constrict and lens focus
|
|
|
glaucoma
|
open-angle & angle closure
Disease that leads to optic neuropathy characterized by changes in the optic nerve leading to visual loss. 2nd leading cause of blindness in US. Characterized by C/D ratio <0.5 and increased IOP |
|
|
How do you treat glaucoma?
|
Prostaglandins/Prostamides & beta-blockers are first line therapy.
Alpha-2 adrenergic agonists Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Parasympathomimetics Non-specific Adrenergic Agonists |
|
|
Prostaglandins/Prostamides
|
Decrease IOP by 25-35% by increasing uveoscleral outflow of aqueous humor.
Adverse reactions: 1. Can change iris pigmentation (typically individuals with mixed colored eyes) 2. hypertrichosis 3. hyperpigmentation of eye lids examples: latanoprost (frig), travaprost, bimatoprost, tafluprost (frig) |
|
|
Beta-Blockers
|
Decrease IOP 20-30% by reducing aqueous humor production in ciliary body.
Adverse Reactions: 1. dry eyes, coreal anesthesia, blepharitis, blurred vision, stinging systemic absorption: decreased heart rate, decreased blood pressure, negative ionotropic effects, bronchospasm, block sx of hypoglycemia Examples: timolol, betaxolol, carteolol, levobunolol, metipranolol |
|
|
Alpha-2 Adrenergic Agonists
|
Reduce IOP by 18-27% by reducing aqueous humor production and increasing uveoscleral outflow (brimonidine).
Adverse Reactions: allergic type, lid edema, eye discomfort, foreign-body sensation, itching, hyperemia Systemic absorption: dry mouth, lower BP, fatigue, dizziness. Examples: brimonidine, apraclonidine |
|
|
Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
|
Decrease IOP by 15-26% topically and 25-40% (systemically) by decrease aqueous humor inflow by blocking the secretion of sodium and bicarbonate ions from the ciliary body to the aqueous humor.
Adverse Reactions: blurry vision, stinging, tearing Systemic Absorption: malaise, fatigue, depression, nausea, anorexia, weight loss, metallic taste, acidosis, electrolyte imbalance, increase uric acid Examples: brinzolamide, dorzolamide, acetazolamide, methazolamide |

