![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
299 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The main reason why the patient is visiting the doctor in the patient’s own words is called the __________. |
Chief complaint
|
|
|
Name at least five areas of good history taking.
|
1.Chief complaint/history of present illness 2.Past ocular history3.General medical history/social history 4.Family ocular/medical history 5.Allergies/medications/vitamins/supplements |
|
|
Name at least four categories of ocular history-related questions you may ask the patient. |
1. History of glasses/contact lenses 2. Surgery to either eye 3. Trauma/eye condition 4. Topical/oral medications for the eye |
|
|
Name at least 3 categories of general medical and social history-related questions you may ask the patient.
|
1. Current/past medical conditions.
2. Current/past medications 3. Surgery/treatment for medical conditions 4. Pregnancy/Nursing (women) 5. Smoking/alcohol/drug use6. Patient’s occupation/hobbies |
|
|
An APD is noted on the patient’s previous chart notes. Before instilling drops, what should the technician check? |
Pupil exam including: 1. Pupil size 2. Speed of pupil constriction to light 3. Pupillary response to near fixation 4. Direct and consensual pupillary reaction |
|
|
Name at least 3 common medical conditions that can affect the patient’s vision. |
1. Diabetes Mellitus 2. Hypertension 3. Cancer/other neoplasm 4. Cardiovascular disease 5. Hyperthyroidism |
|
|
Why is it important to note all prescribed and non-prescribed medications for a patient who is scheduled for ocular surgery? |
Some medications have ocular side effects and some reduce the blood’s ability to clot, potentially causing complications during surgery. |
|
|
True or False: You can assume the person accompanying the patient during the eye exam is someone to whom you may release medical information. |
False. Ask the patient and document to whom you may release the patient’s medical information. |
|
|
How should the technician respond when a returning glaucoma suspect with an IOP reading of 32mmHg at today’s visit, asks you if he has glaucoma? |
The technician should defer to the ophthalmologist for a diagnosis and medical advice. |
|
|
Define HIPAA. |
(Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) 1996 act sets rules for patient privacy, security of health information, & health insurance shifts after leaving an employer. Severe penalties for non-compliance. |
|
|
What is the difference between a sign and a symptom? |
A sign is an objective observation of the patient’s condition as noted by the examiner. A symptom is a subjective observation noted by the patient, such as how well they see or feel. |
|
|
What are the 10 general types of mechanisms of disease and injury? |
1. Infectious 2. Inflammatory 3. Allergic 4. Ischemic 5. Metabolic 6. Congenital 7. Developmental 8. Degenerative 9. Neoplastic 10. Traumatic |
|
|
Why is it important to gather a family history on the patient? |
Various disease processes develop in children or adults due to genetic (inherited) disorders. |
|
|
Name at least 5 different sources of ocular trauma. |
1. Contusions/abrasions 2. Blow (blunt force) 3. Foreign body 4. Thermal injury 5. Chemical injury 6. Toxins |
|
|
What is the difference between hypopyon and hyphema? |
Hypopyon is a pool of pus in the anterior chamber. Hyphema is a pool of blood in the anterior chamber. |
|
|
Describe the symptoms of a patient undergoing an acute angle closure episode. |
Severe ocular pain, redness, blurred vision, rainbow colored halos around lights, headache, nausea, vomiting. |
|
|
What important questions should you ask the patient who has a chief complaint of double vision? |
1. Are there two separate objects instead of one? 2. Is the double vision still noticeable when one eye is covered? 3. Is the 2nd image horizontal or vertical from the main image? 4. When did the double images begin? |
|
|
What is the name of the test used for detecting a RAPD (relative afferent pupillary defect)? |
Swinging Flashlight Test |
|
|
Which muscle of the iris constricts in bright light? |
Iris Sphincter |
|
|
What is the term used for the spasmodic rhythmic dilating and contracting pupillary movements during pupil function testing? |
Hippus |
|
|
What is the term for pupil dilation? |
Mydriasis |
|
|
What is the term used when there is a difference in pupil size? |
Anisocoria |
|
|
What four characteristics of the pupil should be noted? |
Size, shape, reaction to light, reaction to near |
|
|
Which cranial nerve innervates the iris sphincter and dilator muscles? |
CNIII, oculomotor |
|
|
Irregularities in the shape of the pupil may come from __________. |
Congenital abnormalities, inflammation of the iris, trauma, or surgical intervention. |
|
|
A difference in pupil response to direct stimulation from each eye is known as __________. |
A relative afferent pupillary defect (RAPD) or Marcus-Gunn pupil |
|
|
In ordinary room light, what is the diameter of the normal adult pupil? |
Between 3-5 mm |
|
|
Mydriasis, ptosis, and anhydrosis are characteristics of __________ syndrome. |
Horner's |
|
|
Pupils that are small, irregular-shaped, non-reactive to direct or consensual light, but react to near stimulation are signs of what? |
Argyll-Robertson pupils, found in late syphilis. |
|
|
What does the pupil look/act like in an acute glaucoma attack? |
Mid-dilated and poorly reactive. |
|
|
The Swinging Flashlight Test is used to evaluate what two types of reaction to light? |
The direct ad consensual pupillary reaction. |
|
|
What percentage of the population has anisocoria? |
Approximately 10% of the population has a difference in pupil size. |
|
|
What is the impact of increasing the diameter of a contact lens without adjusting the base curve? |
The increased sagittal depth will effectively tighten the fit. |
|
|
The diffusion of oxygen through a contact lens material is referred to as __________. |
DK Value |
|
|
Name the three different toric designs available in rigid materials. |
Front toric, back toric, bitoric |
|
|
What rigid lens position is more acceptable, high riding or low riding? |
High riding |
|
|
True or False: The application and evaluation of a diagnostic lens on the eye is the best way to fit a contact lens? |
True. |
|
|
True or False: Rigid lens fitting nomograms may help determine the initial base curve to be evaluated if a diagnostic lens is not available. |
True. |
|
|
Name the instrument used to determine posterior surface radius of curvature of a rigid contact lens. |
Radiuscope and/or Contacto Guage. |
|
|
What slit lamp filter is used in conjunction with fluorescein to evaluate fluorescein patterns with rigid and silicon hydrogel contact lenses? |
Cobalt/UV |
|
|
Name three reasons to dispense a therapeutic bandage contact lens. |
1. Protect cornea from eyelids and eyelashes 2. Promote corneal healing 3. Provide comfort 4. Stop wound leaks 5. Improve vision 6. Drug delivery |
|
|
What is used to check the calibration of the manual keratometer? |
Metal test spheres provided by the manufacturer with known radius of curvature. |
|
|
The accessory lenses on the outside of the phoropter casing can be cleaned with __________ and __________. |
Photographic lens cleaner, lens tissue |
|
|
List ways to clean the dust off of the lenses or a manual lensmeter: |
1. Blowing the dust off with a clean, rubber bulb syringe 2. A dust brush 3. Compressed canned air |
|
|
True or False: The internal trial lenses of the phoropter can be cleaned with alcohol. |
False. Never use alcohol on any of the phoropter lenses. |
|
|
An alternative to cleaning the applanation tonometer tip with an alcohol sponge is to soak the prism tip for 5 minutes in what two solutions? |
Either in 3% hydrogen peroxide or in 1:10 dilution of household bleach and water. |
|
|
What is used to check calibration of the Goldmann-type applanation tonometer? |
Check the tonometer for calibration using the manufacturer-supplied controlled calibration bar that came with the instrument. |
|
|
What is the best method for storing a Tonopen? |
Store the Tonopen with a tip cover over the tip and handle with care. |
|
|
What should you avoid doing when changing light bulbs for ophthalmic instruments? |
Avoid using your bare hands, as the oil from your fingertips can etch an instrument bulb and diminish the effectiveness and life of the bulb. |
|
|
The light on the slit lamp does not come on, what is the first thing you should check? |
First check all electrical connections. |
|
|
What five things should you check if an electrical instrument fails to work? |
1. Is the electrical connection to the outlet secure? 2. Is the electrical connection to the instrument secure? 3. Is the bulb burned out or darkened? 4. Did the instrument blow a fuse? 5. Is the outlet/electrical fuse working? |
|
|
What two things should you check if battery-operated equipment fails to work? |
1. Is the battery fresh/recharged? 2. Is the bulb burned out or darkened? |
|
|
Name four examples of lenses that contact the eye and may require disinfection or sterilization. |
1. Diagnostic and contact lenses 2. Fundus contact lens 3. Gonio lens 4. Koeppe lens |
|
|
Why is it important to have optical center alignment when performing lensometry? |
Incorrect placement induces prism. |
|
|
What is Prentice’s rule? |
It is a formula to evaluate prism induced by decentration of optical center. |
|
|
True or False: The higher the refractive error, the more important the placement of optical centers. |
True |
|
|
Which type of prism is better for short term use? |
Fresnel press on prism |
|
|
What is the highest range of fresnel press on prism? |
40 diopters |
|
|
What is the highest range for ground-in prism? |
10 diopters in each lens |
|
|
What is the Prince rule used to measure? |
Near Point of Accommodation |
|
|
Where is vertex distance usually measured? |
Back surface curvature of the lens to front surface of the center of the eye. |
|
|
If a right lens is displaced to the right of the 2nd circle, how much prism is in the lens? |
2 Diopters, Base in |
|
|
What are two characteristics of a minus lens image? |
Erect (right side up), virtual |
|
|
What does Snell’s Law determine? |
Index of refraction: Speed of light in air ------------------------------- Speed of light in a substance |
|
|
What is the formula for prism displacement? |
P=C/D Where: P=prism power C=displacement of object in centimeters D=distance of the prism in meters. |
|
|
What is the refractive index of crown glass? |
1.523 |
|
|
What kind of astigmatism is represented by a minus spherical lens and a minus cylindrical lens? |
Compound myopic astigmatism. Example.) -2.00 -1.00 x 180 or -3.00 + 1.00 x 090 |
|
|
The prescriptions +1.00 – 3.00 x 180-2.00 + 3.00 x 090Represent what type of astigmatism? |
Mixed astigmatism |
|
|
What type of corneal astigmatism does the following demonstrate? 45.00 @ 180 / 46.50 @ 90 |
With the rule |
|
|
What amount of corneal astigmatism does the following demonstrate? 44.00 @ 18 / 46.50 @ 108 |
2.5 diopters |
|
|
The distance between the two points at the edge of the reflected mire of the surface being measured is referred to as the __________ __________. |
Chord length |
|
|
When evaluating the mire reflection of the corneal surface, a longer chord length demonstrates what two things? |
Flatter corneal curvature Larger mire |
|
|
Turning the observer’s eyepiece focus dial back and forth will stimulate __________ and result in a false setting that may affect __________. |
Accommodation, the accuracy of the readings |
|
|
True or False: With traditional methods of patient fixation, the readings will always be the apex of the cornea. |
False. There are a number of corneal conditions that the apex of the cornea will not measure. Alternative methods of fixation will be necessary to find the corneal apex. |
|
|
The range of the keratometer may be extended with auxiliary lenses. What loose lens should be attached over the aperture of the instrument to extend the limit from 52D to 61D? |
+1.25 D with the plano lens surface mounted toward the aperture. |
|
|
How many meridians are measured in keratometry? |
Two. (90˚ apart in cases of regular corneal astigmatism) |
|
|
What is the first step in keratometry? |
Focus the eyepiece. |
|
|
The range of the keratometer may be extended with auxiliary lenses. What loose lens should be attached over the aperture of the instrument to extend the limit from 36D to 30D? |
-1.00 D with the plano lens surface mounted toward the aperture |
|
|
Does the mire reflection of a steeper corneal surface reveal a smaller or larger reflex? |
Smaller. The chord length of the steeper cornea is shorter, resulting in a smaller mire reflection. |
|
|
True or False: The principle of keratometry involves the utilization of the properties of the anterior surface of the cornea as a highly polished convex spherical mirror. |
True. To measure the radius of curvature, a target or mire of known size is placed at a known distance. |
|
|
The difference between the two meridians is the amount of corneal __________. |
Astigmatism |
|
|
What is the name of the code of rules and customs to which physicians are expected to adhere? |
Hippocratic Oath |
|
|
Name one principle of medical ethics. |
Autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence, justice, and truth |
|
|
During informed consent, the physician must discuss all __________ no matter how minimal, uncommon, or severe. |
Risks |
|
|
Name two primary roles and responsibilities of the OMP. |
Collect data Perform clinical evaluation as authorized by the physician |
|
|
Ophthalmic technicians are usually knowledgeable about the findings of a test, the __________ makes the diagnosis and estimates the prognosis and discusses with the patient. |
Physician |
|
|
When a procedure or test is recommended to the patient by a physician, an informed consent is obtained giving the physician permission to perform. Who obtains informed consent? |
The physician |
|
|
If a patient calls the office with an emergency problem and the physician is not available, what should the technician do? |
The patient should be referred to another ophthalmologist or emergency room. |
|
|
True or False: Physicians and staff should never criticize the work of another physician. |
True |
|
|
Name two principles of autonomy. |
Principle of disclosure Principle of informed consent |
|
|
True or False: Physicians have a legal obligation to report suspicion of child abuse. |
True |
|
|
If staff makes an error, should it be reported? |
Absolutely; staff should be encouraged to disclose medical errors. |
|
|
Name the four most common microorganisms associated with eye disease. |
Bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa |
|
|
Bacteria can be classified by their reaction when exposed to dyes. Name these dyes procedures. |
Gram Staining and Geisma Staining |
|
|
Name a common Gram-positive bacterium that is a frequent cause of blepharitis, conjunctivitis, and infectious keratitis. |
Staphylococcus aureus |
|
|
Name a Gram-negative organism associated with contact lens overwear. |
Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
|
|
Which virus commonly causes “fever blisters” on the lips and mouth and is responsible for most of the lesions of the cornea and eyelids? |
Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 |
|
|
The protozoan, __________, can be found in homemade contact lens solutions and can cause painful infections of the cornea. |
Acanthamoeba |
|
|
Why must a specimen be collected for testing before empiric treatment can be started? |
Treatment might interfere with the ability to obtain and identify the disease-causing organism. |
|
|
Name the four main components of aseptic technique. |
1. Sterilization of equipment 2. Sterilization of skin adjacent to operative site3. Sterilization of hands of surgeon and assistant4. Use of sterile solutions and ointments during and after the operation |
|
|
Differentiate between disinfection and sterilization. |
Disinfection is the process of inactivation or eliminating most disease-causing organisms. Sterilization is the killing of all living organisms. |
|
|
A __________ is a chemical that kills germs. |
Germicide |
|
|
According to OSHA Universal Precautions, what solution is used to clean spills of blood or blood-containing body fluids on a smooth surface? On a porous surface? |
Household bleach and water in a 1:100 ratio for smooth surfaces 1:10 ratio for porous surfaces |
|
|
What is the most notorious or potentially damaging organism to contaminate ophthalmic solutions? |
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa |
|
|
Subconjunctival injections are used primarily to treat what condition? |
Intraocular infections and inflammation |
|
|
What medication route is used to treat conditions such as cellulitis, uveitis, and acute allergic reactions? |
Treatment of medication may be given by route of injection (subcutaneously, intramuscularly, or intravenously). |
|
|
Autonomic drugs that affect the eyes are divided into what 3 agents? |
Mydriatic, Cycloplegic, and Myotic agents |
|
|
Why are cycloplegic drops essential in the refraction of children’s eyes? |
They paralyze the ciliary muscle so that the eye is no longer able to accommodate. |
|
|
Mydriatic drops act on what musculature to dilate the pupil? |
Iris dilator muscle |
|
|
What mydriatic agent can be used in establishing the diagnosis of Horner’s Syndrome? |
Paredrine or cocaine eye drops |
|
|
Timolol is used in glaucoma management by decreasing what? |
The formation of aqueous humor |
|
|
The most common side effects of Glycerol (glycerin) are what? |
Nausea, vomiting, and headaches |
|
|
What type or class of medication is used for the treatment of Herpes Simplex of the cornea? |
Anti-viral agents such as acyclovir tablets, Viroptic®, vidarabine (Vira-A®) ointment |
|
|
When is topical fluorescein used? |
An ocular stain used to show defects or abrasions in the corneal epithelium and to obtain intraocular pressure by Goldmann applanation. |
|
|
What are the common routes of giving medication to obtain an effect on the eye? |
Topical (drops and ointments); subconjunctival, intracameral, retrobulbar, and intravitreal injections, oral, and continuous-release delivery |
|
|
What is the generic name for the carbonic anhydrase inhibitor Diamox? |
Acetazolamide |
|
|
Why are topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) sometimes preferred over corticosteroids? |
They often achieve the required anti-inflammatory effect without the undesirable side effects, such as elevating the intraocular pressure (IOP), with long term use. |
|
|
What is the ocular stain used to identify defects on the conjunctiva? |
Lissamine Green stain |
|
|
While conducting the Worth 4-dot test, what does it indicate when a patient only sees two dots? |
2 dots seen= left eye (eye behind the green lens) is suppressing. |
|
|
The condition in which eyes shift involuntarily in a rhythmic, beating motion is called __________. |
Nystagmus |
|
|
What is stereopsis? |
Stereopsis is the visual blending of two similar (not identical) images, one falling on each retina, into one, with visual perception of solidarity and depth. |
|
|
How does the Maddox Red dissociate the eyes and prevent fusion? |
It changes the size, shape, and color of a point of light to a line (a streak) of light so that fusion is impossible. |
|
|
What is the near point of convergence? |
NPC is the point at which fusion can no longer be maintained and one eye deviates outward; causing double vision. |
|
|
What is the near point of accommodation? |
NPA is the position closest to the eye where a small object (usually small print) can be kept in sharp focus by maximal accommodation. |
|
|
What is the difference between versions and ductions? |
Version is the parallel movement of BOTH eyes in any direction. Duction is the range of movement of ONE eye (in any direction) considered independently from movement of the other eye. |
|
|
What is fusional convergence amplitude? |
Amount the eyes can turn inward (toward each other) before double vision occurs. Measured in prism diopters. |
|
|
When using prisms to measure the magnitude of strabismus, is the apex of the prism placed in the same or opposite direction of the eye turn? |
The apex is placed in the same direction as the eye turn. |
|
|
Name the cranial nerve that innervates each of the 6 ocular muscles. |
CN III: Superior Rectus, Inferior Rectus, Inferior Oblique, Medial Rectus CN IV: Superior Oblique CN VI: Lateral Rectus |
|
|
After estimating misalignment by conducting the Hirschberg test, you could use prisms to conduct the __________ test to equalize the corneal reflexes. |
Krimsky |
|
|
What is the difference between a tropia and a phoria? |
A tropia is a misalignment that continually manifests, while a phoria is a misalignment found only when covering one eye. |
|
|
What are two common treatments for strabismic amblyopia that may be effective for children up to age six? |
Place a patch over the dominant eye or use eye drops that blur the dominant eye, forcing the amblyopic eye to work. |
|
|
Name the primary and secondary actions of the superior oblique muscle. |
Primary action: Intorsion (rotation downward and inward toward the nose) Secondary action: Depression and abduction |
|
|
What is the term for the movement of both eyes to the left? |
Levoversion |
|
|
Name a solution that is used to disinfect eyelid skin. |
Betadine (Providone-iodine), Ioprep, alcohol, tincture of iodine 2%, pHisoHex |
|
|
What instrument is used to grasp small tissues for either removal or suture insertion? |
Forceps |
|
|
Name the instrument that has a slim handle and bowl-shaped end, either round or serrated, used to remove chalazia and other small cystic material. |
Curet |
|
|
An eye patch applied correctly will prevent __________ and __________. |
Further bleeding, lid edema |
|
|
Name two instruments used for lacrimal irrigation. |
Punctum dilator, lacrimal needle, or lacrimal probe |
|
|
A patient with trichiasis may have this procedure done to permanently remove eyelashes. |
Electrolysis |
|
|
What conditions may arise during or following a minor procedure that may immediate first-aid? |
Fainting, respiratory emergency, allergic reaction, drug reaction, central nervous system stimulation (tremors, convulsions, excitability) |
|
|
What laser is used to coagulate blood or seal off blood vessels? |
Argon laser or blue-green light laser |
|
|
Name three mechanisms of medical lasers that produce tissue damage. |
Thermal, photodisruptive (ionizing), and photochemical |
|
|
What protective equipment is worn to prevent accidental laser exposure to all onlookers (patients, technicians)? |
Laser eye protection (laser goggles) |
|
|
Name four main methods of infiltration anesthesia. |
Nerve block, retrobulbar, peribulbar, direct infiltration subcutaneousl. |
|
|
Name two muscle surgeries that strengthen an extraocular muscle. |
Resection, advancement |
|
|
An A-scan is performed prior to intraocular surgery to assist in determining what? |
Axial length, which is needed to calculate intraocular lens power |
|
|
What condition is a true ocular emergency following cataract surgery when a patient presents with symptoms of a painful red eye and decreased vision within the first week? |
Endophthalmitis |
|
|
What is the name of the glaucoma surgery that permits aqueous to filter out of the anterior chamber and a form of conjunctival bleb? |
Trabeculectomy |
|
|
Name three common errors in aseptic surgical technique with masks and caps. |
Mask covering mouth only and not the nose; mask too loose; hair protruding from cap |
|
|
What is the minimum brush stroke for every portion of the hand when surgically scrubbing? |
20-30 strokes |
|
|
What is the definition of sterilization? Complete destruction of all microorganisms within or about an object |
Complete destruction of all microorganisms within or about an object |
|
|
What are the most commonly used sterilization methods in ophthalmology? |
Autoclave (moist heat), boiling, dry heat, chemical, gas, radiation, ultraviolet |
|
|
What is the difference between enucleation and evisceration? |
Enucleation is total removal of the eye globe.Evisceration is removal of the contents only, leaving the outershell with the muscles attached. |
|
|
What will the patient sign prior to surgery that outlines the procedure, risks, benefits, and possible complications? |
Informed Consent Form |
|
|
Which systemic disease is associated with the eye findings referred to as Graves’ Disease? |
Thyroid Disease |
|
|
Which disease is indicated by the presence of microaneurysms, dot and blot hemorrhages, and lipid exudates from a leakage of the retinal vessels? |
Background Diabetic Retinopathy (Systemic Disease- Diabetes) |
|
|
Name two indications that a contact lens solution is causing a toxicity or hypersensitivity. |
Conjunctival redness, punctate keratopathy or corneal infiltrates. |
|
|
When eye drops are administered, what is the procedure that will eliminate contamination? |
The tip of the eyedropper does not touch the lashes or the eye or any other surface. |
|
|
Who signs the Informed Consent Form prior to surgery? |
The physician, patient (or legal guardian), and a witness |
|
|
What is a major cause of patient dissatisfaction? |
Time spent waiting in the reception area, unmet expectations |
|
|
Name an urgent symptom that needs to be seen the same day. |
Painful red eye; swollen eyelid; flashes of light; sudden double vision or lid droop |
|
|
A patient calls complaining of halos around lights. When should the patient be scheduled? |
This is a priority case to be seen within days |
|
|
What questions would you ask the patient when performing the Amsler grid? |
Is the center spot visible? While viewing the center, can you see all four sides? Do you see the entire grid? Are the horizontal and vertical lines straight and parallel? |
|
|
What is the proper procedure for patching an eye post cataract surgery? |
An eyepad is in place with strips of tape on an angle from the cheek to the forehead. A plastic or metal shield is commonly placed over the eyepad. |
|
|
When instilling more than one eye drop, how long should a patient be instructed to wait between eye drops? |
Wait one minute with eye closed |
|
|
At what age does a child quickly respond to occlusion therapy for amblyopia? |
Ages 1-3 |
|
|
What should be done for your patient that becomes unconscious in the office? |
Begin basic life support. |
|
|
How does the ophthalmic assistant assist the blind patient to the examination room? |
Introduce yourself and offer your arm to the blind person. |
|
|
What should the patient be instructed to do to reduce the systemic absorption of eye drops? |
Punctal Occlusion- Block tear duct at inner canthus with fingertip covered by tissue as drop is being instilled. |
|
|
What should be done to assist a patient who faints in the office? |
Place patient’s head between knees; loosen a tight collar; give smelling salts or ammonia; have patient remain in office 20-30 extra minutes to regain composure. |
|
|
Name a medication that should be kept on hand in case of severe allergic reaction to a drug. |
Epinephrine; intravenous cortisone; Benadryl |
|
|
A patient calls with a chemical contact to the face and eyes. What would be your instruction to this patient? |
Irrigate. Ex: Fill basin or tub with tap water and immerse patient’s head into the water with eyes open under water; water does not have to be sterile for irrigation; shower, sink or anywhere to rinse the eye thoroughly. |
|
|
What instructions should be given to a patient prior to visual field testing? |
Focus on target, do not look around for light, explain to patient what to expect (one of the greatest sources of error is patient not knowing what to expect) |
|
|
Name three true emergencies that should be treated within minutes. |
Chemical burn to eyes, central retinal artery occlusion, penetrating injuries to the eye, sudden loss of vision |
|
|
Using reflected light from the fundus is an excellent technique with which to demonstrate a variety of findings in the lens and cornea. What is this technique called? |
Retro-illumination |
|
|
What filter is used to enhance visibility of the external tissues of the eye when using fluorescein dye? |
Exciter filter |
|
|
For greater reflection intensity to view the lens and cornea, what internal structure can serve as a brighter reflecting surface? |
Optic Nerve |
|
|
Fluorescein angiography requires a fluorescein filter set consisting of what? |
An exciter filter and a barrier filter |
|
|
When photographing the patient’s name tag, which filter and what flash setting should be used? |
A green filter and low flash setting |
|
|
A controlled photograph for pseudofluorescence and autofluorescence is taken with the flash setting for fluorescein and with what filters? |
Both the exciter filter and the barrier filter |
|
|
What are the phases of fluorescein angiography? |
Choroidal, arterial, arteriovenous, and late phase |
|
|
Oral fluorescein discloses which phase of angiography? |
Late phase |
|
|
The arm-to-retina time is usually how many seconds? |
8-16 seconds |
|
|
How do you eliminate a crescent shaped artifact? |
Move the camera in the opposite direction of the artifact. |
|
|
A centrally located spectral reflectance and haze along the periphery of the image area is a result of what? |
Excessive camera-to-cornea distance |
|
|
Short, light-colored streaks arising from the top or bottom of the frame are due to what? |
Patient’s lashes or hair |
|
|
What dyes are primarily used to perform ocular angiography? |
Fluorescein sodium and ICG |
|
|
Fluorescein sodium is available in what two different concentrations? |
10% and 25% |
|
|
What other mild adverse reaction can occur besides a vasovagal response? |
Nausea, vomiting |
|
|
What other moderate adverse reaction can occur besides fainting and phlebitis? |
Hives (Urticaria) |
|
|
If a patient experiences stinging or burning around the injection site, what would be the most likely cause? |
Extravasation of the dye |
|
|
If the posterior pole cannot be visualized, which instrument would be requested? |
B-scan |
|
|
When performing a B-scan, some echoes, such as vitreous membranes, may not be visible if which setting is too low? |
Brightness |
|
|
When performing a B-scan, what would cause reverberation in the eye being scanned? |
Insufficient coupling |
|
|
Does a prism bend light rays toward the base of the prism or toward the apex of the prism? |
Toward the base |
|
|
The power of a prism to bend light depends on the size of the angle at the apex of the prism. In what units is the power of the prism measured? |
Prism diopters |
|
|
What does the formula P=C/D represent? |
This formula explains the relationship between the power of a prism and the ability to bend light. P is prism diopters. C is the displacement of the object in centimeters, and D is the distance between the prism and the virtual image in meters. |
|
|
Two prisms placed base-to-base form the basis of what type of lens? |
Convex (plus) |
|
|
What do convex lenses do to light rays? |
Converge them |
|
|
Two prisms placed apex-to-apex form the basis of what type of lens? |
Concave (minus) |
|
|
What is the Prince rule used to measure? |
Near point of accommodation, and bifocal and trifocal add power |
|
|
What is Prentice’s rule? |
It is a formula to calculate induced prismatic effect caused by spectacle lenses whose optical centers have been decentered so they are not in line with a patient’s visual axis (pupil center). The formula is: Induced prism (in prism diopters) = lens power (in diopters) x optical center displacement (in cm) |
|
|
Find the total amount of prism induced in the following situation: Glasses Rx: OD +12.00 sph; OS +10.00 sph; Both optical centers are displaced 5 mm temporally (decentered out). |
OD has 6 prism diopters Base Out. OS has 5 prism diopters of Base Out. The total is 11 prism diopters of Base Out. |
|
|
What do concave lenses do to light rays? |
Diverge them |
|
|
What is the focal length (in meters) of a 3 diopter lens? |
P=1/f (meters), 3=1/f (meters), 3f (meters) = 1, f (meters) = 1/3, or 33 cm |
|
|
The stronger the power of a plus lens, the (more/less) distance it needs to focus. |
Less |
|
|
What does Snell’s law determine? |
Whether the refracted ray will be bent toward the normal or away from it |
|
|
What does index of refraction (IR) compare? |
Ratio: Speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in a given substance |
|
|
What is astigmatism? |
A refractive error caused by the non-spherical (cylindrical) surface of the cornea or lens, or both |
|
|
“With the rule” astigmatism is corrected by plus cylinders at or near which axis? |
90 degrees |
|
|
“Against the rule” astigmatism is corrected by plus cylinders at or near which axis? |
180 degrees |
|
|
Name the clinical procedure performed by ophthalmic personnel for determining a patient’s refractive error. |
Refractometry |
|
|
When using a streak retinoscope, if you see “with” motion, this indicates the need to place what kind of lens power in front of the eye? |
More plus power |
|
|
When using a streak retinoscope, if you see “against” motion, this indicates the need to place what kind of lens power in front of the eye? |
More minus power |
|
|
Polarized lenses block all light rays except those that do what? |
Vibrate in the same direction |
|
|
Are Fresnel prisms usually applied to the front or the back surface of a patient’s eyeglasses? |
The back surface |
|
|
Name the variable focusing power of the eye provided by the flexibility of the crystalline lens. |
Accommodation |
|
|
Clinically, infinity is determined to be at what distance? |
20 feet (6 meters) and beyond |
|
|
How is astigmatism corrected? |
With spherocylindrical lenses |
|
|
What is the spherical equivalent of the following prescription?: +2.00 + 1.50 x 090 |
+2.75 sphere |
|
|
Transpose the following eyeglass Rx into minus cylinder form: +2.00 + 1.00 x 093 |
+3.00 –1.00 x 003 |
|
|
Transpose the following eyeglass Rx into minus cylinder form: -2.00 + 1.25 x 173 |
-0.75 – 1.25 x 083 |
|
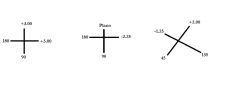
Give the prescription represented by the following optical crosses:
|
a.) +3.00 sphere b.) -2.25 + 2.25 x 180 or pl -2.25 x 090 c.) -1.25 +3.25 x 135 or +2.00 – 3.25 x 045 |
|
|
What eye measurement is one of the primary factors in calculating the optimal IOL power? |
Axial length measurement |
|
|
In order to perform the IOL calculations, what other piece of information is required besides A-scan biometry and keratometry readings? |
A-constant |
|
|
On a preliminary examination, without a slit lamp, how can one make an estimation of the depth of the anterior chamber? |
By shining a small penlight from the side |
|
|
The anterior chamber depth is considered to be shallow at what degree? |
10 degrees |
|
|
What principles are used to measure corneal thickness? |
Optical, ultrasound, and corneal waveform |
|
|
What are the two types of ultrasonic heads? |
Solid and fluid filled |
|
|
A diamond knife may be measured by the caliper on the handle but should also be checked against a coin gauge, a ruler, or what kind of scope? |
Microscope |
|
|
How often should the applanation tonometer be calibrated? |
Manufacturer recommends re-calibration annually with a calibration check (instrument maintenance) daily. |
|
|
What red dye has an affinity for degenerative epithelium? |
Rose Bengal |
|
|
Standardized filter paper is used to measure the amount of tear production. What is the name of the test? |
Schirmer’s test |
|
|
What is TBUT in regards to a tear test? |
Tear Break Up Time |
|
|
What instrument provides reliable comparison of the forward protrusion of each eye in relation to the bony orbit? |
Exophthalmometer (e.g. Hertel) |
|
|
What should be set as the basic figure for comparison at subsequent readings when measuring forward-protrusion at each eye in relation to the bony orbit? |
The distance along the horizontal bar |
|
|
Name some devices available for measuring glare disability. |
TVA, BAT, Eye Con, or Miller-Nadler glare tester |
|
|
Deficient color vision suggests what? |
Retinal or optic nerve disease |
|
|
Normal color vision with decreased visual acuity suggests what? |
Non-organic disease |
|
|
In contrast A-scan, a 1mm compression may result in how many diopters of calculated IOL power error? |
3 D |
|
|
In contrast A-scan, what type of anterior chamber manifests the least evidence of compression? |
The longest ACD (anterior chamber depth) measurement |
|
|
What will distort the sound beam in immersion A-scan? |
Bubbles |
|
|
Why is the non-contact A-scan method considered superior by many experts? |
Compression factor is eliminated |
|
|
The cornea is responsible for what percentage of the aberrations of the entire eye? |
80-85% |
|
|
The corneal sensitivity test can be administered with what? |
With fine hair of the Cochet-Bonnet esthesiometer |
|
|
The imperfections of the optical system, such as refractive errors, and those caused by laser refractive surgery are referred to as what? |
Aberrations |
|
|
Tonometry measures __________ __________. |
Intraocular pressure |
|
|
One of the first and oldest methods used to determine intraocular pressure is __________. |
Tactile (finger) tension |
|
|
What is the name of the tonometer that consists of a footplate with a central moveable plunger fitted into a barrel? |
Schiotz tonometer |
|
|
Name the three common weights used in Schiotz tonometry. |
5.5g, 7.5g, and 10g |
|
|
Which tonometry technique measures the force required to flatten the cornea? |
Applanation Tonometry |
|
|
The calibration bar used to check calibration of the Goldmann tonometer is checked at what settings? |
0, 2, and 6 |
|
|
How much tolerance is allowed when checking the calibration of the Goldmann tonometer? |
+/- 0.05g or 0.5 mmHg |
|
|
What dye and filter are used to perform Goldmann applanation tonometry? |
Fluorescein dye and cobalt blue filter |
|
|
Pulsation of the semi-circles is an indication of the __________. |
Heartbeat |
|
|
To obtain an accurate reading when three diopters of astigmatism or more are present, the prism axis is set at the __________ __________ __________. |
Minus cylinder axis |
|
|
What type of glaucoma is typically associated with a sudden rise in the intraocular pressure caused by mechanical obstructions of the angle, with sudden decrease in vision, red eye, halos around lights, nausea, and excruciating pain? |
Acute angle-closure glaucoma |
|
|
Which glaucoma type is typically termed the “silent thief of sight” and why? |
Chronic open angle/primary open angle, due to the gradual, slow progression of vision loss |
|
|
What classic sign is a characteristic of congenital glaucoma? |
Buphthalmos- an abnormally large eyeball (“ox-eye”) |
|
|
What is the condition called when the iris balloons forward, blocking aqueous flow, causing a sudden increase in IOP? |
Iris Bombe |
|
|
What procedure is performed to relieve the pressure in the anterior chamber secondary to an angle-closure glaucoma? |
Laser Peripheral Iridotomy (LPI) |
|
|
Aqueous humor is produced by the __________. |
Ciliary body |
|
|
Tonometer tips should be wiped clean and disinfected with ___________. |
Alcohol preps, 3% hydrogen peroxide for 10 minutes, or a 1:10 dilution of liquid bleach for 3 minutes |
|
|
Tonopen tonometry utilizes what technique to measure the intraocular pressure? |
Applanation- measures the force needed to flatten the central cornea |
|
|
Why is 20 feet considered a practical distance for assessing distance visual acuity? |
At 20 feet very little accommodation is required. |
|
|
What does the denominator represent in the distance visual acuity fraction 20/50? . |
The 50 represents the distance that a normal eye can see the chart letters. In this case, the normal eye can see the letters at 50 feet |
|
|
What is indicated by improved vision through a pinhole? |
Refractive error; vision can be improved with eyeglasses or contact lenses. |
|
|
Which type of testing determines the retina’s ability to detect subtle differences in brightness or shading between targets and their backgrounds? |
Contrast Sensitivity testing |
|
|
What information is gained from a PAM test? |
It gives the physician an estimate of a patient’s potential visual acuity. |
|
|
Which machine uses laser lights in a pattern of stripes in which the patient indicates the orientation of the stripes? |
Laser interferometer |
|
|
What would be the next step in evaluating the patient’s visual acuity when the patient cannot see the 20/400 line at the standard 20 foot distance? |
Repeating the distance visual acuity test at shorter distance |
|
|
What is the proper way to record the visual acuity if the patient reads all but one chart letter on the 20/40 line? |
20/40 -1 |
|
|
How is visual acuity recorded in infants and preverbal children who cannot read the chart? |
Central – Steady – Maintained (CSM) |
|
|
What does the numerator represent in the distance visual acuity fraction 20/30? |
The patient is 20 feet from the chart. |
|
|
True or False: If a person with nystagmus has a preferred abnormal head posture, vision is tested with the head in this abnormal position. |
True |
|
|
When testing visual acuity, what are the black symbols on a very white background called? |
Optotypes |
|
|
What is the Jaeger system? |
A system of readable print and arbitrarily assigned numbers for near vision testing. |
|
|
What is a small instrument that attaches to the slit lamp projecting a beam of light containing a brightly illuminated Snellen chart through the less dense area of a lens by bypassing the cataract? |
Potential Acuity Meter (PAM) |
|
|
Name the test in which the patient looks into a machine that shines a light directly onto the patient’s eye while the patient reads the letters on the eye chart. |
Brightness Acuity Test (BAT) |
|
|
At what distance are near vision charts designed to be read? |
14-16 inches |
|
|
What is determined by the smallest object that can be clearly seen and distinguished at a distance? |
Visual Acuity |
|
|
Where in the visual field is the physiologic blind spot located? |
15 degrees temporal to fixation |
|
|
What is the term for an area of partial or complete blindness within the confines of a normal or relatively normal visual field? |
Scotoma |
|
|
Which method of perimetry is the most widely used and is essentially a screening test? |
Confrontation visual field test |
|
|
When calibrating a Goldmann perimeter, the light meter should read at which measurement? |
1,000 Apostilbs or 1430 lumens |
|
|
Which type of perimetry device uses mostly kinetic (moving) targets to map out the visual field? |
Manual, such as Goldmann perimeter |
|
|
What color stimulus on an automated perimeter would be chosen to test for macular defects? |
Red |
|
|
What is the benefit of using a blue stimulus on a yellow background in automated perimetry? |
Earlier detection of visual field loss |
|
|
What amount of visual fields is measured using an Amsler grid held at the proper distance? |
Central 20 degrees (or 10 degrees from fixation in any direction) |
|
|
During Godmann perimetry when would the examiner use the patient’s near correction? |
For testing the central 30 degrees in patients over the age of 30 |
|
|
At what mark on the chart is the recording arm positioned and locked for calibrating a Goldmann perimeter? |
70 degrees |
|
|
During manual perimetry, how is the test object introduced to the patient? |
From non-seeing to seeing areas |
|
|
What is the most common type of visual field defect indicated in a hysterical patient? |
Tubular or spiral |
|
|
Which type of defects either extends from the blind spot or points toward it? |
Paracentral |
|
|
The binocular visual field equals how many degrees? |
120 degrees |
|
|
What is the cause of a bitemporal hemianopsia? |
A defect in the optic chiasm, e.g., a pituitary tumor |
|
|
When should the perimetrist add complete cylindrical power to the lens holder as opposed to spherical equivalent? |
If a cylinder is greater than one diopter |
|
|
If the patient responds to a target presented in the physiological blind spot, this is referred to as a __________. |
Fixation loss/false positive |
|
|
Which defect is a compelte nerve fiber bundle defect emanating from the blind spot, arching over or under the macula and ending on the nasal horizontal line? |
Bjerrum’s scotoma or arcuate scotoma |

