![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define Fibromyalgia
|
Chronic muskuloskeletal pain, prolonged morning stiffness, and fatigue associated with multiple tender points
|
|
|
T/F: Fibromyalgia is usually associated with trauma
|
FALSE. Its usually a hreadual onset without trauma
|
|
|
t/F: Fibromyalgia is specific, localized musckuloskeletal pain
|
FALSE, its DIFFUSE pain
Morning stiffness will last longer than that of rheumatoid arthritis, into the day |
|
|
What is a condition a pt suffering from the chronic, diffuse pain associated with fibromyalgia could obtain?
|
Depression, secondary to the chronic pain
|
|
|
KNOW*** What are the criteria for diagnosing fibromyalgia?
|
1. History of widespread pain (=pain in L and R sides of body, and pain above or below the waist)
2. Axial skeletal pain MUST BE PRESENT (cervical spine, anterior chest, thoracic spine, or low back) |
|
|
What are the fibromyalgia tender points?
|
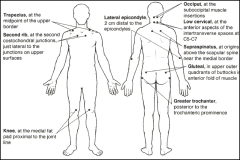
"GGLLOSTS - K"
Gluteal Greater Trochanter Lateral Epicondyle Low Cervical (C5-C7) Occipital Supraspinatus Trapezius Second Rib Knee |
|
|
What are the fibromyalgia control points?
|
"FFAT"
Forearm Forehead Ant. Thigh Thumbnail |
|
|
What were the two most important variables in the 2010 American College of Rheumatology's study regarding fibromyalgia?
|
Widespread pain index (WPI)
Symptom Severity Scale (SSS) |
|
|
KNOW*** be able to distinguish. Whats the difference between Fibromyalgia and Myofascial pain syndrome?
|
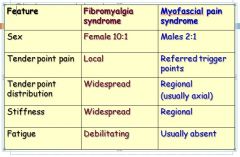
Fibromyalgia occurs in women waaaayyy more than men. Its more diffuse, and usually has fatigue
|
|
|
What are the 3 major types of fibromyalgia syndrome?
|
Primary = unknown cause, most common
Secondary = occurs w/ other problems Post-traumatic = for ex after accident |
|
|
Whats the cause of fibromyalgia syndrome?
|
unknown
But probably an aberration of central pain mechanisms like: 1. Neuroendocrine system 2. immune system |
|
|
Although the cause of fibromyalgia is unknown, pts seem to have central sensitization - define this
|
Heightened sensitivity of neurons
Like when something that normally doesn't hurt a person does, for ex. a sheet brushin over toes (=allodynia) Hyperalgesia = an abnormally heightened response to pain |
|
|
T/F: First degree relative of a pt. with fibromyalgia are 8.5 times more likely to have fibromyalgia that relatives of pts. with rheumatoid arthritis
|
TRUE
|
|
|
T/F: Diagnosing fibromyalgia is a clinical diagnosis, one of exclusion
|
TRUE
Rule out other things by doing a bunch of other tests (CBC, Sed Rate or ESR, ANA, Rheumatoid factor for RA, CK for muscular disease, and thyroid profile) |
|
|
What blood test result may be positive in 10-15% of cases of fibromyalgia?
|
Antinuclear Abs
|
|
|
Even though most fibromyalgia pts pain improves within 5 years, what can you do to help them?
|
Reduce aggravating factors: cold or humid weather, non-restorative sleep, physical or mental fatigue, excess physical activity, anxiety/stress
|
|
|
What are some of the alleviating factors of fibromyalgia?
|
warm, dry weather
hot showers/baths restful sleep moderate activity |
|
|
What is one thing you can do to aid in stress reduction in pts with fibromyalgia?
|
Reassure them
Their problem is real Its not Life-threatening |
|
|
Whats the GOLD STANDARD for fibromyalgia treatment?
|
Life style changes - get rid of aggravating factors
(alcohol, diet, exercise, caffeine, smoking, stress reduction) |
|
|
What are some meds you can give for fibromyalgia?
|
Pregabalin
Antidepressants NSAIDS Acetominophen etc |
|
|
What type of OMT technique do fibromyalgia pts respond best to?
|
gentle, indirect OMT
|
|
|
Can you do HVLA in fibromyalgia pts?
|
NOOOOOOOO
(use indirect techniques) HVLA will result in a flare up of symtpms |
|
|
List some indirect OMT techiques that can be used to treat fibromyalgia
|
Transverse diaphragm restriction
cranial rib raising lymphatic pump |
|
|
If you over-dose with OMT, what can happen to fibromyalgia pts?
|
Their symptoms can flare up for several days
|
|
|
Whats the cornerstone of fibromyalgia treatment?
|
The gold standard for fibromyalgia treatment is lifestyle changes, and one of the most important of these is exercise, because 80% of pts with fibromyalgia are fatties. FACT.
So Exercise is the "cornerstone" of treatment |
|
|
Define Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1
|
Burning pain in the upper or lower extremities associated with swelling, dec. ROM, vasomotor instability, skin nutrition changes, patchy bone demineralization
In Type 1 there is NO definable nerve lesion |
|
|
KNOW*** What is the burning pain of the upper and lower extremity associated with in regional pain syndrome?
|
Swelling
Dec. ROM Vasomotor instability Nutrition skin changes (due to vasculature) Patchy bone demineralization |
|
|
What are some of the most common findings in pts with regional pain syndrome (note: could be good clues in question stem)
|
Weakness
Radicular pain Temp. difference in extremities exaggerated response to painful stimuli extremity edema Hyperhidrosis |
|
|
What percent of cases of regional pain syndrome follow a major or minor trauma?
|
60%
|
|
|
Whats the cause of regional pain syndrome?
|
Unknown, but may be of sympathetic origin
(constant CNS stimulation = pain) |
|
|
What are the three stages of regional pain syndrome?
|
Stage 1 = Acute
Stage 2 = Dystrophic Stage 3 = Atrophic |
|
|
Define Stage 1, Acute stage, of regional pain syndrome
|
weeks to 3 months after injury
severe burning, aching pain, allodynia, perception of non-painful stimulus as painful Hypersensitivity to light touch extremities hot, edematous skin red and blotchy Hyperhidrosis (=sweating) Patchy osteoporosis on x-ray 3 weeks after injury |
|
|
Define Stage 2 of regional pain syndrome, Dystrophic stage
|
3-6 months after injury
persistence of pain and disability skin pale, cyanotic, cool doughy Hyperhidrosis nails brittle/rigid subcu tissue atrophy Dec. ROM |
|
|
Define stage 3 of regional pain syndrome, the Atrophic stage
|
Greater than 6 months after injury
signs and symptoms come and go Pain spreads proximally skin cool, pale, cyanotic etc loss of muscle tone fascia becomes thick Flexion- loss of contractures - loss of ROM Ankylosis |
|
|
How do you diagnose regional pain syndrome?
|

Mostly a clinical diagnosis
Thermography = sig. temp differences in extremities patchy osteoporosis on x-ray three phase bone scan Sympathetic neural blockade = stellate neural ganglion block for upper extremities Epidural steroid injection for lower extremities |
|
|
KNOW*** What is the most important thing in treatment of regional pain syndrome?
|
EARLY TREATMENT
Precention is the best treatment - treat pain early Be suspicious if pain persists |
|
|
Besides early treatment, What are some other treatments for regional pain syndrome
|
Aggressively treat somatic dysfunction and facilitated segments after trauma
OMT Physical Therapy Neural Blockade Trigger pt. injection TENS unit Meds |
|
|
What are some additional treatments that cna help address regional pain syndrome?
|
Smoking cessation
Acupuncture Biofeedback Spinal Cord stimulators Surgery |

