![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an Opioid? |
all exogenous substances natural and synthetic, that binds specifically to any of the several opioid receptors and produce at least some agonist or morphine like effects. |
|
|
What makes a synthetic opioid different? |
Synthetic Opioids are manufactured by synthesis rather than by chemical modificaiton. Meperidine Fentanyl Sufentanil Alfentanil Remifentanil |
|
|
What are the 4 phases of Pain? |
Transduction Transmission Modulation Perception |
|
|
What are the three endogenous substances that can modify pain perception? |
Endorphins Enkephlins Dynorphins |
|
|
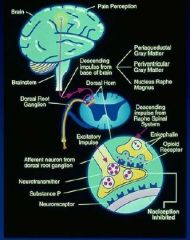
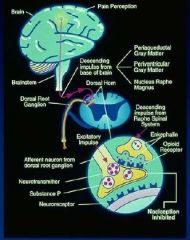
What is transduction and how does it work? |
It is the changing of chemicals from an injured cell into an action potential. A Delta fast pain fibers (sharp well localized pain) C fibers slow pain (dull and not well localized) visceral |
|
|
How is an AP transmitted? |
Through an afferent pathway along the spinothalamic tract passing through 3 levels of neurons. First order (peripheral to dorsal horn) Second order (Dorsal horn to thalamus) Third order (Thalamus to cerebral cortex) Can be blocked at each synapse. |
|
|
What is the most important site of modulation? |
Substantia Gelatinosa in the dorsal horn (rexed lamina II, III) Inhibited in the brain by GABA and in the spinal cord by glycene. |
|
|
|
|
|
What is perception? |
The processing of afferent pain signals in the cerbral cortex and limbic systems. |
|
|
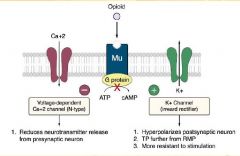
G Protein Coupled Receptor that inhibits Adenylate Cyclase Intracellular cAMP is Decreased Ca++ Conductance is Decreased K+ Conductance is Increased |
|
|
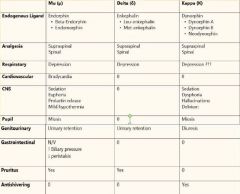
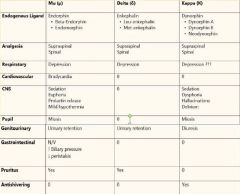
What receptors are opioids highly specific to? |
Mu Receptors located in the CNS Mu1- Supraspinal stimulating Euphoria, Miosis, Hypothermia, Bradycardia, Urinary Retention, and Pruitis Mu2-Spinal Hypoventilation, Physical Dependence, Ileus, Constipation |
|
|
What do Delta Receptors do? |
Modulate Mu Receptor Activity. |
|
|
What do Kappa Receptors responsible for? |
Sedation, Dysphoria, and Miosis. Opioid Agonist-antagonists often act on Kappa Receptors |
|
|
|
|
|
What are the Opioid Agonists Systemic Effects (CV and Ventilation)? |
CV-Dose dependent vasodilatation, Minimal BP, bradycardia, Histamine (with Morphine & Demerol) Ventilation-Decreased Rate, Increased TV, Shift CO2 to the right, Increased PACO2, Increased ICP |
|
|
What are the Opioid Agonists Systemic Effects (Nervous System)?
|
Analgesia, Drowsiness, Euphoria Skeletal Muscle Rigidity Miosis-excessive constriction of the pupil of the eye N&V (Chemoreceptor zone, Vestibular) Cerebral Vasoconstriction Depression of Cough Reflex (Codeine) |
|
|
What are the Opioid Agonists Systemic Effects (GI/GU)
|
GI- Spasm of Biliary smooth Muscle, Decreased motility and gastric emptying GU- Increased Genitourinary tone and peristaltic activity of uteter |
|
|
What are the effects of opioid use and MAOIs? |
May experience exaggerated CNS depression & Hyperpyrexia (High Fever), HTN, Hyperthermia, and Seizures |
|
|
How long does it take to develop addiction to Opioids? |
About 25 days of continual use, or 2-3 weeks |
|
|
What is hyperalgesia? |
When trivial stimuli cause pain (decrease in pain threshold) caused by release of chemical mediators that sensitize pain receptors especially in the PNS. (Possibly caused by upregulation of NMDA) |
|
|
Which Two Opioids have a Histamine Release? |
Morphine and Demerol |
|
|
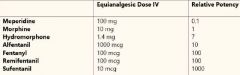
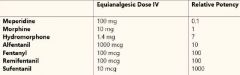
What is the order of lipid solubility of Opioids from Most to least? |
Sufentanil Fentanyl Alfentanil Demerol Remifentanil Morphine |
|
|
What are the Pharmacokinetics of Morphine? |
Poor lipid solubility (90% ionized) Highly Protein Bound Has an active metabolite Metabolized (Liver & Kidneys) by Rapid conjugation with Glucouronic acid |
|
|
What Opioid can cause Seratonin sydrome if administered to a patient taking MAOIs? |
Meperidine (Demerol) Has a Histamine release Is utilized in PACU to treat Post op Shivering (k & a2 receptors) |
|
|
What are the side effects of Demerol? |
Tachycardia Decreased Myocardial Contractility Histamine Release Orthostatic Hypotention Delirium and Seizures with prolonged use |
|
|
How is Demerol Metabolized? |
Goes through extensive first pass metabolism PO 90% metabolized by CYP450 Has active metabolite (Normeperidine) |
|
|
How potent is Fentanyl compared to Morphine? |
75-125 times more potent More rapid onset and shorter duration Lungs store inactive drug in 1st pass Pulmonary intake (75%) Has inactive metabolites CYP3A |
|
|
How does Sufentanyl compare to Fentanyl?
|
5-10 more potent Decreases CMRO2 Faster Intubation time Longer Period of Analgesia with less ventilation depression |
|
|
What is the significant Side effect of Sufentanyl? |
Bradycardia causing decreased CO and Decreased BP |
|
|
How does Alfentanil compare to Fentanyl? |
1/5-1/10 as potent Very rapid Onset of action (crosses BBB) Brief duration of action by redistribution Eliminated faster than other opioids (except remifentanil) |
|
|
What are the significant side effect of Alfentanil? |
Bradycardia and Hypotension |
|
|
How does Remifentanil Compare to Fentanyl? |
Similar Potency Brief action (hydrolysis by Plasma Esterases) Noncumulative effects-No Context sensitive half time (always gone after 4 Minutes) Reduces MAC and Propofol need by 50% |
|
|
Side Effects of Remifentanil? |
Skeletal Muscle Rigidity Hypotension |
|
|
How does Hydromorphine compare to Morphine? |
Is a derivative of morphine Eight times more potent Has a slightly shorter duration |
|
|
How does Oxymorphone compare to Morphine? |
10 times more potent than Morphine Causes more Nausea and Vomitting |
|
|
What are the pharmacokinetics of Codeine? |
Has limited first pass metabolism 10% is metabolized into Morphine in the Liver Minimal sedation, Nausea, or Vomitting Constipation is main side effect |
|
|
|
|
|
List the Opioids in order of Potency from Most to least: |
Sufentanil Fentanyl/Remifentanil Alfentanil Oxymorphone Hydromorphone Morphine Demerol |
|
|
What are the pharmacokinetics of Methadone? |
High bioavailability 80% Metabolized by CYP450 to inactive metabolite Mu Receptor agonist NMDA Receptor Antagonist Inhibits reuptake of MOA in synaptic Cleft |
|
|
Side effects of Methadone? |
Similar to Morphine Can increase QT interval |
|
|
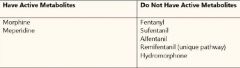
Which Opioids have active metabolites and stimulate a histamine release? |
|
|
|
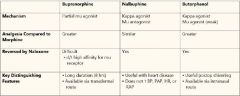
What are three opioid agonist/antagonists (Partial Agonists)? |
Nalbuphine (nubain)-Reverses resp depression of Fentanyl while maintaining analgesia and treating itching Butorphanol (Stadol) Buprenorphine (Talwin) |
|
|
|
|
|
What are the Pharmacokinetics of Naloxone (Narcan)? |
Reverses opioid induced respiratory depression and analgesia Antagonizes all opioid receptors but has greatest affinity for Mu Metabolized in the liver (undergoes first pass) Can Cross the Placenta Causes Nausea and Vomitting Stimulates CV |
|
|
What is a longer acting opioid Antagonist that is given to patients in ETOH withdrawl? |
Naltrexone- longer acting lasting up to 24 hours Does not undergo first pass metabolism |

