![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
When to urgently refer patients with diabetic retinopathy? |
*Maculopathy
*Severe non-proliferative retinopathy --large blot hemorrhage, cotton whool spots, engorged toruos veins.
*Proliferative retinopathy -- fine new vessels appear on the optic disc, retina and can cause viterous hemmorhage.
(Also, sudden losse of vision, retinal detachment, viteral or pre-retinal hemorrhage, rubeosis iridis) |
|
|
|
Dots? |
Microaneurysm |
|
|
|
Blots? |
Hemorrhages / flame shaped |
|
|
|
Hard exudates? |
Yellow patches |
|
|
|
Squint other names? |
Strabismus, tropia |
|
|
|
Vincristine ophthalmologic SE? |
Toxic optic neuropathy |
|
|
|
Ethambutol SE? |
Color blindness, restriction of visual fields, loss of visual acuity |
|
|
|
Ptosis is due to? |
dysfunction of the muscles that raise the eyelid or their nerve supply (oculomotor nerve for levator palpebrae superioris and sympathetic nerves for superior tarsal muscle). |
|
|
|
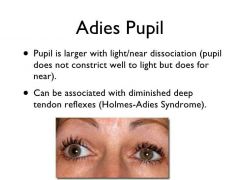
Holmes Adie Syndrome? |
Tonically dialated pupil that doesn't respond to light (but responds to near) |
|
|
|
Tx of posterior viterous detachment in the elderly? |
No tx is required |
|
|
|
Cupping of optic disk --> characteristic of glaucoma |
|
|
|
Mean value of intraocular pressure? |
15-16 mmHg (21 is the upper limit for normal) |
|
|
|
Common causes of cataract over the age of 40? |
Diabetes Glaucoma Macular degeneration |
|
|
|
Sudden loss of vision, pale disk and cherry red spot fovea suggests? |
Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) |
|
|
|
Seidle's sign? |
Sickle shaped scotomata in chronic simple glaucoma |
|
|
|
Treatment for chronic glaucoma? |
Pilocarpine (mitotic) - direct cholinergic agonist - |
|
|
|
RP |
|
|
|
Emedastine, olopatadine? |
Anti-histamine drops |
|
|
|
Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) presentation? |
Dramatic visual loss Afferent pupil defect Retina appears white + red cherry spot on fovea |
|
|
|
CRAO Mx |
Reduce the IOP to improve perfusion by: Occular massage or Remove aqeous surgically or Use of antihypertensive treatment |
|
|
|
Which is commoner CRAO or CRVO (Vein)? |
CRVO |
|
|
|
CRVO Subtypes? |
Ischemic and non-ischemic |
|
|
|
Finding on examination of CRVO? |
Ischemic: cotton whool spots, swollen optic nerve, macular edema, risk of neovascularization. |
|
|
|
CRVO Mx? |
Do fundus fluorecence angiogram to determine the degree of ischemia Pan-retinal photocoagulation to treat or prevent neovascularization |
|
|
|
Age related macular degeneration main symptom? |
Central vision loss |
|
|
|
Primary open angle glucoma main symptom? |
Visual firld defect from optic nerve damage |
|
|
|
Associations of eye Disease to systemic conditions? |
Anterior uveitis - Ankylosing spondylitis Scleritis - Rheumatoid arthritis, SLE, Spondyloarthropathies, vasculitis |
|
|
|
Mooren's ulcer? |
Progressive painful ulcerative keratitis |
|
|
|
Keratotorus? |
Pellucid marginal degeneration - degenerative thinning of the cornea (marginal dystrophy of the cornea) |
|
|
|
Optic papillitis? |
Form of optic neuritis - inflm if the optic nerve head |
|
|
|
Symptoms of optic papillitis? |
Loss of visual field Painful eye movement |
|

