![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
257 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a lay rescuer? |
A first aid provider, also known as a rescuer |
|
|
What is a first aid provider?
|
Defined as someone with formal training in first aid, emergency care or medicine who provides first aid.
|
|
|
What are the objectives of a Lay Rescuer? |
Preserve life and promote recovery Prevent further illness or injury |
|
|
What is consent and why is it important? (In context of first aid) |
An injured or ill person must give consent for any proposed care
The injured or ill person agrees to accept care and gives the rescuer permission to provide care Minors under age of 16 do not have the same rights to medical consent Their parents or guardians hold this right for them Lay rescuers should respect the wishes of the parents or guardians |
|
|
What is implied consent? |
If a person becomes physically unable to provide consent, life saving treatments can be provided |
|
|
What is Right to Refuse? |
Injured or ill person who are conscious may refuse treatment If the lay rescuer is concerned about their injuries or mental state, it is highly advisable to activate EMS |
|
|
What is EMS?
|
Emergency Medical Services
|
|
|
What is Gross Negligence?
|
If a person acts or treats a patient as they are trained to do, and does not exceed the training, the rescuer is not in a negligent position.
|
|
|
What is abandonment?
|
Once the lay rescuer begins care, they may not stop until a person of equal or greater training assume responsibility.
|
|
|
When can a lay rescuer stop providing care? |
Personal safety is threatened Must leave to call for help Patient no longer wants assistance Relieved by someone with higher training |
|
|
What is Bill C20
|
In Ontario, it is the Good Samaritan Act and state that a lay rescuer cannot be sued for helping a person who is injured, provided the lay rescuer does not exceed his or her training.
|
|
|
What is The Approach?
|
Scene Assessment/Protect Yourself
Mechanism of Injury/Illness Identify Yourself/Obtain Consent Level of Consciousness Call 911 Primary Survey -airway -breathing -chest compressions -deflibrillation -deadly bleed checks |
|
|
What is Scene Assessment? |
A complete visual check of the surrounding area for any potential hazards |
|
|
Why must you wear gloves when treating an injured patient and what type of glove?
|
Diseases are always present and can be transmitted through blood and other body fluids.
Always wear nitrile (non-latex) gloves. |
|
|
Where should used gloves usually go? |
Gloves should ideally go into Biohazard waste bins |
|
|
What is Mechanism of Injury? |
The identification of the causes of the injury or illness This will give the lay rescuer clues as to the injury and/or illness and hopefully give an idea of what treatment and medical assistance the patient may need |
|
|
What should you do with a patient who are injured with suspected head or spinal injuries? |
Do NOT move the patient unless there is an immediate danger or inability to access the airway |
|
|
What is a medical Sign? |
Something the rescuer sees on a patient |
|
|
What is a medical Symptom?
|
Something that patient feels and describes to the rescuer.
|
|
|
What is ABCs?
|
Airway, Breathing and Circulation.
Needed for lay rescuer to first check patients responsiveness before this. |
|
|
If the patient is not obviously alert, what should rescuer do?
|
Carefully Tap and Shout "Are you okay?"
|
|
|
What is AVPU?
|
Alert - patient is awake, conscious and answers questions appropriately
Voice - the patient responds to your loud voice Pain - a patient can be classified as only responding to pain when you must use shoulder pinch or earlobe pinch to wake them up Unresponsive - a patient is considered 'unresponsive' when the patient does not respond to any verbal or painful stimulation |
|
|
What is normal breathing in adults?
|
12 to 15 breaths per minute (one ever four seconds), rhythm is regular
|
|
|
What is agonal breathing?
|
Respiration in an unresponsive patient are an abnormal pattern of breathing characterized by shallow, slow (3-4 per minute), irregular breaths followed by irregular pauses.
Extremely serious medical sign requiring immediate medical attention as condition generally progresses to complete respiratory arrest and heralds death. Not actual breathing. Thought to be caused by random flashes of electricity from very sick brain cells in the respiratory centers in brain. |
|
|
What is CPR?
|
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation, provision of two basic life support techniques that are administered when a person's natural heart and lung actions have stopped.
|
|
|
What does chest compression or cardiac resuscitation do? |
By performing chest compression, a lay rescuer can provide blood flow for an individual whose heart is unable to circulate the blood itself Though application of rhythmic pressure to lower half of patient's breastbone (aka sternum), blood is forced from heart via various blood vessels to brain and vital organs |
|
|
What are the type support techniques of CPR?
|
Chest Compressions/Cardiac Resuscitation and Rescue Breathing
|
|
|
Who is considered an adult?
|
8+
|
|
|
What is the CPR ratio
|
30 Chest Compression to 2 Rescue Breathes
|
|
|
Depth of chest compression in an adult?
|
~5cm
|
|
|
Who is considered a child?
|
1-8 years old
|
|
|
Depth of chest compression on a child?
|
Max 5cm, use only one hand
|
|
|
Who is considered an infant?
|
Less then one years old
|
|
|
Depth of chest compression on an infant?
|
Max 4cm, use only 2 fingers
|
|
|
How do you do rescue breath on infant?
|
Puff breaths, not deep breaths.
|
|
|
What are three main causes of unconsciousness?
|
Trauma, medical, fainting
|
|
|
What is trauma? |
Force acts on body from outside, causing injuries Traumatic injuries range from mild to extremely severe |
|
|
What is the medical definition for fainting? |
Also known as syncope, it is sudden (and generally momentary) loss of consciousness due to lack of sufficient blood and/or oxygen reaching the brain |
|
|
What are signs and symptoms of fainting? |
Dizziness
|
|
|
What are treatment for fainting?
|
Place person in recovery position
Discourage patient from sitting up ABCs Look for injuries Request medical assistance if needed |
|
|
What is shock? |
Occurs when an inadequate amount of oxygen is delivered to body tissues such as brain Circulatory system is divided into three components: the heart, the blood vessels and the blood |
|
|
What are causes of shock?
|
Sepsis - infection
Bleeding - large amount of blood loss externally and/or internally Obstruction - airway obstruction or a chest wound causing lung to collapse Cardiogenic - heart attack Anaphylaxis - severe allergic reaction causing airway swelling potentially leading to cardiac arrest Neurological |
|
|
Signs and symptoms of shock?
|
light headedness, dizziness, confusion
rapid pulse anxiousness, restlessness, irritability chills, cool, pale skin nausea and vomiting unconsciousness |
|
|
Treatment for shock?
|
Call 911
ABCs Stop visible bleeding with direct pressure If no suspected spinal and/or head injuries, recovery position ABCs again Reassure patient Keep warm |
|
|
What is history gathering, SAMPLE?
|
Symptoms
Allergies Medications Past medical history Last food Events leading up to injury/illness |
|
|
What must you do when assisting a patient with medications? |
Must make absolutely certain that the medication is the patient's own Medication provided by a spouse, bystander or other person that is not the patient's own is not to be used |
|
|
What are the 5 R's of medication administration?
|
Right patient
Right symptoms/time Right medication Right dose Right route |
|
|
What is the heart's function as a pump?
|
Through its rhythmic pressure (caused by electrical impulses), moves blood from the heart throughout all parts of the body and back to the heart. Specifically the blood is directed from the heart via the pulmonary artery to small capillaries and alveoli in the lungs, where it is oxygenated (by respiration)
Oxygenated blood returns to the heart through the pulmonary vein, travels through the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart, where it is pumped out to the body via the aorta and the corresponding series of arteries. |
|
|
What is hypertension?
|
Medical term for excessively high blood pressure
If left untreated or unnoticed, it can lead to tissue damage, decreased elasticity and an enlarged heart. |
|
|
What is atherosclerosis?
|
Results from an accumulation of fatty deposits (plaque) in inner lining of the blood vessels and coronary arteries of the heart.
|
|
|
What is arteriosclerosis?
|
Hardening of the arterial walls, which is the result of both the calcification (calcification is the build-up of calcium deposits) and degeneration of the blood vessel lining.
If one of the arteries of the heart or brain becomes completely blocked, a heart attack or stroke may occur. |
|
|
What is ACS?
|
Acute Coronary Syndrome. Caused by a lack of oxygen to heart muscle.
|
|
|
What is a heart attack?
|
Occurs when some of the heart muscle dies because of a blockage of blood flow in coronary artery(s)
|
|
|
What is Angina?
|
Caused by narrowing of an artery
If patient exerts themselves, they increase the pumping demand on their heart. Unfortunately, narrowed arteries are unable to supply the heart with the increased oxygen it needs, causing similar sign and symptoms of heart attack. Having the patient stop what they are doing and rest will lower the oxygen demand on the heart. The patient will usually start to feel better. |
|
|
What are signs and symptoms of ACS?
|
pain, pressure, squeezing sensation, dull ache, in the chest
Pain may radiate to the neck, jaw, arms or back General weakness & lethargy (very common in women) Shortness of breath Nausea, heartburn and vomiting Abnormal colour Sweating Denial by patient is common |
|
|
What are treatment for ACS?
|
Approach
911 ABCs (airways***) Put in comfort Keep warm If have Nitroglycerin, give If need, CPR and AED |
|
|
What is a stroke? |
Stroke occurs when a blood vessel becomes blocked, or a blood vessel ruptures within the brain |
|
|
What is Transient Ischemic Attack?
|
TIA, it is a mini-stroke. Caused by reduced blood flow to the brain.
|
|
|
What is sudden cardiac arrest?
|
Term used within the medical community to describe a patient suffering an unexpected cardiac arrest. Though sudden cardiac arrest can be caused by any one of a number of different illnesses & injuries, the most common causes are Heart Attack and Stroke
Patients in cardiac arrest no longer have regular, rhythmic pumping action required to move blood around their body. One of the first things that happens in Sudden Cardiac Arrest is that the patient's heart will go into a chaotic wildly irregular rhythm that does not pump blood. CPR and AED immediately. |
|
|
What are the special considerations in CPR when it comes to submersion or near-drowning? |
Patients of submersion may develop hypothermia
If the submersion occurs in icy water (below 5C), hypothermia may develop rapidly Start rescue breathing on the patient as soon as possible, even in water
All patients of submersion who require resuscitation must be transported to hospital |
|
|
What are the special considerations in CPR when it electric shock and lightening strikes?
|
Do not touch patient who is still connected to the source of electricity. Make sure the source of electricity is disconnected before touching a patient who has been electrocuted. Assess the patient's condition and start CPR if necessary. The treatment of choice is applying an AED as soon as possible to defibrillator the patient of an electrocution.
|
|
|
What are the special considerations in CPR when it pregnancy?
|
When a cardiac arrest occurs in a pregnant women, activate EMS first and start CPR as soon as possible. Put a pillow or some wedge-shaped object under the right side of the women's abdomen to shift to uterus to the left side. This will help blood return to the heart.
|
|
|
When do you stop CPR?
|
An AED is available
Trained emergency personnel arrive on scene to provide assistance You are too fatigued to continue It is unsafe for you to continue The patient starts breathing normally on their own |
|
|
What is Asystole?
|
Also known as "flat line", it is defined as the absence of both electrical and mechanical activity of the heart and cannot be treated with defibrillator.
|
|
|
How does defibrillator work? |
It works by resetting the electrical activity of the heart, allowing the heart's natural pacemaker to re-establish an organized electrical rhythm After the shock, the heart can regain control The outcome of defibrillator is that the patient's heart should resume rhythmic muscular contractions |
|
|
What should you do if a patient require and AED but they are in water/are wet? |
Water is a good conductor of electricity and may provide a pathway for energy from the AED to rescuers
It is critical to quickly remove the patient from freestanding water and dry the patient's chest before using the AED |
|
|
What is the special situations with AEDs towards implanted pacemakers/defibrillators?
|
Pacemakers and/or defibrillators have been implanted in patients by cardiac surgeons to aid in maintaining heart function. These devices create a hard lump beneath the skin of the upper chest or abdomen, usually on the patient's left side.
The lump is about half the size of a pack of cards and usually has a small overlying scar. Placement of an AED electrode pad directly over an implanted medical device may reduce the effectiveness of defibrillator attempts. Instead, place the pad at least 1 inch (2.5 cm) away from the implanted device. Then follow the usual steps for operating an AED. |
|
|
What is allergic reactions & anaphylaxis?
|
Allergic reactions are a response to a substance that has entered or makes contact with the patient that they have a hypersensitivity to. The first time a person is exposed to the substance that very rarely have a reaction.
Allergic reaction is caused by uncontrolled release of a substance called Histamine. This substance causes blood vessels to dilate, makes the vessels leak fluid and causes breathing passageways to constrict. Allergic reactions can develop into Anaphylactic Shock, which is life threatening. |
|
|
What is internal bleeding?
|
This is bleeding beneath the skin that is not always visible. The most common cause of an internal bleed is an external force hitting, twisting or penetrating the body.
|
|
|
What is external bleeding?
|
The soft tissue injury caused by a cut, scrape or puncture to the skin.
|
|
|
What is arterial bleed?
|
Blood from an artery will be bright red and may be spurting from the wound. Additional pressure may need to be applied.
|
|
|
What is venous bleed?
|
Blood from a vein will be dark red and will oozing from the wound.
|
|
|
What is a contusion? |
Also known as bruising is internal bleeding within damaged skin tissue Both lead to swelling and discoloration Ice is the best treatment for contusions and bruising Do not apply pressure |
|
|
What is lacerations?
|
Tears in the skin and underlying tissues.
|
|
|
What is abrasions? |
Scrapes to the surface of the skin Treat lacerations and abrasions by washing the wound with clean running water for 5 minutes, or until the wound is free of foreign matter |
|
|
What are impaled wounds? |
Penetrations into the skin by foreign objects Do not remove the penetrating object Immobilize and treat by bandaging (stacking) the penetrating object in place |
|
|
What is an amputation?
|
Loss of a limb due to external force. Partial or complete amputations are possible. Complete amputations are much more serious, as there is greater potential for fatal blood loss (always monitor the ABC's)
|
|
|
What is oral bleeding?
|
Cheek, tongue or gum can be treated with direct pressure with a clean dressing. Recommend the patient refrain from rinsing his or her mouth for several hours after the bleed has stopped.
|
|
|
What is a fracture? |
A break in a bone |
|
|
What is an open fracture?
|
Bone has protruded through the skin. Treat the exposed bone as an impaled object.
|
|
|
What is a closed fracture?
|
The bone is broken but the skin around it is still intact.
|
|
|
What is a dislocation? |
Separation of two bones at a joint Usually happens at what is called a "ball and socket" joint; a long bone with a round head on the end of it pulled or stretched, causing it to pop out of the bowl-shaped bone (or socket) it typically sits in |
|
|
What is a strain?
|
Stretching or tearing of muscles and/or tendons.
|
|
|
What is a sprain?
|
Stretching or tearing of ligaments.
|
|
|
What is a blunt abdominal injury?
|
It is a abdominal trauma may be caused by direct force to the abdomen and may have few outward signs. Even bruises may take several hours to develop.
|
|
|
What is abdominal injury penetration? |
Injuries to the abdomen may results from knives, bullets and a variety of other instruments |
|
|
What is an evisceration? |
Organs protruding from the abdomen Should be covered with sterile moist dressing DO NOT ATTEMPT TO MOVE OR PUT ORGANS BACK |
|
|
What is tetanus?
|
An infection that is often indicated by muscle spasms. If left untreated it can became fatal. Causes can include animal bites and would exposure to soil, dust or animal feces.
|
|
|
What is elapid?
|
Also known as (coral) snake bites. In addition to treatments below, the entire extremity should be immobilized by wrapping it with an elastic bandage that still allows one finger to fit under it.
|
|
|
What is type 1 diabetes?
|
Insulin dependent.
It is child onset, IDDM. More severe form of the disease. Insulin Dependent Diabetics either do not make any Insulin at all, or what they do make does not work properly. These patients are required to take regular injections of insulin, either from needles, or via an implanted pump. |
|
|
What is type 2 diabetes?
|
Non insulin dependent
Adult onset, NIDDM This is the less severe form of the disease, but still significant. Non Insulin Dependent patients still make insulin, but they do not make sufficient amounts of it. They control their sugar levels with combination of what they eat, when they eat and oral medications. |
|
|
What is section (2) of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedom?
|
Everyone has the following fundamental freedoms:
a) Freedom of conscience and religion; b) Freedom of thought, belief, opinion and expression, including freedom of the press and other media of communications c) Freedom and peaceful assembly; and d) Freedom of association/freedom to join trade union |
|
|
What is section (7) of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedom? |
Life, Liberty and Security of person: Everyone has the right to life, liberty and security of the person and the right not to be deprived thereof except in accordance with the principles of fundamental justice Free to do whatever as long as it does not violate rights of others |
|
|
What is section (8) of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedom?
|
Search or Seizure (SS)
-#1 charter violation - can only search after arrest - Everyone has the right to be secure against unreasonable search and seizure |
|
|
What is section (9) of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedom?
|
Detention or Imprisonment
-Everyone has the right not to be arbitrarily detained or imprisoned |
|
|
What is section (10) of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedom?
|
Arrest or detention
-Everyone has the right on arrest or detention 1) To be informed promptly of the reasons therefor; 2) To retain and instruct counsel without delay and to be informed of that right; and 3) To have validity of the detention determined by the way of habeas corpus and to be released if the detention is not lawful |
|
|
What is section (43) of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedom?
|
Correction by force
-"parent" justified by using force by way of correction of force toward pupil or child if force does not exceed what is reasonable under the circumstances - Use tactical communication is situation like 43 to calm the individual down instead of using force |
|
|
In Canadian Law, what does CCC stand for?
|
Criminal Code of Canada
|
|
|
What is Section 25 of CCC?
|
1. Everyone who is required or authorized by law to do anything in the administration or enforcement of the law
a) As a private person/security guard b) As a peace officer or public officer, c) In aid of a peace officer or public officer, or d) By virtue of his office, Is, if he acts on reasonable grounds, justified in doing what he is required/authorized to do and in using as much force as necessary for that purpose 2. Where a person is required or authorized by law to execute a process or to carry out a sentence that person or any person who assists him is, if that person acts in good faith, justified in executing the process or in carrying out the sentence not withstanding that the process or sentence is defective or that it was issued or imposed without jurisdiction or in excess of jurisdiction - As long as not excessive ○ Section 25 CCC gives me authority to arrest -You are responsible for other people who are involved |
|
|
What is Section 26 of CCC? |
Excessive force/use of force: - Do not use more force than is necessary Everyone who is authorized by law to use force is criminally responsible for any excess thereof according to the nature and quality of the act that constitutes the excess: |
|
|
What is Section 27 of CCC? |
Use of force to prevent commission of offence Everyone is justified in using as much force as is reasonable necessary a) To prevent the commission of an offence b) To prevent anything being done that one reasonable grounds mentioned in paragraph (a) |
|
|
What is Section 34 of CCC? |
Self defence against unprovoked assault a) Everyone who is unlawfully assaulted without having provoked the assault is justified in repelling force by force if the force he uses is not intended to cause death or grievous bodily harm and is no more than is necessary to enable him to defend himself b) Everyone who is unlawfully assaulted and who causes death or grievous bodily harm in repelling the assault is justified if 1) He causes it under reasonable apprehension of death or grievous bodily harm from the violence with which the assault was originally made or with which the assailant purses his purposes; and 2) He believed, on reasonable grounds that he cannot otherwise preserve himself from death or grievous bodily harm |
|
|
What is Section 494.1 of CCC?
|
Arrest without warrant by any person/citizen arrest authority
1. Anyone may arrest without warrant a) A person whom he finds committing (witnessing) an indictable (serious criminal offence) offence; or b) A person who, on reasonable ground, believing 1) Has committed a criminal offence, and 2) Is escaping from and freshly pursued by a person who have lawful authority to arrest that person 2. Any who is a a) Owner, occupier or a person in lawful possession of property b) A person authorized by the owner or by a person in lawful possession of property, may arrest without warrant a person whom he finds committing a criminal offence on or is relation to that property 3. Anyone other than a peace officer who arrests a person without warrant shall forthwith deliver the person to a peace officer |
|
|
What is a summary offence?
|
Less serious criminal offence
|
|
|
What is an indictable offence?
|
Serious criminal offence
|
|
|
What is a hybrid offence and some examples?
|
Summary or indictable
ex) theft, fraud, mischief |
|
|
What are the 6 steps to arrest?
|
1. Identify yourself
§ As a security guard (uniform or not) 2. Tell subject they are under arrest 3. Tell them why they are under arrest 4. Take physical control § Come from side 5. Tell them they have the right to council 6. Inform the police |
|
|
What is a Justice of the Peace?
|
aka "Your worship"
They receives information (documents which commence a criminal proceeding) and the formal reading of charges |
|
|
What is the TPA?
|
Trespass to Property Act
Arrest only, no removal Provincial |
|
|
What is Section 1 of TPA?
|
Definition
1. In this act, "occupier" includes a) A person who is in physical possession of premises, or b) A person who has responsibility for and control over the activities there carried on, or control over persons allowed to enter the premises □ Even it there is more than one occupier of the same premises c) Water, ships, and vessels d) Trailers and portable structures designed or used for residence; business or shelter e) Trains, railways cars, vehicles, aircrafts, except while in operation |
|
|
What is Section 2 of TPA?
|
Trespass an offence
1. Every person who is not acting under a right or authority conferred by law and who, a) Without an express permission of the occupier, the proof of which rests on the defendant 1) Enters on premises when entry is prohibited under this Act or 2) Engages in an activity on premises when the activity is prohibited under this Act; or b) Does not leave premises immediately after he or she is directed to do so by the occupier of the premises or a person authorized by the occupier is guilty of an offence and on conviction is liable to a fine of not more than $2000.00 |
|
|
What is Section 3 of TPA?
|
Prohibited of entry
1. Entry on premises may be prohibited by notice to that effect and entry is prohibited without any notice on premises a) That is a garden, field, or other land that is under cultivation, including a lawn, orchard, vineyard, and premises on which trees have been planted and have not attained an average height of more than two meters and woodlots on land used, primarily for agricultural purposes or; b) That is enclosed in a manner that indicated the occupier's intention to keep persons off the premises or to keep animals on the premises |
|
|
What is Section 4 of TPA?
|
Method of giving notice
1. A notice under this act may be given, a) Orally or in writing b) By means of signs posted so that a sign is clearly visible in day light under normal conditions from the approach to each ordinary point of access to the premises to which its applies; or c) By means of marking system set out in section 7 |
|
|
What is Section 7 of TPA? |
Red markings
|
|
|
What is Section 8 of TPA?
|
Yellow markings
1. Yellow markings made and posted in accordance with subsections (3) and (4) are sufficient for the purpose of giving notice that entry is prohibited except for purposes of certain activities and shall be deemed to be notice of the activities permitted |
|
|
What is Section 9 of TPA?
|
Arrest without warrant on premises
1. A police officer; or the occupier of premises, or a person authorized by the occupier may arrest without warrant any person he or she believes on reasonable and probably grounds to be on the premises in contravention of section 2 R.S.O. 1999, c T.21, s 2. Deliver to police officer a) Where the person who makes an arrest under subsection (1) is not a police officer, he or she shall promptly call for the assistance of a police officer and give the person arrested into the custody of the police officer |
|
|
What is Colour of Right as a Defense?
|
It is the defense to a charge under subsection
a) In respect of premises that is land that person charged reasonable believed that he or she had title to or an interest in the land that entitled him or her to do the act complained |
|
|
What is possession?
|
Even if given to someone else, or hidden, it is still considered of that individuals possession
With two or more, all can be charged if one does not claim |
|
|
What is considered a weapon?
|
Anything used, design to be used or intended for use
|
|
|
What is considered bodily harm?
|
Means any hurt or injury to a persons that interferes with that health or comfort of the person and that is more than merely transient or trifling in nature
Ex) broken bone, a lot of bruises, knocking teeth out |
|
|
What is parties to offence?
|
Everyone in a party to an offence who
- Actually commit - Does or omits to do anything for the purpose of aiding |
|
|
What is theft?
|
Everyone commits theft who fraudulent and without colour of right takes, or fraudulently and without colour of right converts to his or to one of another persons
To deprive |
|
|
What is considered uttering threat?
|
Causes death or bodily harm to one person
To burn, destroy or damage real or personal property To kill, poison or injure an animal or bird |
|
|
What is considered assault?
|
A person commits an assault when
Without the consent of another person, he applies force intentionally to that other person, directly or indirectly (cannot consent to bodily harm) Attempts or threatens Weapon |
|
|
What is considered robbery?
|
Theft with violence
Steals and for purpose of extorting whatever is stolen or to prevent or overcome resistance to stealing, uses violence or threatens Assault person with intent to steam from them |
|
|
What is mischief?
|
Willfully:
- Destroys or damages property - Renders property dangerous, useless, inoperative or ineffective - Obstructs, interrupts or interferes with the lawful use, enjoyment or operation of property |
|
|
What is fraud?
|
Everyone who, by deceit, false hand or other fraudulent means whether or not it is a false pretence within the meaning of this Act, defrauds the public or any person, whether ascertained or not, of any property, money or valuable security or any service
|
|
|
What is false pretence or false statement?
|
By a false pretence, whether directly or through a medium of a contract obtained by false pretence, obtains anything in respect of which the offence of theft may be committed or cause it to be delivered to another person
|
|
|
What is another name for fraudulently obtaining food?
|
Dine N'Dash
|
|
|
What is resist arrest?
|
Resist or prevent the lawful arrest or detention
|
|
|
What is intimidation in the court of law? |
Everyone is guilty of an indictable offence and liable |
|
|
What is Injunction?
|
A court order that prohibits a party from doing something (restrictive injunction) or compels them to do something (mandatory injunction)
|
|
|
What is documentary evidence?
|
Any document which is presented and allowed as evidence in a trial or hearing, as distinguished from oral testimony
|
|
|
What is circumstantial evidence?
|
Circumstantial evidence relates to a series of facts other than the particular fact sought to be proved
|
|
|
What is real evidence?
|
Physical evidence
|
|
|
What is hearsay evidence
|
3rd party utterance
Usually not admissible |
|
|
What is opinion evidence?
|
Expert evidence
|
|
|
What is character evidence?
|
A character witness is an individual who testifies as to the habitats and reputation of the another person
|
|
|
What is similar fact evidence?
|
Evidence of prior bad acts by the accused
|
|
|
What is direct evidence?
|
Testimony
|
|
|
What is trace evidence?
|
finger prints, hairs, blood cosmetics, plant fibers, mineral fibres
|
|
|
What is demonstrative evidence?
|
Include photos, x-rays, videotapes, movies, sound recording, diagrams, forensic animation, maps, drawings, graphics/graphs, animations, models and simulation
|
|
|
What is conscripted evidence?
|
Evidence obtained from a person against his or her interest, such as bodily fluids, or a confession or admission; usually through Charter Violation
|
|
|
What is best evidence rule?
|
The legal doctrine than an original piece of evidence, particularly a document, is superior to a copy if the original is available, a copy will not be allowed as evidence in a trial
|
|
|
What is fabrication of evidence?
|
Everyone who, with intent to mislead, fabricates anything with intent that it shall be used as evidence in a judicial proceeding, existing or proposed, by any means other than perjury, or incitement to the jury is guilty of an indictable offence and liable to imprisonment for a term not exceeding fourteen years
|
|
|
What are the 6 steps to containing evidence? |
1) Collect 2) Secure |
|
|
What is voir dire?
|
Trial within a trial
|
|
|
What are public laws? |
Deal with issues that affect everybody like major crimes, provincial laws or federal laws |
|
|
What is private/civil law?
|
Deals with relationships between individuals
Civil cases is an action between two or more people or businesses, mainly dealing with contracts disputes, property ownership disputes or damage |
|
|
What does the provincial court include?
|
Youth, divorce, tickets
|
|
|
What does provincial/territorial superior courts include?
|
High profile cases
|
|
|
What does provincial courts of appeal include?
|
Hearing appeals
|
|
|
What does supreme court of Canada include?
|
Nine judges
All supreme court judgement are final |
|
|
What is legal aid?
|
When you cannot afford a lawyer
|
|
|
Who's responsibility is health and safety?
|
Both employee and employer
|
|
|
What is OHSA? |
Occupational Health and Safety Act Provincial |
|
|
What is WHMIS?
|
Workplace Hazardous Material Information System
|
|
|
What is MSDS and what does it contain?
|
Material safety data sheet
It contains information on the use, storage, handling and emergency procedures all related to the hazardous of the materials |
|
|
What are the 8 WHMIS symbols?
|
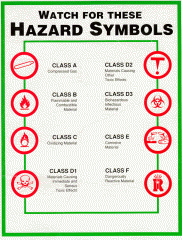
|
|
|
Reconstruct the Fire Triangle:
|
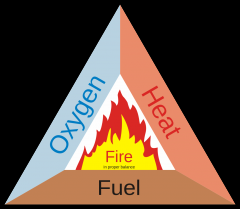
|
|
|
What is a Class A fire? |
Ordinary fire |
|
|
What is Class B fire?
|
Flammable liquids
|
|
|
What is Class C fire?
|
Electrical fire
|
|
|
What is Class D fire?
|
Flammable metals
|
|
|
What is a Class A WHMIS?
|
Compressed Gas
|
|
|
What is a Class B WHMIS?
|
Flammable and Combustible Material
|
|
|
What is a Class C WHMIS?
|
Oxidizing Material
|
|
|
What is a Class D1 WHMIS?
|
Materials causing immediate and serious toxic effects
|
|
|
What is a Class D2 WHMIS?
|
Materials causing other toxic effects
|
|
|
What is a Class D3 WHMIS?
|
Biohazardous infectious material
|
|
|
What is a Class E WHMIS?
|
Corrosive material
|
|
|
What is a Class F WHMIS?
|
Dangerously reactive material
|
|
|
What is a Class A fire extinguisher?
|
Water based
|
|
|
What is a Class B fire extinguisher?
|
Chemical foam
|
|
|
What is a Class C fire extinguisher?
|
Dry chemical
CO2 Inert Gas |
|
|
What is PASS?
|
Pull
Aim Squeeze Sweep |
|
|
What is an IED?
|
Improvised explosive device
Can look like anything |
|
|
What can a Emergency Measured Plan include?
|
Bomb Threats
Building evacuation Fire alarm procedure |
|
|
What are Point Standing Orders
|
Policies
- Adaptive by each site/work site that sets procedure and policy including administration Picking line - Crowd of people protesting, on strike, demonstrate - Have signs - Writer remain vigilant, go with or escort for replacement workers - Tactically best beside escort beside a person Cordoning off area - Yellow tape to isolate are - Do not let it go contaminated |
|
|
What is a sensor and two common types?
|
Sensor - detect a change in the environment
Microwave transmitters Photoelectric beams |
|
|
What is an Alarm/Annunciator panel and most common type?
|
Is a part of an alarm system that shows states of equipment and location of trouble and alarms
Field alarm -Use to guard things like banks, jewellery |
|
|
What is another name for handcuffs?
|
Mechanical restraints
|
|
|
What is includes in the Liquor License Act?
|
Drunk people have a safe way home
Underage drinking Intoxicated isn't still being served alcohol Club doesn't exceed capacity Not leaving premise without alcohol |
|
|
What is 10-09?
|
Repeat message
|
|
|
What is 10-52?
|
Ambulance
|
|
|
What is included in the residencies, tendency act?
|
You cannot help evict tenants
- Landlords most go through a process You cannot collect bills Landlords can change locks but must give tenants key immediately Landlords cannot interfere with a tenants reasonable enjoyment |
|
|
What are the 3 instances when a landlord can enter a unit? |
Emergency
|
|
|
What is PIPEDA?
|
Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act
PIPEDA of Privacy Act are federal laws PIPEDA is designed to protect a persons personal and sensitive information People can access sensitive information in medical incidents/emergencies - Or under investigation PIPEDA allows for electronic signatures Unlimited fines Three provinces are exempted; Alberta, Quebec & BC |
|
|
What is FIPPA? |
Freedom of information and protection of privacy
|
|
|
When you make a mistake in your notebook, how should you correct it?
|
Put a line through it and initial the error
|
|
|
What are the basic 4 levels of Canadian court?
|
Provincial Court
Superior Court Provincial Court of Appeal Supreme Court of Canada |
|
|
Ultimately, security guards reports go to who?
|
The client
|
|
|
What is tactical communication? |
Verbal option opposed to use of force |
|
|
A complaint against a security guard can be reported by?
|
Anyone
|
|
|
Does a security guard serve the public?
|
No, private interests
|
|
|
What are some basic duties of a security guard?
|
Protect person(s), property and information
|
|
|
What is 'Mens Rea'?
|
Guilty mind
|
|
|
What equipment should you check before shifts as a security guard?
|
Radio and other equipment issues to you |
|
|
What is 10-1? |
Unable to copy - change local |
|
|
What is 10-3? |
Stop transmitting |
|
|
What is 10-4? |
Acknowledgement (ok) |
|
|
What is 10-6? |
Busy |
|
|
What is 10-7? |
Out of service |
|
|
What is 10-9? |
Repeat |
|
|
What is 10-10? |
Fight in progress |
|
|
What is 10-12? |
Stand by (stop) |
|
|
What is 10-15? |
Civil disturbance |
|
|
What is 10-16? |
Domestic disturbance |
|
|
What is 10-20? |
Location |
|
|
What is 10-22? |
Disregard |
|
|
What is 10-26? |
Detaining subject |
|
|
What is 10-30? |
Unnecessary use of radio |
|
|
What is 10-31? |
Crime in progress |
|
|
What is 10-32? |
Man with gun |
|
|
What is 10-33? |
Emergency |
|
|
What is 10-35? |
Major crime alert |
|
|
What is 10-37? |
Suspicious vechicle |
|
|
What is 10-50? |
Accident (fatal, personal injury, property damage) |
|
|
What is 10-44? |
Permission to leave site for period of time |
|
|
What is 10-52? |
Ambulance needed |
|
|
What is 10-55? |
Suspected DUI |
|
|
What is 10-56? |
Intoxicated pedestrian |
|
|
What is 10-57? |
Hit and run (fatal, personal injury, property damage) |
|
|
What is 10-70? |
Fire |
|
|
What is 10-89? |
Bomb threat |
|
|
What is 10-94? |
Drag racing |
|
|
What is 10-95? |
Prisoner/subject in custody |
|
|
Can a doorman deny entry for intoxicated people to enter? |
Yes |
|
|
Who is Smart Serve? |
Division of the Hospitality Industry Training Organization of Ontario (HITOO), a non-profit organization dedicated to developing and delivering responsible alcohol service training to all individuals who serve alcohol beverages or work where alcohol beverages are sold or served in Ontario |
|
|
What must an establishment have to sell alcohol? |
They must have a Liquor Sales License |
|
|
What is THTR and what must be met for it? |
Take Home The Rest
Licensed establishments may allow guests to remove an unfinished bottle of commercially made wine that has been brought onto premise under the BYOW program or ordered from the licensed establishment as part of the guest's meal
Can only be done if: * Wine bottle must be recorked* Cannot bring wine bottle home unopened unless brought by guest * Only applies to wine and does not apply if is or near intoxicated |
|
|
How old must someone be to drink? |
19 |
|
|
How old must someone to be to sell/serve/handle alcohol? |
18 |
|
|
Can a server water down a drink without permission? |
No |
|
|
What is Sandy's Law? |
It makes it an offence to sell or supply liquor unless a sign is displayed warning women that drinking alcohol during pregnancy can cause Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder |
|
|
What are the hours of operations for an alcohol establishment? |
11am - 2am (3am on New Years)
All alcohol and containers must be cleared away within 45 min of stop-service time |
|
|
What is the AGCO responsible for? |
Reviewing license applications Issuing, transferring and renewing sale license Issuing endorsements In Add terms and conditions to license Taking administrative actions |
|
|
What is a SOP? |
A Special Occasion Permits (SOP) not required in private places which are: * Indoors * Not available for rent and public not invited/permitted * No sale of alcohol |
|
|
In the types of endorsements by AGCO, what is Brew Pub? |
Allows sale and service of beer manufactured on the premises for consumption on the same premises |
|
|
In the types of endorsements by AGCO, what is Win Pub? |
Allows sale and service of wine manufactured on the premises for consumption on the same premises |
|
|
In the types of endorsements by AGCO, what is Caterer? |
Allows catered event must be sponsored by someone other than the license holder and light meals must be available |
|
|
In the types of endorsements by AGCO, what is Room Service? |
Allows licensee to sell and serve alcohol to registered guests in a hotel room that is rented for overnight accommodations |
|
|
In the types of endorsements by AGCO, what is Mini-Bar? |
Allows license to sell and serve alcohol from a minibar in a room that is rented for overnight accommodation |
|
|
In the types of endorsements by AGCO, what is Golf Course? |
Allows the license to sell and serve alcohol for consumption on the playing area of a golf course |
|
|
In the types of endorsements by AGCO, what is BYOW? |
BYOW = Bring Your Own Wine
Allows the license to serve commercially made wine brought by a guest in the same manner as wine selected from the menu |
|
|
What are the max fines for not meeting regulations of LLA? |
* Individual/non-corporations: $100000 or imprisonment up to 1 year or both
* Corporation: $250000 |
|
|
What are the max fines for selling or supplying aochol to a minor? |
* Individual: $200000 or imprisonment up to and no more than one year or both
|
|
|
Under the LLA, when do you have the right to deny entry for a person and who can you not deny? |
You can deny if: * If the person is already intoxicated* If the person is underage * If the person is disruptive * If the premise it too crowded
You cannot deny: AGCO inspectors, law enforcement officers, firefighters or government inspectors |
|
|
Under the LLA, when can you eject guests? |
Guests who are drunk, aggressive or out-of-control are not allowed on the premises. The LLA require that a person be ejected when it is reasonably believed that he/she
Not permitted, by law, on the premises: * A person under 19 years of age when a condition of the license states no entry to minors* A guest who has been previously barred from the establishment * A guest who has been previously asked to leave but returns on the same day * A person who, according to a condition of the license is not permitted to be in the establishment at any time * A guest who is rowdy or is intent on causing a fight * A guest who is selling illegal products, gambling illegally, or soliciting for prostitution |
|
|
Under the LLA, when can you use Use of Force? |
If a guest does not leave as requested, the person can be removed with "no more force than is necessary" |
|
|
How do you calculate a standard drink? |
(% of alcohol)*(ounces)=60 |
|
|
How does alcohol absorption work? |
Alcohol travels down throat to the stomach Alcohol is absorbed into the blood by stomach and intestines Bloodstream carries the alcohol throughout the body including the brain and other tissues Alcohol is metabolized in the liver by body chemicals that break down the alcohol at a rate of approximately one hour per standard drink ~90% of the alcohol is then slowly eliminated from the bloodstream Remaining 10% of alcohol is removed through the person's sweat, breath and urine Alcohol is metabolized more slowly that it is absorbed |
|
|
What is BAC? |
Blood Alcohol Concentration
If a person drinks more than one drink an hour, their BAC increases In Ontario, BAC of 50mg per 100mL of blood (0.05) can lead to driver suspension and (0.08) is a criminal offence |
|
|
What are the five signs of intoxication? |
Change in vital signs and physical appearance Loss of self control and inhibitions Poor judgement Reason, caution and memory Coordination and balance |
|
|
What must be on an ID for it to be acceptable? |
Issued by government
Person's photo Birth date |
|
|
What are valid ID's in Ontario? |
Driver's License (Ontario) Canadian Citizenship Card Canadian Armed Forces Identification Card Bring Your Identification card (BYIC) issued by Liquor Control Board of Ontario Secure Indian Status Card (Canada) Permanent Residence Card (Canada) Photo card issue under Photo Card Act, 2008 Ontario Health Card (but use at caution) |
|
|
What are four things to note before you decide the number of drinks to safely serve? |
Asses your guest: Tone of voice, loud, aggressive, slurring, behaviours Slower speech and movement may already have impaired but could be medications Driving, Designated Driver?, feeling, mood
Keep communication |

