![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
CML: Peripheral Blood Smear
|
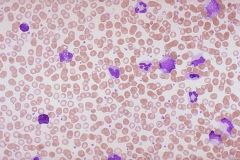
a
|
|
|
CML - BM aspirate - Lots of meloid and very few erythroids – so ME ratio is quite elvated in CML
|
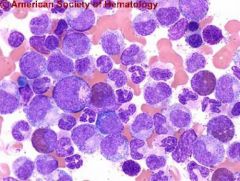
a
|
|
|
often seen in CLL
|
a
|
|
|
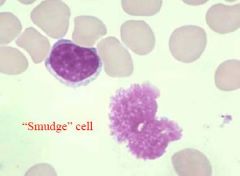
CLL - Lots of mature looking lymphocytes that all look the same – different from AML and ALL and CLL
|
a
|
|
|
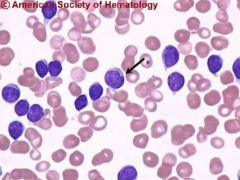
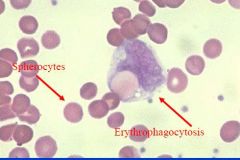
CLL - Autoimmune hemolysis is very common – going to see shperocytes here – can see monocyte phagnocytising an RBC in the peripheral blood
|
a
|
|
|
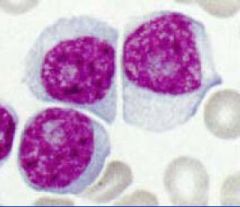
CLL - Prolymphocytes in a patient previously diagnosed with CLL - a bad transforming event
|
a
|
|
|
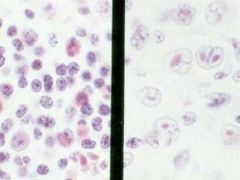
Richters syndrome - CLL (left) and large cell NHL (right) in the same node of a single patient
|
a
|
|
|
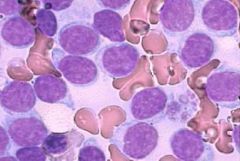
Bone marrow involvement in CLL
|
a
|
|
|
Immunohistochemistry detects faint Bcl2 expression in a normal lymphoid follicle in the mantle area
|

a
|
|
|
CML - presentation
|
pretty nonspecific, but have Splenomegaly and Hepatomegaly
|
|
|
CML - pathophysiology
|
- Neoplastic transformation of a hematopoietic stem cell
- can self-renew and diff - w/ inc prolif, and dec diff → accelerated phase and eventual blast crisis |
|
|
CML - Common Laboratory Findings
|
- Neutrophilia with left shift
- Basophilia - low LAP - BM is Hypercellular, Dec fat, Inc ME ratio |
|
|
CML - cytogenics
|
- conventional
- Philadelphia (Ph) chrom - t(9;22) - bcr on 22 and abl on 9 make a fusion gene product on 22 - Brc/Abl - FISH and PCR will find it but wont find other abnormalities - conventional might not find it but will find other abnormalities |
|
|
Bcr-Abl
|
- Ras → MAPK, STAT1 and 5 and that causes inc prolif
- PI-3 kinase → AKT leads to inc survival - adhesion defect |
|
|
CML stages
|
- Chronic - Median 3-5 years
- Accelerated phase - 6–9 months, Increasing WBC, splenomegaly, increasingly unresponsive to therapy - Blast crisis - Median survival 3–6 months, worsening constitutional symptoms, complications of cytopenias , extramedullary disease (skin, CNS, bone) |
|
|
CML treatment
|
- Chemotherapy with hydroxyurea, busulfan - old
- IFN-a - bad SEs - SCT - only curative therapy but high mortality - Gleevec - Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitors |
|
|
Gleevec resistance
|
- Amplification of Brc/Abl
- Mutations within the ABL kinase domain - Drug efflux – - Activation of downstream signaling pathways |
|
|
Docs overcoming gleevec resistance
|
- Higher-dose Gleevec
- Second generation ABL kinase inhibitors (inhibit things downstream) - Gleevec + novel therapies |
|
|
Benign Neutropenia
|
- Left shift not as marked as CML
- Increased granulocytes but Normal basophil count - will still see fat in BM - molecular test normal |
|
|
CLL - pathophys
|
accumulation of slowly dividing, mature B or (much more rarely) T cells in the peripheral blood, marrow, lymph nodes and spleen
|
|
|
CLL - lab findings
|
- Lymphocytosis greater than 5,000/µl3 - mature-appearing with numerous smudge cells
- BM has increased lymphocytes |
|
|
CLL - assocated factors
|
- Autoimmune hemolytic anemia is common
- TRAP is negative in cytochemistry |
|
|
CLL - Tranforming events
|
- Prolymphocytic leukemia is an uglier disease - poor prog
- Richter’s Syndrome - large cell NHL - Fever, abd. pain, wt. loss, adenopathy, HSM, anemia, thrombocytopenia |
|
|
CLL - Flow cytometry
|
- Mature B-cell population (+CD19, 22 & k light chain)
- Monoclonal (light chain restricted, + for k only) - Population expresses CD5 (normally a T-cell marker) & CD23 |
|
|
Bcl-2
|
- Inhibits release of cyto c from mito which activate caspases which are are the effectors of apoptosis
- so it inhibits apoptosis |
|
|
CLL - genetics
|
- overexpression of Bcl-2
- 13q deletion most common - 17p realted to p35 - 11q, Tri12 |
|
|
CLL and p53 dysfunction
|
- 17p, point mutations of p53, ATM mutations (16%)
- ass w/ resistance to chemo and short survival |
|
|
CLL - IgVH Gene Mutation Status
|
- if no mutation, very bad prognosis
- Zap-70 associated w/ |
|
|
CLL - treatment
|
- only if the patient is symptomatic
- Fludarabine - Rituxan – binds to CD20 on B-cells - Chlorambucil + prednisone - Campath 1-H – targets CD52 on B and T cells - making them HIV |
|
|
Benign Lymphocytoses
|
- associated w/ mono
- blood has Atypical lymphocytes - Normal BM – negative (TRAP) - mixture of B and T w/ polyclonal B-cell |
|
|
Atypical Lymphocytoses
|
- Flow cytometry - predominance of Ts and polyclonal Bs
- shows + k and l - The negative cells are Ts |
|
|
Hairy cell leukemia
|
- Abnormal cells that are TRAP positive
- Middle aged man - Massive splenomegaly -> panyctopenia - Mature B-cell population (19, 22 & k), monoclonal w/ k - Population expresses CD11c, CD25 & CD103 - Treat w/ 2CDa, IFN-a, or deoxycoformycin |

