![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
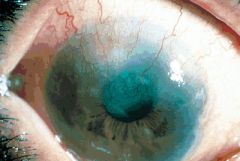
trachoma
|
|
|
|
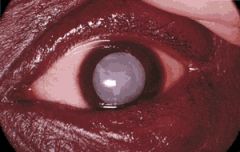
cataract
|
opacification of crystalline lens
anterior subcapsular - fibrous plaque beneath anterior capsule, metaplastic anterior lens epithelial cells posterior subcapsular - posterior migration of lens epithelium, "bladder of Wedl" cell formation, interfers w/ near vision, flares Cortical Degeneration - fragmentation of lens fibers, Morgagnian globules Nuclear Sclerosis - inevitable growth and development of lens, old lens fibers degenerate, blue-yellow color defects |
|
|
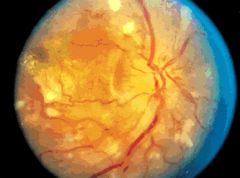
HTN retinopathy
|
HTN --> vasospasm --> muscular and endothelial necrosis and vascular incompetence --> retinal edema --> exudates --> disc edema
|
|
|
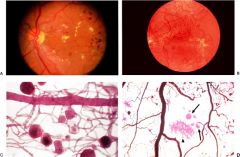
diabetic retinopathy
|
pericyte loss - sorbitol plays a role
thickened basement membrane capillary nonperfusion --> VEGF --> neovascularization (proliferative) microaneurysms hemorrhages, hard exudates, retinal edema Cataracts aldose reductase predisposition to infections (mucormycosis) |
|
|
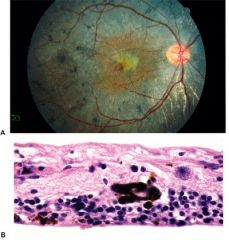
retinitis pigmentosa
|
|
|
|
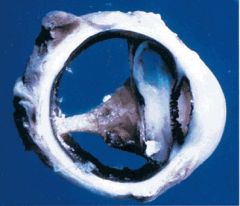
retinopathy of prematurity
|
|
|
|
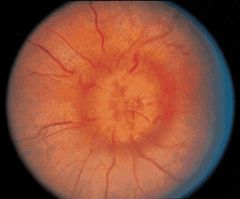
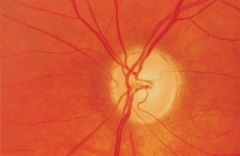
chronic papilledema
|
systemic htn, increased intracranial pressure, decreased intraocular pressure, increased intraocular pressure, increased intraorbital pressure, hypercapnia (basically a change in pressure in any direction anywhere)
--> blockage of axoplasmic flow at lamina cribrosa swollen nerve head, narrowing of physiological cup, lateral displacement of peripapillary retina, Paton's folds of outer retina |
|
|
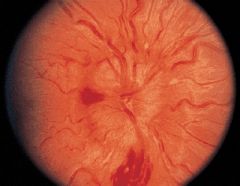
hemorrhage in papilledema
|
|
|
|
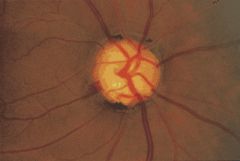
optic atrophy
|
|
|
|
glaucoma
|
cupping of optic nerve, death of retinal ganglion cells and optic nerve axons
elevation of intraocular pressure blockage of aqueous outflow open or closed angle variants insidious loss of vision |
|

|
phthisis bulbi
|
|
|
|
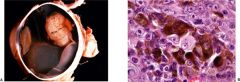
malignant melanoma
|
most common intraocular tumor in white adults
iris, choroidal, ciliary tumors choroidal have mushroom configuration 25% fatal in spindle clel variations, 66% fatal in epithelioid cell variants mets to liver |
|
|
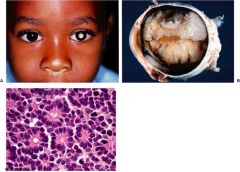
retinoblastoma
|
most common intraocular tumor in children
average age at dx - 18 months tumor arises from and destroys retina Flexner-Wintersteiner rosettes Rb gene on chromosome 13 (typically bilat presentation) |
|

|
Central Renal Artery Occlusion
|
sudden severe visual loss
cherry red spot early - coag necrosis, pyknosis, edema of inner layers late - inner ischemic retinopathy atherosclerosis, emboli, vasculitis (r/o Giant Cell in elderly pts!!!) |
|

|
Diabetic Retinopathy
|
pericyte loss - sorbitol plays a role
thickened basement membrane capillary nonperfusion --> VEGF --> neovascularization (proliferative) microaneurysms hemorrhages, hard exudates, retinal edema Cataracts aldose reductase predisposition to infections (mucormycosis) |
|
|
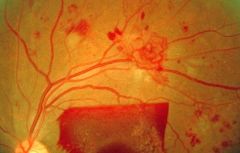
Diabetic Retinopathy
|
pericyte loss - sorbitol plays a role
thickened basement membrane capillary nonperfusion --> VEGF --> neovascularization (proliferative) microaneurysms hemorrhages, hard exudates, retinal edema Cataracts aldose reductase predisposition to infections (mucormycosis) |
|
|
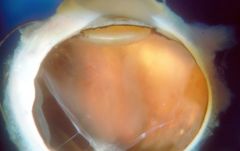
Diabetic Retinopathy
|
pericyte loss - sorbitol plays a role
thickened basement membrane capillary nonperfusion --> VEGF --> neovascularization (proliferative) microaneurysms hemorrhages, hard exudates, retinal edema Cataracts aldose reductase predisposition to infections (mucormycosis) |
|
|
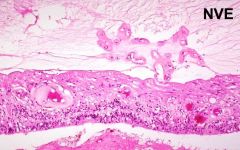
Neovascularization
|
seen in diabetic retinopathy
|
|
|
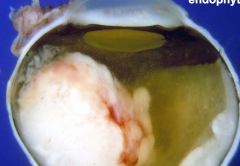
Retinoblastoma
|
most common intraocular tumor in children
average age at dx - 18 months tumor arises from and destroys retina Flexner-Wintersteiner rosettes Rb gene on chromosome 13 (typically bilat presentation) |
|
|
|
Retinoblastoma
|
most common intraocular tumor in children
average age at dx - 18 months tumor arises from and destroys retina Flexner-Wintersteiner rosettes Rb gene on chromosome 13 (typically bilat presentation) |
|
|
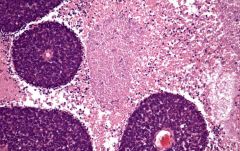
Retinoblastoma
|
most common intraocular tumor in children
average age at dx - 18 months tumor arises from and destroys retina Flexner-Wintersteiner rosettes Rb gene on chromosome 13 (typically bilat presentation) |
|
|
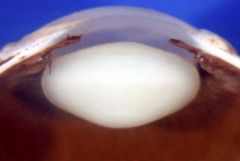
cataract
|
opacification of crystalline lens
anterior subcapsular - fibrous plaque beneath anterior capsule, metaplastic anterior lens epithelial cells posterior subcapsular - posterior migration of lens epithelium, "bladder of Wedl" cell formation, interfers w/ near vision, flares Cortical Degeneration - fragmentation of lens fibers, Morgagnian globules Nuclear Sclerosis - inevitable growth and development of lens, old lens fibers degenerate, blue-yellow color defects |
|
|
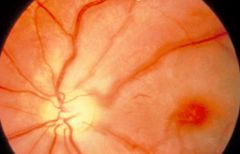
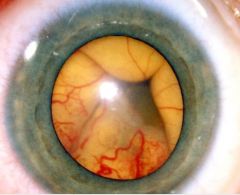
Central Retinal Artery Occlusion
|
sudden severe visual loss
cherry red spot early - coag necrosis, pyknosis, edema of inner layers late - inner ischemic retinopathy atherosclerosis, emboli, vasculitis (r/o Giant Cell in elderly pts!!!) |
|
|
coat's dz
|
|
|

|
copper wiring
|
|
|
|
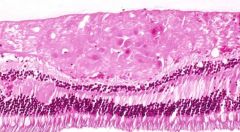
cotton wool spots
|
DM, collagen vascular dz, AIDS
microinfarcts of nerve fiber layer s/p occlusion of precapillary arterioles blockage of axoplasmic flow cytoid bodies (swollen axons w/ eosinophilic nucleoid) |
|
|
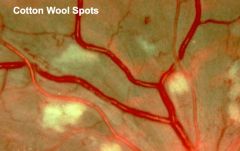
cotton wool spots
|
DM, collagen vascular dz, AIDS
microinfarcts of nerve fiber layer s/p occlusion of precapillary arterioles blockage of axoplasmic flow cytoid bodies (swollen axons w/ eosinophilic nucleoid) |
|
|
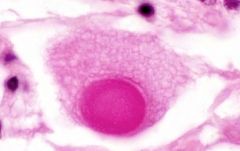
cytoid body
|
seen in cotton wool spots
swollen axons w/ eosinophilic nucleoid composed of dammed organelles |
|
|
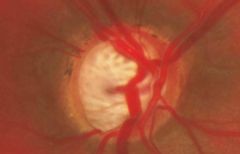
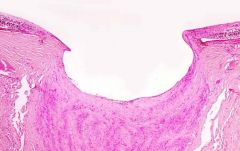
glaucoma
|
cupping of optic nerve, death of retinal ganglion cells and optic nerve axons
elevation of intraocular pressure blockage of aqueous outflow open or closed angle variants insidious loss of vision |
|
|
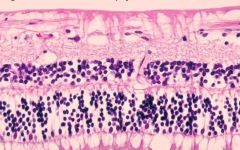
glaucoma
|
cupping of optic nerve, death of retinal ganglion cells and optic nerve axons
elevation of intraocular pressure blockage of aqueous outflow open or closed angle variants insidious loss of vision |
|
|
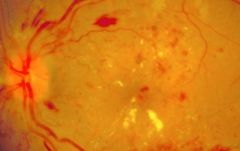
glaucoma
|
cupping of optic nerve, death of retinal ganglion cells and optic nerve axons
elevation of intraocular pressure blockage of aqueous outflow open or closed angle variants insidious loss of vision |
|
|
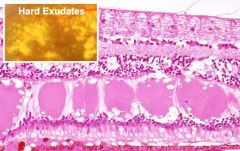
hard exudate
|
pools of eosinophilic lipoproteinacous material in outer plexiform layer
may be phagocytized by macrophages (Gitter cells) circinate retinopathy - ring of exudates reflecting radial orientation of henle fibers Macular star - also showing orientation of henle fibers |
|
|
hemorrhage and exudate
|
|
|
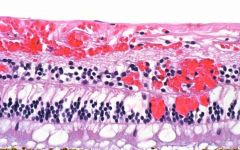
2 types present ... what are they?
|
hemorrhage (flame and dot)
*types on next slide |
flame or splinter - tracks along nerve fiber axons
blot of dot - deep retinal layers scaphoid - boat shaped - flat, top fluid level Sub retinal - dark colored, similar to choroidal melanoma Roth Spot - white centered hemorrhage - bacterial endocarditis |
|
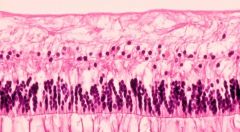
|
inner ischemic retinal atrophy
|
seen in central renal a. occlusion
|
|
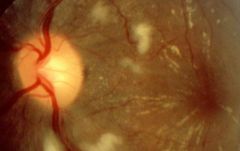
|
malignant HTN
|
HTN --> vasospasm --> muscular and endothelial necrosis and vascular incompetence --> retinal edema --> exudates --> disc edema
|
|
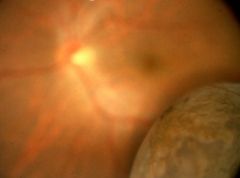
|
malignant melanoma
|
most common intraocular tumor in white adults
iris, choroidal, ciliary tumors choroidal have mushroom configuration 25% fatal in spindle clel variations, 66% fatal in epithelioid cell variants mets to liver |
|

|
malignant melanoma
|
most common intraocular tumor in white adults
iris, choroidal, ciliary tumors choroidal have mushroom configuration 25% fatal in spindle clel variations, 66% fatal in epithelioid cell variants mets to liver |
|
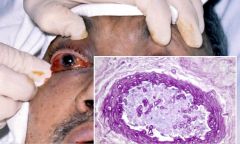
|
mucormycosis
|
typically only seen in diabetic pts b/c of immunocomp
|
|
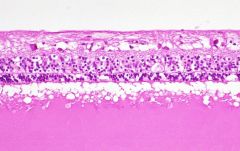
|
rentinal detachment
|
|
|
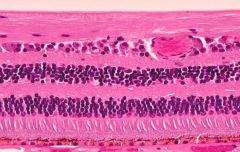
|
retina
|
|
|
|
"Dry" Age Related Macular Degeneration
|
Retinal Pigmented Epithelium and outer retina Degeneration, pigment clumping
|
|
|
|
"Wet" Age Related Macular Degeneration
|
Changes in Bruch's Membrane
PAS pos focal calcification Drusen - marker for stressed RPE cells tx: inject anti-VEGF Ab |
|
|
|
Thyroid Ophthalmopathy
|
unilateral or bilateral exophthalmos
elargement of extraocular muscles |
|
|
|
cavernous hemangioma
|
can affect orbit (not in lecture, no details in syllabus)
|
|
|
|
Orbital Rhabdomyosarcoma
|
most common malignant orbital tumor of childhood
on ddx of all kids w/ orbital dz rapid growth mimics inflammation average age of onset = 8 yrs |
|

