![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
111 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the hybridization at the O- in CH3COO-?
|
Sp2
|
|
|
What is unusual about the C-C sigma bond joining two double bonds in conjugated dienes?
|
it is short because it is actually partially a double bond
|
|
|
what do you need for conjugation?
|
3 adjacent p orbitals
|
|
|
CH2=CHCH2+
|
allyl arbocation
|
|
|
why is an allyl carbocation more stable than a one degree carbocation?
|
because of p orbital overlap
|
|
|
In any system X=Y-Z, Z is ___ hybridized to allow the lone pair to ___ __ __ ___, making the system ___
|
occupy a p orbital, making the system conjugated
|
|
|
Four things to watch for with resonance:
|
1.three atom 'allyl system (x=y-Z*<-->X*---Y=Z
2.conjugated double bonds 3.cations having positive charge adjacent to a lone pair 4.double bands having one atom more electronegative than the other |
|
|
Structures with ___ bonds and ___ charges are more stable.
|
more, fewer
|
|
|
structures in which every atom has an ___ are more stable.
|
octet
|
|
|
Structure that place a ___ charge on a more ____ element are more stable.
|
negative, electronegative
|
|
|
products of electrophilic addition to conjugated dienes. which one is more stable? which one is faster?
|
1,2 and 1,4 addition products. 1-4 is more stable. 1,2 is faster.
|
|
|
1,2 product, 1,4 product (other names). why? under whatconditions do each happen?
|
kinetic product and thermodynamic product. kinetic happens in cold temps, thermodynamic warmer. Thermodynamic is preferred because it is exothermic.
|
|
|
CH2=CH-CH-CH2---HX-->>
|
CH2-CH-CH=CH2,
| | H X CH2=CH-CH-CH2, | | x H |
|
|
electrophilic addiction of HX
1.steps 2.markovnikov rule followed? what kind of intermediate? 3.Products? Nature? 4.More stable product? |
1.two steps
2.mark rule is followed, allylic carbocation formed. 3.1,2 product is kinetic because when H+ adds to double bond X- just adds to the closest one. Kinetic is formed faster at low temp. 4.Thermodynamic product has more substituted, more stable double bond, and predominates at equillibrium |
|
|
Diels alder-reaction forms 2 ___ bonds and one___ bond in a six-membered ring.
|
sigma, pi
|
|
|
what initiates diels-alder rxn?
|
heat
|
|
|
concerted mechanism
|
all bonds broken, formed in single step
|
|
|
what condition must the diene meet to react in D-A reaction
|
it must be s-cis
|
|
|
what increases the reaction rate in a diels-alder reaction?
|
electron-withdrawing groups on dienophile
|
|
|
s. chemistry of diels-alder
|
retained
|
|
|
endo product
|
product closer to the two-carbon bridge
|
|
|
draw:
1.(2E,4E)-2,4-octadiene 2.(3E,5Z)-3,5-nonadiene in s-cis |
see ssm 16-5
|
|
|
draw
(3Z,5Z-4,5-dimethyl-3,5-decadiene in a)cis and b)trans conformation |
see 16-5
|
|
|
does a more stable reaction have higher or lower heat of hydrogenation?
|
lower
|
|
|
if two conjugated dienes are equal, what do you look for for a tiebreaker regarding reactivity and stability?
|
look for the most substituted double bond.
|
|
|
sum up the addition reaciton with conjugated diene
|
1.pi bond steals the hydrogen
2.2+ carbocations form 3.1,2 and 1,4 products form (nucleophilic attack on the carbocation_ |
|
|
Addition of H+ forms a ____ __ ___
Nucleophilic attack of X- forms _,_ and _,_ products |
resonance-stabilized carbocation, 1,2 and 1,4
|
|
|
what is an endo product?
|
it's on a six-membered result of the diels-alder reaction, in the axial position, closest to the two member bridge with the double bond
|
|
|
3 steps to finding diene and dienophile needed to make products
|
1.find six-membered ring with c-c double bond
2.draw three arrows to work back 3.follow arrows to show diene and dienophile |
|
|
16.38
just do |
see ssm 16-13
|
|
|
steroid
|
tetracyclic lipid
|
|
|
200-400 nm is what type of light?
|
uv
|
|
|
400-750 nm is what type light?
|
visible
|
|
|
750+ nm is what type light?
|
infrared
|
|
|
what wavelength of light do electrons in unconjugated systems need to reach an excited state?
|
greater than 200 nm
|
|
|
the more conjugated a diene is, the ____ wavelength of light it needs to reach an excited state
|
shorter, least, less
|
|
|
chemical that makes tomatoes red. why?
|
lycopene makes tomatoes red. it has 11 conjugated pie bonds and so absorbs all clors except red.
|
|
|
different s and trans on the same bonds are different (stereoisomers/conformations)
|
conformations
|
|
|
different E and Z are different (s.isomers/conformations)
|
conformations
|
|
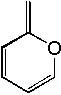
How many pi electrons in this? Why?
|
There's 8, the O lone pairs make it sp hybridized
|
|
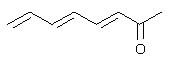
Will this or a diene like this with a phenyl at the end absorb longer wavelengths?
|
this one, because it's trans and more stable and reactive.
|
|
|
Which of the following compounds absorbs at the longest wavelength?
a1,3,5-Hexatriene b1,3,5,7-Octatetraene c1,7-Diphenyl-1,3,5-heptatriene d1,6-Diphenyl-1,3,5-heptatriene |
d
|
|
|
In comparing kinetic control to thermodynamic control for the reaction of butadiene and HCl, which of the following statements respresents kinetic control?
1.The intermediate is more stable and the product is more stable. 2.The intermediate is less stable and the product is more stable. 3.The intermediate is more stable and the product is less stable. 4.The intermediate is less stable and the product is less stable. |
intermediate is more stable, product is less stable
|
|
|
When 1,3-butadiene reacts with HCl, two products form: 3-chloro-1-butene and 1-chloro-2-butene. At low temperatures (–78˚C), which of the following statements is correct?
1.Thermodynamic control favors formation of 3-chloro-1-butene. 2.Kinetic control favors formation of 3-chloro-1-butene. 4.Thermodynamic control favors formation of 1-chloro-2-butene. Kinetic control favors formation of 1-chloro-2-butene. |
Kinetic control favors formation of 3-chloro-1-butene.
|
|
|
In the addition of HBr to 1,3-butadiene, one product is called the kinetic product and the other is called the thermodynamic product. Which of the following descriptors applies to the kinetic product?
a) 1,2 product b) 1,4 product c) most stable d) least stable e) formed slowest f) formed fastest g) formed at low temperature h) formed at high temperature i) most substituted alkene j) least substituted alkene k) bromide attack at more substituted site l) bromide attack at least substituted site a, c, e, g, j, l b, c, f, g, i, l, a, d, f, g, j, k b, d, f, h, i, k |
a, d, f, g, j, k
|
|
|
How many products are expected from 1,2- or 1,4-addition of HBr to 1,3-pentadiene? Disregard stereoisomers.
|
3
|
|
|
Which of the following conjugated dienes gives a single product upon 1,2- or 1,4-addition of HCl?
1.Butadiene 2-Methylbutadiene 1,3-Cyclohexadiene 2,3-Dimethylbutadiene |
1,3-Cyclohexadiene
|
|
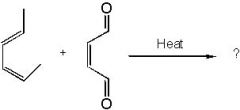
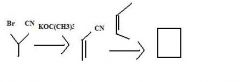
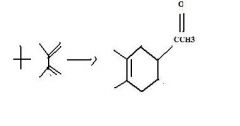
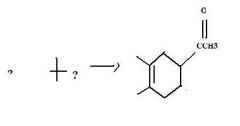
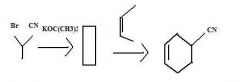
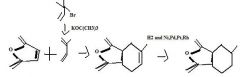
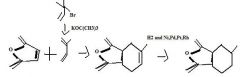
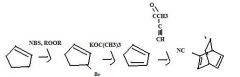
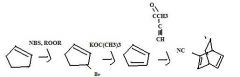
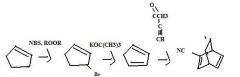
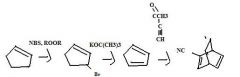
Find the product.
|
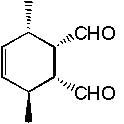
f
|
|
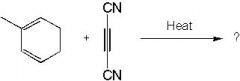
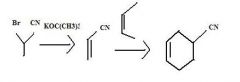
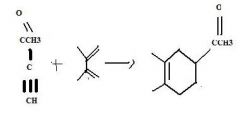
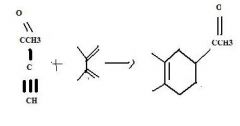
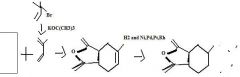
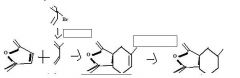
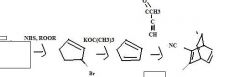
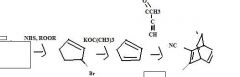
What's the final product
|
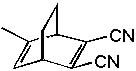
|
|
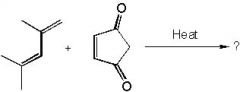
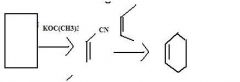
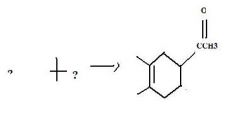
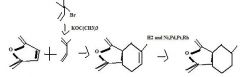
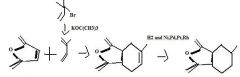
product
|
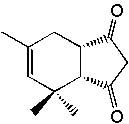
|
|
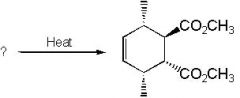
|
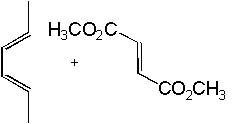
|
|
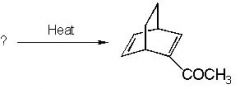
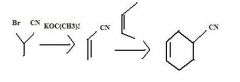
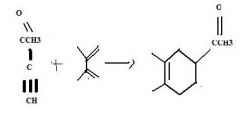
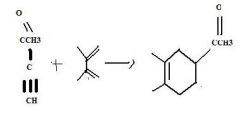
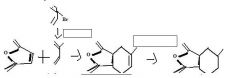
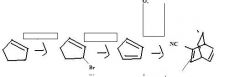
do the retro
|
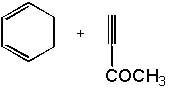
|
|
|
What do you need to make a cyclohexadiene?
|
an alkyne having an electron withdrawing group attached directly to it
|
|
|
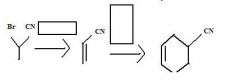
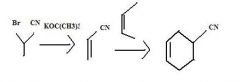
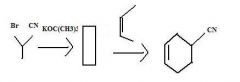
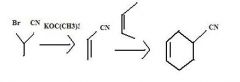
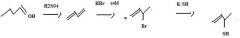
What to use to make alkyl cyanides by direct substition?Why?
|
1o and 2o alkyl bromides. They are reactive enough.
|
|
|
Under special conditions, conjugated dienes will undergo 1,4-addition to add H and Br to the ends of the diene, forming a
C-C double bond with the middle two carbons. |
make fc tom
|
|
|
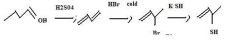
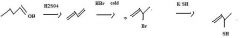
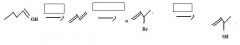
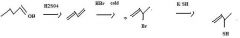
Use conc. H2SO4 to make an alkene by dehydration of an alcohol.
|
make fc
|
|
|
Use HBr with modest heating to accomplish 1,4-addition to a conjugated diene.
|
make fc tom
|
|
|
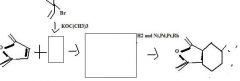
KCN provides CN- for nucleophilic substitution to convert 1o and 2o alkyl halides into alkyl cyanides.
|
make fc tom
|
|
|
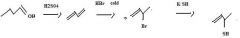
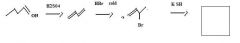
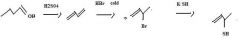
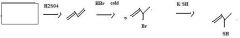
Thiols are best made by direct substitution using a precursor that has a good leaving group. In this case, the alkyl bromide precursor is the best choice, considering the starting material available.
|
make fc tom
|
|
|
Use KSH to replace bromide to make a thiol.
|
make fc tom
|
|
|
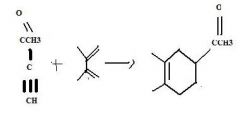
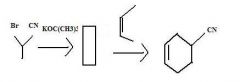
Use an alkene having an electron withdrawing group attached directly to it as one of the partners in a Diels-Alder reaction to make a substituted cyclohexene.
|
make fc tom
|
|
|
You can make disubstituted alkenes preferentially having the Z stereochemistry by reducing an alkyne.
|
make fc tom
|
|
|
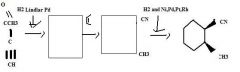
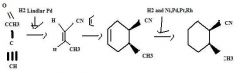
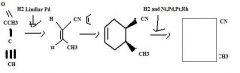
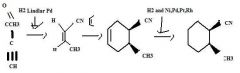
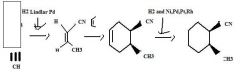
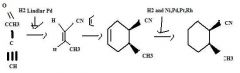
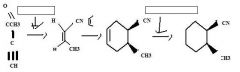
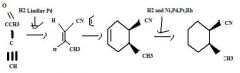
Use H2 together with a special catalyst, Lindlar Pd, to reduce a disubstituted alkyne to an alkene preferentially having the Z stereochemistry.
|
TOM
|
|
|
H2 together with Ni, Pd, Pt, or Rh as a catalyst reduces alkenes.TOM
|
TOM
|
|
|
Use this bulky base to eliminate HX from an alkyl halide to make an alkene.
|
TOM
|
|
|
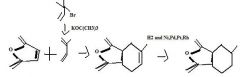
Use an alkyne having an electron withdrawing group attached directly to it as one of the partners in a Diels-Alder reaction to make a substituted cyclohexadiene.
|
TOM
|
|
|
Removal of HBr from an alkyl bromide is an effective way to make alkenes. Use a precursor having the Br at an allylic position, because it is readily made and will result in forming a conjugated diene.
|
TOMM
|
|
|
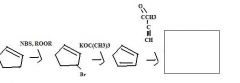
Use NBS together with a radical source, such as a peroxide, to replace an allylic H by Br.
|
TOM
|
|
|
H2 together with Ni, Pd, Pt, or Rh do what?
|
alkenes.
|
|
|
What to use to remove HX from an alkyl halide? Makes what?
|
bulky base to eliminate HX from an alkyl halide to make an alkene.
|
|
|
alkyne with electron withdrawing group attached to it in DL reaction makes whta?
|
Use an alkyne having an electron withdrawing group attached directly to it as one of the partners in a Diels-Alder reaction to make a substituted cyclohexadiene.
|
|
|
How to make alkene with a br
|
Removal of HBr from an alkyl bromide is an effective way to make alkenes. Use a precursor having the Br at an allylic position, because it is readily made and will result in forming a conjugated diene.
|
|
|
What should you use to replace allylic H by Br?
|
Use NBS together with a radical source, such as a peroxide, to replace an allylic H by Br.
|
|
|
use what to make alkene by dehydration?
|
Use conc. H2SO4 to make an alkene by dehydration of an alcohol.
|
|
|
use what to get 1,4 addition conjugated diene
|
Use HBr with modest heating to accomplish 1,4-addition to a conjugated diene.
|
|
|
How to make thiols
|
Thiols are best made by direct substitution using a precursor that has a good leaving group. In this case, the alkyl bromide precursor is the best choice, considering the starting material available.
|
|
|
How to make a thiol out of a bromide
|
Use KSH to replace bromide to make a thiol.
|
|
|
how to make disubstituted alkenes with z stereochemistry
|
You can make disubstituted alkenes preferentially having the Z stereochemistry by reducing an alkyne.
|
|
|
H2 + Lindar Pd. does what?
|
Use H2 together with a special catalyst, Lindlar Pd, to reduce a disubstituted alkyne to an alkene preferentially having the Z stereochemistry.
|
|
|
how to discern heat of hydrogenation
|
the most conjugated and most substituted diene will have the lowest heat of hydrogenation.
|
|
|
16.43
a cis or trans dienophile will form a ____ or ____ thinger |
cis or trans product of diels-alder
|
|
|
steps for doing retro diels-alder
|
1.identify ring
2.draw lines 3.disconnect |
|
|
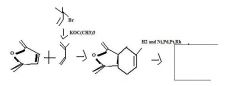
what happens when you mix an alkyne in a diels-alder rxn?
|
you get kind of a box-looking thing with double bonds on both ends of the bottom folds and a two-carbon bridge across the top.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
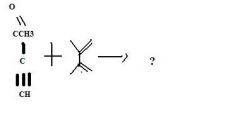
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
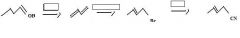
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

