![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Latitude |
Latitude lines also called parallels run East to West. The distance between these lines are always the same. The letters will always be N or S for north or south of the equator. The 0 mark is the equator. |
|
|
What is longitude |
Longitude or meridians run north to south. The Prime meridian is in Greenwich England. The letters will always be W or E for West or East of England. |
|
|
What information do you need to determine latitude? |
Latitude is calculated by finding the ships angle in relation to the north star, or Polaris |
|
|
What information do you need to determine Longitude? |
Longitude is calculated by having a clock set to Greenwich time and calculating the difference between you and Greenwich. Then multiplying by 15. |
|
|
What expedition is considered the beginning of modern oceanography? |
Thompson and Murray on the HMS Challenger is considered the first oceanography expedition |
|
|
Why is the Golmar Challenger important? |
It is the first drilling ship to collect oceanic crust cores, and start the JOIDES program. |
|
|
How is the Surface of the Earth distributed over continents and oceans? Including regular and Corrected for continental shelfs. |
71% Ocean and 29% land Corrected 60% ocean and 40% land |
|
|
Characteristics of Pacific Ocean |
Largest, oldest, least salty and deepest ocean. Extremely active and has many islands and sea mounts |
|
|
Characteristics of Atlantic Ocean |
Long, narrow and young. Second largest ocean, about 68% of the worlds freshwater runs into this ocean. |
|
|
Characteristics of Indian Ocean |
About the same depth, age and saltiness of the Atlantic. Delivers many sediments to the northern part of the ocean. |
|
|
Characteristics of Arctic Ocean |
Depth is only about 1km average with broad continental shelves. |
|
|
What are continual margins and how are they subdivided? |
Contintal margins are the continuation of a content below sea level Passive and Active Margins |
|
|
Passive Margins |
Geologically passive, Atlantic Ocean, Has a rise but no trench |
|
|
Active Margins |
Geologically active, Pacific ocean. Has no rise but has a trench |
|
|
Continental Shelf |
Shallow submerged extension on a continent |
|
|
Continental Slope |
Transition between defending continent and deep ocean floor |
|
|
Rise |
Beginning of the ocean basin which is formed from the accumulation of sediments |
|
|
Diagram of a passive margin |
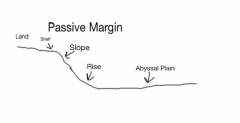
|
|
|
Digram of an active margin |
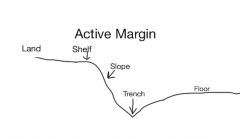
|
|
|
Who proposed Continental Drift? |
Alfred Wegener |
|
|
What is Pangea? |
Pangea was the massive single landmass |
|
|
What is Panthalassa? |
Panthalassa was the single ocean. |
|
|
Four sets of evidence for continental drift |
1. Glaciation 2. Stratification of Plants and animals 3. Mountains and rocks match other conts. 4. The conts. fit like puzzle pieces. |
|
|
Describe the classification of the earths interior based on physical properties of the material inside the earth |
Lithosphere - rigid outer layer, crust + upper mantle Asthenosphere - Deformable layer of upper mantle Lower Mantle - Denser and less deformable Outer Core - Dense and viscous liquid Inner Core - Solid and very dense |
|
|
What is the Lithosphere |
Rigid outer layer, contains the crust and the uppermost mantle |
|
|
What is the Asthenosphere |
Deformable layer of the upper most mantle, Plastic. Not liquid but moldable like play dough or clay. |
|
|
What is the chemical composition of the earths core |
Iron and Nickel |
|
|
What are the two kinds of crust |
Oceanic crust Continental crust |
|
|
What are the differences between oceanic and continual crust |
Continental crust is mainly composed of light colored granite, it has a low density Oceanic crust is made of dark colored basalt and has a high density |
|
|
What is isostasy |
Isostasy is how the plates sit on the asthenosphere. Balance of an object floating upon a fluid |
|
|
Why is the continual thickest under the tallest mountain? |
Because continental crust does not subduct typically. Instead they pile up on each other creating mountains. |
|
|
What are the positive and negative magnetic anomalies found on the seafloor? What is the significance? |
Rocks on the sea floor with different magnetic fields, indicated that at different periods the magnetic field was in different positions. This showed that there have been changes and even reversals of the Earth's magnetic field Negative anomalies represent region where the crust is revered Postive anomalies represent a region where the crust is normal |
|
|
What is a plate? What does in it consist of? |
A plate is part of the lithosphere that sits on top of the asthenosphere It is made of oceanic lithosphere or ocean and continental lithosphere |
|
|
Divergent Boundary + example |
Plates move apart from each other mid Ocean ridge |
|
|
Convergent Boundary + example |
Plates move toward each other Eurasian plate and Indian plate |
|
|
Transform boundary + example |
Two plates move along side each other, Shearing. San Andreas Fault line, California |
|
|
Describe the stages of the formation of a new ocean like the Atlantic Ocean |
Uplift (Rift Valleys) --> Divergence (Narrow Seas) --> Divergence ( Ocean Basins) |
|
|
How fast do plates move How do you calculate the spreading rate? |
Typically anywhere from 1 - 10 cm a year Cm/age |
|
|
What closes oceans |
Convergent plate boundaries with subduction zones typically close oceans |
|
|
What are hot spots |
Hot spots are plumes of magma rising from the mantle |
|
|
What do hot spots create on the earths surface |
They create islands, like Hawaii |
|
|
What are hotspots useful in tracing the motion of the plates? |
Since they leave behind islands you can tell how fast and in which direction the plate is moving |
|
|
What are sediments |
Particles of various sizes derived from sources and deposited on the ocean floor
|
|
|
What are terrigenous sediments |
Terrigenous sediments come from erosion of the continents |
|
|
What are terrigenous source |
Rivers winds Glaciers turbidity volcanic eruptions |
|
|
How do you classify terrigneous sediments based on size |
Grain size is classified by diameter called particle size. This indicates how grains are transported and where they end up. |
|
|
Major type of Marine organism Carbonate or Calcareous |
Foraminifera - Animal / zoo Coccolithophores - plant / phyto |
|
|
Major type of marine organism Silica |
Radiolaria - animal / zoo Diatoms - plant / phyto |
|
|
What is an ooze |
Biogenous sediments that dominant in mid depth oceans. Made up of skeletal remains. |
|
|
What is a hydrogenous sediment |
Sediments that precipitate or crystallize directly from seawater. |
|
|
Diffrent kinds of hydrogenous sediments |
Manganese nodules Phosphorite Nodules Evaporites Sulfides |
|
|
Manganese nodules |
Round hard lumps of Mn and Fe found on top of the ocean floor. typically form around an object in the center |
|
|
Phosphorite nodules |
found on the continental shelf which show an abundance of biological activity |
|
|
Evaporites |
Form where evaporation is high Forms gypsum or salt |
|
|
Sulfides |
Larde deposits of metals, typically around vents |
|
|
What are cosmogenous sediments? |
Interplanetary space dust, consists of silt / sand and micrometeoroids |
|
|
Where do Cosmogenous sediments come from |
They come from large/small asteroids, meteors and comets. |
|
|
Neritic sediments |
Sediments that are found on the continental shelf These are terrigenous sediments made of coarse gravel, sand and silt |
|
|
Pelagic sediments |
Deep ocean sediments Most common type are red clay and biogenies ooze |
|
|
How would you expect grain size to be distributed ideally along the cont. self? |
Along the cont. shelf the grain size would begin large and get smaller at deeper depths. Sand > Muddy Sand > Sandy Mud > Mud |
|
|
How do sea level changes affect the distribution of sediment grain size |
The lower the sea level the smaller the grain size along the shelf. This is due to the depositional processes not being able to carry bigger sediments into deep water |
|
|
What are the most common types of pelagic sediments |
Red clay / Abyssal Clay Biogenous ooze |
|
|
What are red clays / abyssal clay |
Fine grained
Reddish brown terrigenous sediments |
|
|
Where are red clays / abyssal clays found |
They are found in the deepest parts of the abyssal basins |
|
|
How do red clays / abyssal clays accumulate and form? |
They are produced by chemical weathering and typically are carried by wind blow dust. they accumulate very slowly |
|
|
What controls the distribution of biogeous sediments |
production in surface water - how many nutrients are in the water Dilution on the sea floor - to much terrigneous seds then no bio seds Dissolution in deep water - particles dissolve as they move deeper in water. CCD. After a certain depth there will be no more biogenic particles |
|
|
What is the calcium carbonate compensation depth? CCD? |
The depth at which the rate of calcium carbonate equals the rate of dissolution At a certain depth there will be no more calcium carbonate. |
|
|
Where do you find calcareous oozes |
along mid ocean ridges, warm water help the oozes not dissolve |
|
|
Explain what the difference between voyaging and scientific exploration |
Voyaging is similar to exploring, just looking around and typically for economic reasons Scientific exploration started around 1700AD. This was to study the ocean by its geology, currents, life and finding an understanding for the ocean |
|
|
Why is deep sea drilling important |
Finding cores of ocean rock and sediments we can tell the climate of the oceans in the past. |
|
|
Why is satellite oceanography important |
We can get accurate maps and measure the shape and depth of the ocean floor easily. |
|
|
Oceanography
|
The scientific study of the ocean |
|
|
What is the hypsographic curve |
A plot that shows the amount of the earths surface at each elevation or depth |
|
|
What is a continental margin |
Continuation of the continent below sea level |
|
|
Deep ocean basins |
True ocean floor typically marked by the continual rise |
|
|
Parts of a continental margin in order (Passive) |
Shelf Slope Rise |
|
|
Parts of a continental margin in order (Active) |
Shelf Slope Trench |
|
|
How is new crust formed and old destroyed |
Divergent plate boundaries allow magma to rise to the surface and form new oceanic crust Convergent plate boundaries destroy old crust. |
|
|
Importance of source terrigonous sediments |
Sediments contain a "library" that records the geological, oceanographic and climatic conditions |
|
|
Importace of environmental conditions for hydrogenous sediments. |
Without perfect conditions hydrogenous seds will not form. |
|
|
WHy changes in sea level affect sed distribution on the cont. shelf |
Cont. shelf distribution is called neritic seds. these are primarily terrigenous sediments made of coarse gravel silly, and sand. Deeper the sea level the smaller the grain size |

