![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
116 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Chest tightness on Mondaymorning, better as week progresses
|
Byssinosis (cotton, flax, hemp, or sisal or other fiberous material)
|
|
|
angina symptomdeveloped after withdrawal (over weekends)– “Monday Morning death”
|
Nitroglycerin workers/explosive workers: Also increased risk of CHD, even when exposure removed; increased risk of sudden death |
|
|
OSHA 300 LOG
|
Employers must record all new cases of workrelated fatalities, injuries and illnesses if theyinvolve:– Death– Days away from work– Medical treatment beyond first aid– Loss of consciousness, or– A significant injury or illness diagnosed by aphysician or other licensed health careprofessional
|
|
|
Which labor sector has the highest injury/illness rate?
|
Goods-Producingsector– Manufacturing highest within goodsproducingsector
|
|
|
the Service sector, which has the highest injury/illness rate?
|
Transportation & public utilities highestin Service sector
|
|
|
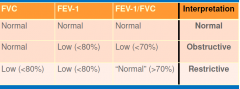
“Normal” FEV-1 & FVC
|
usually both ≥ 80%of predicted value
|
|
|
“Normal” FEV-1/FVC ratio
|
≥ 70% predicted
|
|
|
Spirometry chart
|
|
|
Most common occupational lung disease |
silicosis Associated with lung cancer |
|
|
progression through increasinglysevere disease stages– small rounded opacities → confluentopacities → progressive massive fibrosis• Spirometry shows restrictive pattern• Carcinogenic |
silicosis These pts are at risk of TB (+PPD >10mm) |
|
|
Spirometry is primarily obstructive initially,restrictive in later phases |
Coal Workers’Pneumoconiosis Associate with Kaplans syndrome and other rheumatic diseases |
|
|
Most common type of asbestos?
|
chrysotile (serpentine)
|
|
|
protein coated fiberwhich contains iron (ferruginous body)
|
Asbestos body
|
|
|
True or false? Smoking + asbestos = increased risk for mesothelioma |
False. Increased risk of bronchogenic carcinoma. Note that mesothelioma develops after lung cancer~25 years. From earliest to latest: benign pleural effusion->plaque-> asbestos-> Meso |
|
|
High single irritant exposures may cause
|
Reactive Airways Dysfunction Syndrome(RADS)
http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/722307_1 |
|
|
Spirometry features for occupational asthma:
|
Obstructive
Reduced FEV1 , Normal FVCReduced mid-flow volumes & PEFRReversibility |
|
|
“Monday morning fever”
|
Exposure to freshly generated metal fumes- primarily zinc in galvanized steel.
|
|
|
Byssinosis-Obstructive or restrictive
|
Restrictive
|
|
|
True or false water soluble chemical settle in lower airways? |
False-upper airways Water insoluble settle in lower are ways. Upper: S02, HCL, H2SO4, ammonia, chlorine Lower: No2 (silo filler's disease), phosgene, ozone |
|
|
Determinates of pulmonary toxicity
|
particle size
solubility Agent |
|
|
Examples of water soluble pulmonary toxins?
|
– Ammonia, chlorine, formaldehyde– Sulfur dioxide
|
|
|
Examples of water insoluble pulmonary toxins?
|
– Nitrogen oxides (Silo-filler’s disease)– Phosgene (COCl2 ) - hydrolyzes in lung toHCl
|
|
|
When should imaging be done for low back pain?
|
Avoid imaging unless red flags, or notimproved in 4-6 weeks
|
|
|
True or false. Most people with carpal tunnel syndrome have motor weakness?
|
False. The median nerve is 90% sensory. Motor weakness is a late sign
|
|
|
At risk groups for carpal tunnel syndrome?
|
– Meat, fish, poultry workers– Garment workers– Assemblers, electricians
|
|
|
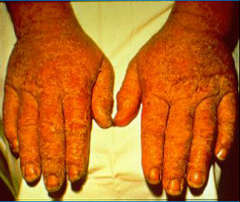
Most common occupational skindisease |
70-80% exposure to irritants 20-30% from exposure to allergens Irritant contact derm= type I hypersen rx Allergic=type 4
|
|
|
Irritant contact dermatis in a cement worker
|
|
|
What type of rxn is allergic contact dermatitis?
|
Cell-mediated immune response –Type IV delayed cellular immunity (like PPD reaction
|
|
|
Hives after direct contact•Immediate reaction – often seconds to minutes•Immunologic: IgE-mediated Type I allergy–or non-immunologic (Histamine release)•Other Type I sx may accompany (rhinitis, asthma)•Anaphylaxis is possible
|
Contact Urticaria
|
|
|
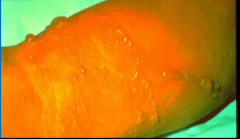
Allergic contact dermatis
|
|
|
|
Examples of occupational agents causing Increased melanin production
|
Coal tar pitch• Psoralens• Heavy metals (Arsenic)• Ionizing and nonionizing radiation
|
|
|
Occupations at risk for stap/strep skin infections
|
Barbers, beauticians, butchers
|
|
|
Lead inhibits which enzyme?
|
–Delta-aminolevulinic dehydratase (ALA-D)
|
|
|
OSHA standard for blood lead levels
|
< 40 ug/dl
|
|
|
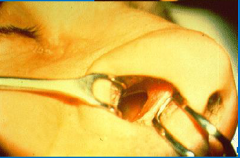
Chromium toxicity
|
|
|
Consequences of Chromium exposure.
|
Painless skin ulcers (chrome holes) •Lung cancer•Pulmonary irritant•Renal tubular acidosis•Hepatic necrosis
|
|
|
Sources of cadium exposure |
industry, hobbies( use of colored pigments), cigarette smoking |
|
|
target organ(s) for cadium |
Kidney and liver *causes: HTN, prostate, bladder Cancer; osteoporosis from CA+ waisting (Ouch, ouch disease) |
|
|
Metals causing lung cancer
|
Arsenic
Cadium Chromium Beryllium Nickel |
|
|
occupational sources of phosphorus.
|
Munitions, flares, match production
|
|
|
Sources of occupation phosphorus exposure
|
Munitions, flares, match production
|
|
|
Consequences of phosphorus exposure
|
Phossy jaw–Bone necrosis
|
|
|
Nuclear industries, metal reclamation•Used in alloys – risk to dental technicians•Risk to household contacts of workers•Exposure by inhalation
|
Beryllium
|
|
|
Beryllium toxicity
|
•Acute – conjunctivitis, pneumonitis•Chronic – )–Lung and skin granulomas–Cough and exertional dyspnea–Interstitial abnormalities on chest X-ray
|
|
|
90 dBA 8 hour TWA –
|
OSHA PEL for hearing conservation
|
|
|
Cancer of the paranasal sinuses and lungs |
Nickel *Also#1 cause of contact dermatis * can cause occupational asthma |
|
|
Central nervous system toxicants
|
•Carbon disulfide•Chlorinated hydrocarbons•Carbon monoxide (CO)•Metals – arsenic, lead (epilepsy), manganese (Parkinsons), mercury•Solvents – benzene, halothane, methylene chloride, perchloroethylene (PERC), styrene, toluene, trichloroethylene (TCE)
|
|
|
N-hexane & methyl n-butylketone cause...? |
peripheral neuropathy; generally lower first, sensory before motor |
|
|
Toulene causes...?
|
encephalopathy
|
|
|
Cobalt & manganese affect...?
|
basal ganglia
|
|
|
Causes of Parkinsonism from occupational exposure?
|
Carbon disulfide•Carbon monoxide•Manganese•N-methyl-4-phenyltetrahydropyridine (MPTP)
|
|
|
N-hexane & methyl n-butylketone cause...?
|
peripheral neuropathy
|
|
|
Toulene causes...?
|
renal tubular necrosis
|
|
|
Carbon tetrachloride causes?
|
Myocardial sensitization
|
|
|
Methyl bromide (used by model building hobbyists for joining plastic components together) causes...?
|
seizures
|
|
|
“Painter’s Syndrome” =
|
headaches, dizziness, asthenia, mood and personality change, inattentiveness, forgetfulness, and depression
|
|
|
OSHA action level for hearing conversation
|
Integrated, continuous, or intermittent noise levels of 85 dBA or greater
|
|
|
What is the OSHA Hazard communication Standard? |
Employees must be made aware of possible occupational hazards. Employers must post a material data safety sheet. |
|
|
What are some key differences b/t irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatits? |
1) ICD requires a high exposure to the agent and affects most people; ACD only requires a small amount of exposure and affects few people. 2. ACD rash may be pruritis and a sysmetrical |
|
|
Usually enters through the skin. Used as a wood preservative. Interferes with cellular respiration. Causes anorexia and respiratormtooms. In high doses, coma a nd death |
Pentachlorophenol |
|
|
Absorbed readily through the lungs. Damages kidney and liver |
Carbon tetraflouride |
|
|
Enters the body through the lungs and stimulates the respiratory system. When concentrations reach 3%, causes rapid breathing |
carbon dioxide |
|
|
Enters the nody via the lungs or GI tract. Is a chemical asphyxiant. Causes headaches, parid breathing, and frequently death |
Hydrogen cyanide |
|
|
Absorbed through the lungs and skin. Used to make plastics. Causes sclerodematous skin lesions, Raynaud phenomenon, bone lesion is the had, and liver damage. Can cause hemangoscarcomia of the liver. |
Vinyl chloride |
|
|
Common causes and occupations associated with Irritant Dermatitis |
*Fiberglass - construction * Oil - machining * Solvent - painting, cleaning * Detergent -housekeeping, cosmetology * Cement- Construction |
|
|
Common causes and occupations associated withcontact Dermatitis |
* Latex or rubber - lab and health workers * Nickel - electroplating * Colophony *Epoxy resin painting * Hair dye -cosmetology |
|
|
Occupational asthma agents and associated industries |
*Isocynates - wood industry * Wood dust - wood work * Wheat flour * Cutting oils - machining |
|
|
1) Is the evidence based on a testable theory or technique? 2) Has the theory or technique been per reviewed? 3) In the case of a particular technique, does it have a known error rate and standards controlling his technique's? 4) Is the underlying science generally accepted? |
Daubert criteria |
|
|
How many times greater is the radiation from exposure from a chest x Ray than from the normal yearly background radiation |
20x |
|
|
In 2010, how many workers sustained a work related injury or illness? |
3.5% |
|
|
Please select the best match.a. OSHA; RELb. NIOSH; PELc. REL; STELd. ACGIH; BEI |
Correct answer: D. OSHA=Permissible exposure limits (PEL) NIOSH=Recommended exposure limits (REL) ACGIH=Biological exposure index (BEI) and short-term exposure limits (STEL) |
|
|
Who are these exposures measured? Lead, organophasates, benzene, arsenic? |
Organophosphates- inhibition of RBC and plasma cholinesterase *Benzene: urine metabolite * Arsenic: urine *lead: blood |
|
|
Low back pain: disc pathology |
L4: numbness mostly above knee, weakness on quad ext., decread knee jerk L5: -week dorsiflexion of great big toe and foot 21: lat foot and toe numbness, dec ankle jerk |
|
|
Imagining guidelines for low back pain |
Unless red flags, no imaging for <1 month; MIR 4-6 weaks for sub-acute or radicular pain. Most people have asymptomatic disc pathology. Thus, not great corelation between disease and discs |
|
|
Causes of carpel tunnel syndrome? |
Occupations, DM, obesity, RA, pregnancy. Keyboarding is contraversal |
|
|
Please select the best match.a. OSHA; RELb. NIOSH; PELc. REL; STELd. ACGIH; BEI |
Correct answer: D. OSHA=Permissible exposure limits (PEL) NIOSH=Recommended exposure limits (REL) ACGIH=Biological exposure index (BEI) and short-term exposure limits (STEL) |
|
|
Who are these exposures measured? Lead, organophasates, benzene, arsenic? |
Organophosphates- inhibition of RBC and plasma cholinesterase *Benzene: urine metabolite * Arsenic: urine *lead: blood |
|
|
Low back pain: disc pathology |
L4: numbness mostly above knee, weakness on quad ext., decread knee jerk L5: -week dorsiflexion of great big toe and foot S1: lat foot and toe numbness, dec ankle jerk |
|
|
Imagining guidelines for low back pain |
Unless red flags, no imaging for <1 month; MIR 4-6 weaks for sub-acute or radicular pain. Most people have asymptomatic disc pathology. Thus, not great corelation between disease and discs |
|
|
Causes of carpel tunnel syndrome? |
Occupations, DM, obesity, RA, pregnancy. Keyboarding is contraversal |
|
|
Risk factors for carpal tunnel syndrome |
occupations, DM, obesity, RA, pregnancy. Keyboarding is controversal. |
|
|
Arsenic sources? |
Sources: pesticides, lumbar, mining, smelting, glass, pharma, mines, electroplating |
|
|
Effects of chronic arsenic exposure? |
Hyperpigmentation, neuropathy (sen>motor), megablastic anemia, sking, lung, bladder CA * EPA standard <10 mcg/L |
|
|
True or false? perpheral Neuropath in lead poisoning is more motor than sensory |
True |
|
|
Sx of organophosphate poisoning? Atropine |
"DUMBBELLS" Diarrhoea Urination Miosis Bradycardia Bronchorrhea Emnesis Lacrymation Salivation
|
|
|
How long to a PPD becomes positive? |
2-10 weeks |
|
|
Given a positive ppd, what is the risk of developing active tb? |
5-15% But 30% if HIV positive |
|
|
Which occupation setting has a higher risk of having a positive ppd? Nursing home or prison |
Nursing homes (10-40% have positive ppd). |
|
|
Is a prior BCG vaccination a contraindication to occupation PPD testing? |
No |
|
|
Can a health worker with latent TB continue to work? |
Yes, even without treatment, as long as no evidence of active TB. They pose no risk. |
|
|
What are PCB? |
Use: coolants and insulating fluids (transformer oil) for transformers and capacitors, such as those used in old fluorescent light ballasts.[13] PCBs were also used as plasticizers in paints and cements, stabilizing additives in flexible PVC coatings of electrical wiring and electronic components, pesticide extenders, cutting oils, reactive flame retardants, lubricating oils, hydraulic fluids, and sealants Exposure: air, food, breast milk, skin Acute high dose: chlorachne Children: low IQ, dec immunity Crash dieter at increased risk because concentrate PCPs Cancer: rare liver CA, and also melanoma Control: incineration, irradiation, others Banned since 1970 |
|
|
Dose response assessment |
2nd step in risk assessment: quantitative relationship between exposure and toxic effect |
|
|
quantitative estimate of population and individual exposure to a chemical under expected exposure situations |
Step 3: exposure assessment |
|
|
- integration of the toxic effect, dose-response, and exposure assessment information in order to estimate the risk associated with particular exposures |
Risk characterization, last step in hazard evaluation |
|
|
What are Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons? |
Source: incomplete combustion of carbon-containing fuels such as wood, coal, diesel, fat, tobacco, and incense. +Cancer: lung, skin, bladder, kidney, GI, liver CA |
|
|
Screening for Hep B among workers? |
Don't check titer EXCEPT in HCWs. Check titers in 1-6 mo (1-2 mo ideal) |
|
|
What is the risk of Hep B after a needle stick? |
2-40% |
|
|
Hep B post-exposure ppx from high risk/positive source? |
1) Determine vaccination status 2) Check titers in previously vaccinated: < 10 consider additional HB vac; > no rx, immune 3) No vac: 1 dose HBIG and start vac |
|
|
What is the risk of acquiring Hep C after a needle stick? |
Seroconversion rates after needlestick injury 1.8% (range 0 - 7% |
|
|
What is the post-exposure prophylasix for HCV? |
There is no effective PEP. Test and follow. |
|
|
What are the main differences between FIFRA and TSCA? |
FIFRA: Labeling, registration, and setting tolerance standards TSCA: prevent new hazardous chemicals from entering the market; producer must study environmental impact. Does NOT regulate pesticides |
|
|
Maxium contaminant levels set at zero under EPA safe drinking water act? |
Short list: crypto, giardia, legionella, enteric viruses; Arsenic, lead,benzene, dioxin, PCB, PAH. Mercury=0.002 |
|
|
determination of the health effects or toxicological endpoints that result from exposure to a chemical |
1st step in risk assessment: Hazard identification |
|
|
What dose response relationships hold true for carcinogenesis? |

Back (Definition) |
|
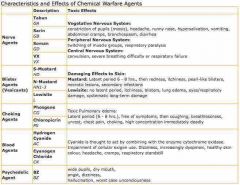
Front (Term) |
Chemical warfair agents |
|

Front (Term) |
Hypothermia |
|
|
Anthropogenic natural disasters |
Man made natural disasters |
|
|
What is the post exposure prophylaxis for anthrax? |
Cipro/doxycycline for 60 days: rx is 400 mg Cipro IV q12 hr |
|
|
PEP for tularemia! |
Same as anthrax. Rx is streptomycin or gentamicin |
|
|
Category A terrorism agents transmitted by droplets? |
1) small pox 2) plague 3) botulism( not contagious but could be aerosolized Ebola is NOT airborne ( transmitted through bodily fluids, semen, blood) |
|
|
Which toxins producing organism have an association with cancer: fusarium, aflatoxin, claviceps purpua ( weight alkaloids) |
fusarium-esophagus aflatoxin-liver |
|
|
Carb oxyhemoglobin levels digestive of poising ? |
10% O2 sat unreliable. ABGs for monitoring respiratory status and oxygenation of perperal tissues |
|
|
What businesses are exempt from OSHA duty cause? |
1) family farms 2) self employed 3) public employees (except federal ) unless they have adopted OHSA standard |
|
|
Carpal tunnel syndrome is characterized by which of the following? A) Hypothenar muscle atrophy in severe or longstanding cases Correct answerB) Nocturnal paresthesias C) Numbness in the 4th and 5th fingers D) Reduced sensory latency in the median and ipsilateral ulnar nerves |
Answer: B. Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) results from compression of the median nerve at the wrist. Symptoms include burning or tingling in the palm of the hand and fingers, often occurring at night because many people sleep with flexed wrists. Classic symptoms are usually described in the thumb-3rd fingers, the areas innervated by the median nerve. Muscular innervation of the median nerve encompasses the thenar muscles, particularly the abductor pollicis brevis, but not the hypothenar muscles (supplied by the ulnar nerve). Guyon’s canal, through which the ulnar nerve passes at the wrist, is relatively spacious, therefore the ulnar nerve is usually unaffected by pressure in the carpal tunnel, and has normal conduction velocity and latency in CTS cases.
|
|
|
Chronic exposure to cadium can cause this |
Fanconi syndrome: a disease of the proximal renal tubules[1] of the kidney in which glucose, amino acids, uric acid, phosphate and bicarbonate are passed into the urine, instead of being reabsorbed. Fanconi syndrome affects the proximal tubule, which is the first part of the tubule to process fluid after it is filtered through the glomerulus. It may be inherited, or caused by drugs or heavy metals. |
|
|
|
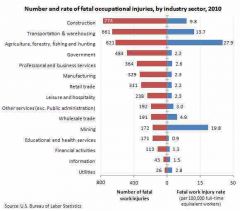
Back (Definition) |

