![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
79 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Postnatal Check for mother at 6 weeks:
|
weight, BP
urine vaginal discharge, period wounds breasts contraception, sex +/- pap |
|
|
isoimmunisation
|
development of antibodies to antigen
(eg. Rh incompatibility) |
|
|
Group & Hold
|
Determines ABO group and screening for antibodies to common red cell antigens that can cause transfusion reactions
|
|
|
Group & Crossmatch
|
In additionto group & hold, crossmatching involves mixing samples from donor blood with the patient's blood
|
|
|
1 unit of blood raises the Hb by
|
1 g/dl (non-bleeding adult)
|
|
|
When should you order a group & hold or crossmatch?
|
If the patient needs blood, you should crossmatch the number of units they will need.
Group & Hold if the patient is unlikely to need a blood transfusion but it will reduce the time required for cross-matching later. |
|
|
Infections that can be passed down to the neonate during pregnancy due to transplacental IgG :
|
Toxoplasmosis
Other (varicella, parvovirus, listeria, TB, malaria, fungi) Rubella CMV HSV / HIV Syphilis |
|
|
Explain the risks of having C-Section
|
TO MOTHER:
General Surgical Risks - infection - bleeding (PPH) - clotting (DVT/PE) Anaesthetic Risks -anaphylactic reactions Injury to adjacent structures - bowel, bladder ↑ risk of complications in later pregnancies - uterine rupture Family Planning - size of family desired TO BABY: - TTN - RDS - surgical injury |
|
|
LGA vs. macrosomia ?
|
LGA:
≥ 90th percentile for GA Macrosomia: ≥ 4000g (or 4500g in USA) regardless of GA |
|
|
clinical sx of ovulatory/anovulatory failure?
|
regular cycles = ovulatory
irregular cycles = anovulatory |
|
|
biochemical factors responsible for growth of the endometrial lining?
|
ovaries (estrogen & progesterone) → PG, cytokines, MMPs → endothelium
|
|
|
Breast Feeding OSCE explanation
|
.
|
|
|
Signs of Pregnancy
|
Presumptive (skin & mucous membrane changes)
- Chadwick's sign, linea nigra, cholasma Probable (uterus changes) Positive (fetal movement & heart beat) |
|
|
gestational sac visualised by US at
|
week 5
|
|
|
fetal heart beat visualised by US at
|
6-8 weeks
|
|
|
Pfannenstiel incision
|
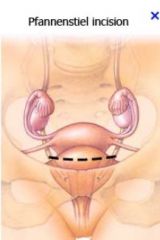
- horizontal (slightly curved) line just above the pubic symphysis
- commonly used for c-section or hernia repair |
|
|
Role of Theca and Granulosa cells in the ovary
|
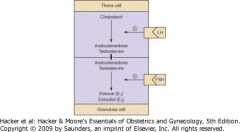
|
|
|
Cycle Development from primodial follicle to corpus luteum
|
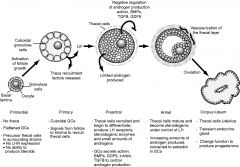
|
|
|
Ovarian cycle
|
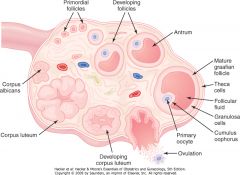
|
|
|
Overview of Menstrual Cycle Diagram
|
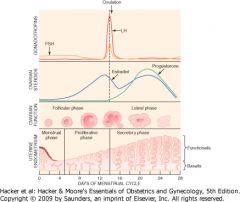
|
|
|
Steroidogenesis Pathway
|
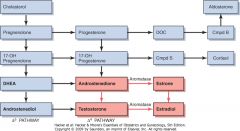
|
|
|
circulating estrogens & androgens are mostly bound to
|
SHBG
serum albumin + small unbound fraction (biologically active) |
|
|
Phases of menstrual cycle:
|
Follicular vs. Luteal phase
Proliferative vs. Secretory phase |
|
|
What causes the LH surge which leads to ovulation?
|
a burst of estradiol synthesis at the end of the follicular phase causes +ve feedback on secretion of FSH & LH
|
|
|
Hormonally, what happens if fertilisation occurs?
|
placenta → HCG → recues corpus luteum from regression → estradiol & progesterone
|
|
|
peak levels of HCG occur at
|
week 9
|
|
|
Hormonally, what happens in the 2nd & 3rd trimesters of pregnancy?
|
placenta → progesterone
fetal adrenal gland → DHEA → placenta → estriol |
|
|
Which hormones cause growth & development of breasts during pregnancy?
|
estrogen
progesterone |
|
|
Comment on prolactin levels during pregnancy
|
estrogen → anterior pituitary → prolactin increases steadily during pregnancy
|
|
|
Why doesnt lactation occur during pregnancy?
|
estrogen & progesterone block the action of prolactin on the breast
|
|
|
What causes lactation after parturition?
|
sharp fall in estrogen & progesterone
|
|
|
lactation is maintained by
|
suckling → oxytocin & prolactin secretion
|
|
|
Effects of prolactin in suppressing ovulation?
|
inhibits GnRH secretion
antagonizes LH & FSH on the ovaries |
|
|
Absence of adequate amniotic fluid during mid-pregnancy is associated with
|
pulmonary hypoplasia at birth
(incompatible with life) |
|
|
When does engagement of the fetal head occur?
|
primip - 37 weeks
multip - up to the onset of labour |
|
|
How is non-engagement of the fetal head investigated?
|
US
|
|
|
What are causes of non-engagement of the fetal head?
|
placenta previa
fetal abnormality |
|
|
Positions of the fetal head (pelvis diagram)
|
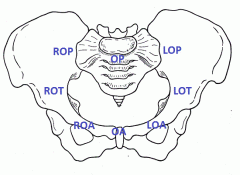
|
|
|
When is a head considered to be engaged?
|
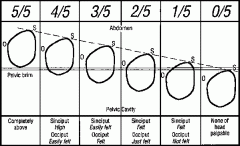
2/5 palpable (not ballotable)
|
|
|
what are the pelvic floor muscles?
|
levator ani
coccygeus |
|
|
Shapes of the female pelvis
|
gynocoid (50%)
anthropoid android platypolloid |
|
|
Can one assess pelvic adequacy for childbirth?
|
Not unless there is a gross abnormality (from gait or hx)
- fetal head "moulds" & the joints of the pelvis can move slightly |
|
|
Breech Presentations
|
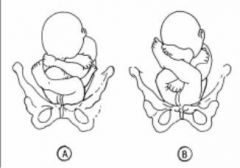
A - complete (thighs & knees flexed) 5-10%
B - frank (thighs flexed knees extended) 50-75% |
|
|
Fetal Position - diagram of different presentations
|
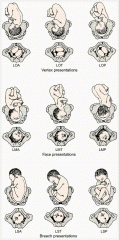
|
|
|
Positions of the fetal head
|
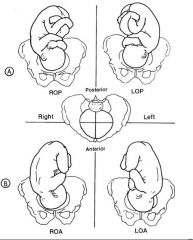
|
|
|
5 bones of fetal skull
|
2x parietal
2x frontal 1x occipital |
|
|
4 sutures of fetal skull
|
coronal
frontal sagittal lambdoid |
|
|
fontanelle =
|
where 2 or more sutures meet
|
|
|
fontanelles of the fetal head
|
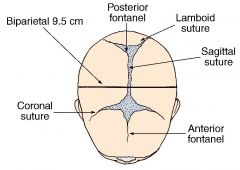
anterior fontanelle = bregma (diamond)
posterior fontanelle = lambda (triangular) |
|
|
Regions of the fetal head
|
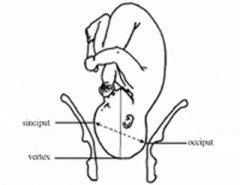
|
|
|
Outline the Stages of Labour
|
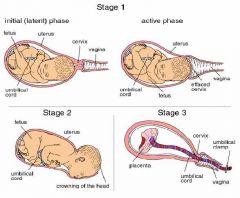
|
|
|
Types of Twin Pregnancies
|
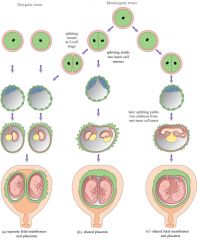
|
|
|
caput succedaneum
|
- occurs when the dilating cervix presses against the fetal scalp, preventing normal venous blood & lymphatic fluid flow → tissue swelling
- soft & boggy - disappears <24 hours after birth |
|
|
Describe physiological "moulding" of the fetal head during labour
|
- process of slipping/overlapping of the cranial bones
- disappears a few hours after birth |
|
|
types of placenta circulations?
|
uteroplacental (maternal side)
fetoplacental (fetal side) |
|
|
interaction between maternal & fetal blood flow?
|
side by side but in opposite directions (counterflow faciliates exchange)
|
|
|
Functions of the placenta
|
- anchor the fetus
- barrier against infection - gas & substance exchange - endocrine organ (HCG, estrogen, progesterone) |
|
|
when is oxytocin released by the posterior pituitary?
|
first stage of labour
suckling |
|
|
effect of pregnancy on thyroid
|
thyroid gland enlarges due to ↑ demand
↑ renal clearance of iodine = relative iodine deficiency → ↑iodide uptake → follicular enlargement slight ↑ in T3/4 & ↓TSH but in normal range |
|
|
Haemodynamic changes in pregnancy
|
↑ plasma volume
↑ red cell volume ↓ platelets ↑ WCC ↑ clotting factors |
|
|
Cardiovascular changes in pregnancy
|
↑ cardiac output
↓ peripheral vascular resistance = ↓BP nu mid pregnancy which returns to normal levels by term |
|
|
Respiratory changes in pregnancy
|
↑ tidal volume
↑ inspiratory capacity only slight change to RR, therefore breathe more deeply SOB (↓pCO2) |
|
|
Uterus changes in pregnancy
|
↑ weight x10
stretching hypertrophy of uterine & ovarian arteries → ↑ uterine blood flow ↑ vaginal discharge due to glandular hypertrophy |
|
|
Urinary tract changes in pregnancy
|
↑ renal blood flow (in line with ↑CO) → ↓plasma creatinine & urea
(creatinine in normal range indicates renal impairment in pregnancy) |
|
|
GIT changes in pregnancy
|
↓ esophageal spincter tone → reflux
↓ gastric emptying ↓ GI motility |
|
|
conception occurs on day
|
14
|
|
|
When does implantation occur?
|
6-7 days after fertilisation
|
|
|
inner cell mass forms the
|
embryo
|
|
|
trophoblast forms the
|
placenta
|
|
|
cytotrophoblast produces
|
hCG
|
|
|
syncytiotrophoblast produces
|
estrogen & progesterone
|
|
|
Pregnancy can be diagnosed by
|
b-hCG
US (FHR) fetal movements (17-22 weeks onwards) |
|
|
embryo =
|
from fertilisation until end of week 8 of gestation (10 weeks from LMP)
|
|
|
fetus =
|
from week 8 of gestation (10 weeks from LMP)
|
|
|
miscarriage =
|
delivery <20 weeks OR <400g
|
|
|
previable =
|
<24 weeks
|
|
|
preterm =
|
<37 weeks
|
|
|
term =
|
37-42 weeks
|
|
|
post term =
|
>42 weeks
|

