![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
110 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Very Premature |
<32 weeks |
|
|
Premature |
32-34 weeks |
|
|
Late premature |
34-37 weeks |
|
|
AGA |
Appropriate for gestational age: 5.7-9.1 lb |
|
|
SGA |
Small for gestational age: <5.7 lb |
|
|
LGA |
Large for gestational age: >9.1 lb |
|
|
Low birth weight (LBW) |
< 2500 grams |
|
|
Very low birth weight (VLBW) |
<1500 grams |
|
|
Extremely low birth weight |
<1000 grams |
|
|
Why are preterm neonates at higher risk for intracranial bleed? |
Small blood vessels; crying > increases ICP > ruptures vessels. |
|
|
What should you avoid putting on a preterm neonate's fragile skin? |
Alcohol, adhesives. |
|
|
What kind of tape is okay to use on preterm neonates? |
Tegaderm |
|
|
What are reasons that preterm neonates have trouble with thermoregulation? |
Large surface area in relation to size, limited brown fat, immature temperature regulation in the brain, decreased/absent capillary reflexes. |
|
|
Why might hyperglycemia occur in a preterm neonate? |
Immature kidneys secrete glucose slowly. |
|
|
How often do preterm neonates need to be fed and why? |
q2-3 hours; ~8 times per day. Small stomachs. |
|
|
What are the reasons for anemia of prematurity? |
Red blood cell life is short; low bone marrow production until ~32 weeks. |
|
|
What is kernicterus? |
Destruction of brain cells by invasion of indirect bilirubin. [Bili level: ~20] |
|
|
Why are preterm neonates susceptible to kernicterus? |
Low serum albumin available to bind and excrete direct bilirubin. |
|
|
Why do preterm neonates start with supplements before getting breast milk? |
It takes ~3 days for mother to begin producing milk. |
|
|
What is persistent patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)? |
Failure for the PDA to close: blood stays in the pulm. artery which leads to pulm. hypertension, which causes the PDA to persist. |
|
|
What does Indocin (indomethacin) do and what is it? |
Causes PDA to close; causes uterine relaxation. It is a prostaglandin inhibitor. |
|
|
When can the pregnant woman receive Indocin (indomethacin) and why? |
>32 weeks gestation, otherwise drug will cause premature PDA closure in the womb. |
|
|
Neonatal Sepsis s/s |
LOW TEMP, resp. distress, hypotension, tachycardia, tachypnea, lethargy, poor feeding, diarrhea, vomiting. |
|
|
Neonatal sepsis diagnostics |
CBC with Differential (increased bands, decreased neutrophils, decreased platelets), blood culture. |
|
|
Neonatal sepsis treatment |
Broad spectrum AB, VS, nutrition, fluids, O2, parental support. |
|
|
What is Retinopathy of Pre-Maturiy (ROP) and what is it caused by? |
Damage to immature blood vessels in the retina that results in scarring and possible blindness. Caused by high O2 levels. |
|
|
Who is most at risk for retinopathy of pre-maturity? |
Very low birth weight (VLBW) neonates |
|
|
What is intracranial hemorrhage and what can cause it? |
Bleeding into ventricles r/t hypoxia, increased BP, increased fluids (pneumothorax), resp. distress syndrome. |
|
|
What is necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) and what are the risk factors? |
Bacteria in bowel, leads to infection, which leads to destroyed bowel tissue, which can lead to sepsis. Factors: prematurity and tube feedings |
|
|
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) treatment |
Stop tube feeding, start IVF + TPN, AB, ventilator, platelet transfusion. |
|
|
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) s/s |
Abdominal swelling, sepsis, emesis, blood in stool. |
|
|
What is transient tachypnea of newborn (TTN) and what is it related to? |
Rapid, shallow RR 70-80/min r/t slow absorption of lung fluid. |
|
|
When should amnioinfusion be done? What is no longer accepted practice? |
Done for late decels. No longer used to dilute meconium staining. |
|
|
How does jaundice spread? |
Cephalocaudal: from head to toe. |
|
|
Is Hyperbilirubinemia very concerning in a 1-2 day old infant? |
No, less significant. Need proper nutrition to increase alb binding; parents may place crib near window to expedite bilirubin breakdown. |
|
|
Is hyperbilirubinemia very concerning in a 4-5 hour old infant? |
Yes, more significant. May rise steadily. |
|
|
Pathologic hyperbilirubinemia treatment |
Immediate exchange transfusion, phototherapy, frequent bilirubin checks, increased feeding to speed up alb binding. |
|
|
What are important things to remember for an infant under bili lights? |
Cover eyes and genitalia. Place infant prone or lateral to protect internal organs. |
|
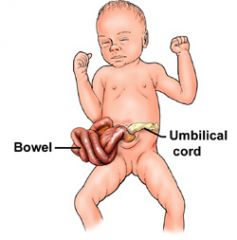
What is this called? |
Gastroschisis |
|
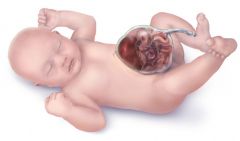
What is this called? |
Omphalocele |
|
|
How is gastroschisis and omphaceles treated? |
IV + NGT, TPN, silastic "silo" covering over viscera which allows gravity to brings viscera back into cavity, surgical closure after contents returned to abd. cavity. |
|
|
What is bladder extrophy? |
Extrusion of bladder through abd wall. |
|
|
Normal temperature in a term infant? |
97.7-99.9 |
|
|
What APGAR score would prompt further evaluation by NICU? |
Less than 7 consistently. |
|
|
APGAR HR: 0 |
Absent |
|
|
APGAR HR: 1 |
<100 bpm |
|
|
APGAR HR: 2 |
>100 bpm |
|
|
APGAR Resp. Effort: 0 |
Absent |
|
|
APGAR Resp. Effort: 1 |
Slow/irregular |
|
|
APGAR Resp. Effort: 2 |
Good cry/good respirations |
|
|
APGAR Muscle Tone: 0 |
Flaccid |
|
|
APGAR Muscle Tone: 1 |
Some flexion |
|
|
APGAR Muscle Tone: 2 |
Active motion |
|
|
APGAR Reflex Irritability: 0 |
None |
|
|
APGAR Reflex Irritability: 1 |
Grimace |
|
|
APGAR Reflex Irritability: 2 |
Strong cry/reflexes |
|
|
APGAR Color: 0 |
Pale/blue |
|
|
APGAR Color: 1 |
Acrocyanosis |
|
|
APGAR Color: 2 |
Pink |
|
|
What is caput succedaneum and is it concerning? |
Fluid-filled swelling under scalp; Normal variation. |
|
|
What is a cephalohematoma and is it concerning? |
Hemorrhage of blood between the skull and periosteum; needs to be watched. |
|
|
Bulging fontanels (w/o crying) may indicate: |
IICP |
|
|
Depressed fontanels (w/o crying) may indicate: |
Dehydration |
|
|
Normal respiration rate of a newborn |
40-60/min, may be irregular |
|
|
Normal heart rate of newborn |
120-160/min |
|
|
What is the point of maximal impulse (PMI) in a newborn? |
Lower left sternal border |
|
|
A newborn female has red-tinged vaginal discharge. What is this and is it a concern? |
Pseudomenstruation related to hormones; normal variation. |
|
|
How long is the postpartum phase? |
6 weeks after birth |
|
|
Define involution |
Uterus returns to pre-pregnant shape |
|
|
Define afterpains |
Moderate to severe cramp-like pain r/t involution. More severe in multi-parous women. |
|
|
Define lochia |
A bloody discharge from the uterus that contains sloughed off necrotic tissue and reflects uterine healing. |
|
|
Define endometrium |
Mucous membrane that lines the uterus. |
|
|
What is the first intervention for a boggy uterus (assuming bladder is empty)? |
Massage fundus. |
|
|
By what day is the endometrium fully restored in a postpartum woman? |
By 16th day. |
|
|
Lochia rubra appearance, duration |
Red; 1-3 days |
|
|
Lochia serosa appearance, duration |
Pink, brown-tinged; 3-10 days |
|
|
Lochia alba appearance, duration |
Yellowish-white; 10-14 days but may last longer |
|
|
What is considered heavy lochia? |
Saturating 1 pad per hour |
|
|
What is normal blood loss from vaginal delivery? |
Usually does not exceed 500 ml |
|
|
1 mL blood = ___ gram in weight |
1 |
|
|
What is methergine (methylergonovine)contraindicated in? |
HTN. BP > 140/90 |
|
|
What is hemabate (carboprost tromethamine) contraindicated in? |
Asthma |
|
|
How does methergine (methylergonovine) work? |
Stops postpartum bleeding by causing vasoconstriction. Also increases BP. |
|
|
How does hemabate (carboprost tromethamine) work? |
Stops postpartum bleeding by constricting soft tissues (like the uterus). |
|
|
1st degree laceration/tear |
Shallow; involves just below or just inside vagina |
|
|
2nd degree laceration/tear |
Involves skin below vagina, the perineum, and muscles of the perineum |
|
|
3rd degree laceration/tear |
Extends to anal sphincter |
|
|
4th degree laceration/tear |
Extends through anal sphincter |
|
|
What should the nurse assess in women with episiotomies or tears? |
REEDA: Redness, edema, ecchymosis, discharge, approximation |
|
|
How long should the woman refrain from inserting anything into her vagina? |
6 weeks |
|
|
How soon can a women resume menstruation after birth? |
usually 7-9 weeks; by 12 weeks |
|
|
How much should a postpartum women be voiding? |
250-300 mL q4-6 hrs |
|
|
What treatment is available for a spinal headache? |
Blood patch. |
|
|
What is a spinal headache caused by? |
Loss of spinal fluid r/t epidural. |
|
|
What is diastatis recti abdominis? |
Separation of the abd. rectus muscles. Common; should resolve in 6 weeks. |
|
|
Taking-In Phase |
Focused on self, dependent on others for care, needs assistance, may last for several hours or days. Needs comfort-rest-food. |
|
|
Taking-Hold Phase |
Focus on infant, self care, responds well to instructions and praise. Lasts from 2 days to 12 week. |
|
|
Letting-Go Phase |
Giving up previous role, see self as separate from infant, gives up fantasy delivery and baby. Lasts from 1 week on. |
|
|
Who received Rhogam? |
In Rh-neg women with Rh-pos baby. |
|
|
When is Rhogam given (in relation to birth)? |
Within 72 hours after birth. |
|
|
What is Healthy People 2020's goal for breastfeeding? |
95% of mothers breastfeed |
|
|
When does colostrum occur and what does it contain? |
1-3 days; electrolytes, protein, fat soluble vitamins, IgA, passive immunity via establishment of GI flora. |
|
|
When does transitional milk occur and what does it contain? |
7-10 days; high protein, low fat, increased H2O content, higher calories than colostrum. |
|
|
When does mature milk occur and what does it contain? |
About 14 days postpartum; ~20 kcal/oz, primary carbohydrate (lactose), appears similar to skim milk, higher fat content in AM. |
|
|
How often should a woman breastfeed? |
q2-3 hrs (8 feedings per 24 hrs) |
|
|
Postpartum hematoma s/s |
Severe pain that cannot be controlled with analgesics, tachycardia, hypotension, heaviness/fullness of vagina or rectal pressure. |
|
|
For Gomco or Mogen clamp: how do you care for the circumcision site? |
Apply protective lubricant over site after each diaper change for 1st week. |
|
|
Should parents clean any yellow crusts that form after a circumcision? |
No, this should not be removed or washed. |
|
|
For plastibell: how do you care for the circumcision site? |
Do not apply lubricant; allow plastic ring to fall off on its own in 7-10 days. |
|
|
How should a car seat be used in infants less than 1 year and less than 20 lbs? |
Rear-facing, backseat. |

