![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a "resonance hybrid"
|
A resonance hybrid is a set of more than one Lewis structures for the same substance that are equally as stable as one another. The actual molecule is really a sort of "average" of them all, resulting in partial bonds and partial charges.
|
|
|
True or False: When the stability of a resonance hybrid is more than it's Lewis structures indicates, this is called "resonance stabilization energy"
|
True.
|
|
|
What does this arrow mean?
↔ |
Resonance arrow
|
|
|
Define "electronegativity"
|
Electron attracting ability. Atoms that are more electronegative will "pull" atoms more, resulting in uneven distribution of the electrons (polar charges)
|
|
|
What is a "dipole"?
|
When a positive and negative pole are present in a molecule.
|
|
|
What is this?
µ = (e)(d) |
The equation for a "dipole moment", where µ = the value of the dipole moment, e = amount of charge separation, and d = distance of charge separation
|
|
|
What does VSEPR stand for?
|
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
|
|
|
True or False: When the stability of a resonance hybrid is more than it's Lewis structures indicates, this is called "resonance equilibrium energy"
|
False. When the stability of a resonance hybrid is more than it's Lewis structures indicates, this is called "resonance stabilization energy"
|
|
|
What does this arrow mean?
→ ← |
Equilibrium arrows
|
|
|
True or False: All molecules that are shaped trigonal planar have a dipole.
|
False.
|
|
|
True or False: The presence of formal charges in a molecule is usually an indication of stability.
|
False. The presence of formal charges in a molecule is usually a destabilizing factor.
|
|
|
True or False. Hydrogen almost always has 1 or 2 bonds.
|
False. Hydrogen almost always has 1 bond.
|
|
|
Define "carbanion".
|
An instance of a carbon atom with three bonds and 1 lone pair, giving it a negative charge
|
|
|
Most organic compounds are based primarily on covalent bonds to __________.
|
carbon
|
|
|
True or False: Carbon commonly bonds to Hydrogen, Nitrogen, and Oxygen.
|
True.
|
|
|
What is a "constitutional isomer".
|
Same atoms, different arrangement within the molecule.
|
|
|
True or False. The presence of formal charges in a molecule is usually a destabilizing factor.
|
True.
|
|
|
True or False: Carbon commonly bonds to Bromine, Chlorine, and Astatine
|
True. Carbon bonds easily with the halogens, especially Br, and Cl
|
|
|
As the number of atoms in a formula increases, the number of possible constitutional isomers:
a) stays the same b) decreases to 0 c) decreases by an indeterminate amount d) increases dramatically e) impossible to determine |
As the number of atoms in a formula increases, the number of possible constitutional isomers:
d) increases dramatically |
|
|
True or False: Carbon commonly bonds to Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Sulfur, and Phosphorus
|
False. While carbon will bond and form stable compounds with S and P, it is not common.
|
|
|
Define "ketone"
|
Functional group containing a carbonyl group attached to two other carbon-containing functional groups (R & R')
|
|
|
What is a "functional group"?
|
A specific group of atoms within molecules that is responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules.
|
|
|
What is a "carbonyl group"?
|
A carbonyl group is the functional group C = O (must be a double bond)
|
|
|
Which of these is an example of a four carbon ketone in condensed form?
a) C6H6 b) CH3-CH2-C-O-CH3 c) OH-PO2H-OH D) C2H60 |
Which of these is an example of a four carbon ketone in condensed form?
b) CH3-CH2-C-O-CH3 |
|
|
The ______________ provides useful information about possible molecular structures that will fit a molecular formula
|
The degree of unsaturation provides useful information about possible molecular structures that will fit a molecular formula (useful for determining constitutional isomers)
|
|
|
What is a "skeletal structure"?
|
Quick way of diagramming organic compounds, where lines are assumed to have carbons at either end, and all necessary hydrogens are assumed to be present.
|
|
|
True or False: Oxygen is ignored when calculating DU.
|
True.
|
|
|
Define "endothermic"
|
Energy is added to the system.
|
|
|
How is the degree of unsaturation calculated?
|
DU = [(Maximum possible H's) - (Actual H's)] /2
|
|
|
True or False: Hydrogen is ignored when calculating DU.
|
False. Oxygen is ignored when calculating DU.
|
|
|
Stronger covalent bonds tend to be _____________.
|
Shorter. Also, they have higher "bond dissociation energy"
|
|
|
Bonds between H and the second row elements C,N, and O are all __________.
|
Strong. (or "short in length")
|
|
|
True or False: chains of carbon and chains of nitrogen are common, but not oxygen.
|
False. Chains of nitrogen are weak, and break easily. Chains of carbon are common, chains of nitrogen and chains of oxygen are not.
|
|
|
What happens to carbon-halogen bonds as the atomic number of the halogen increases?
|
The bond becomes weaker and longer.
|
|
|
True or False: a carbon/carbon triple bond is 3 times as strong as a carbon/carbon single bond.
|
False. Double bonds are not exactly twice as strong as single bonds, and triple bonds are not exactly three times as strong.
|
|
|
True or False: Spherical molecules have more surface area than rod-shaped molecules, so their boiling points are slightly higher.
|
False. Rod-shaped molecules have more surface area than spherical molecules, so their boiling points are slightly higher.
|
|
|
What is an "alkyl group"?
|
Group of SINGLY BONDED C's and H's that contributes very little to chemical reactions.
|
|
|
ROH depicts what functional group?
|
Alcohols.
|
|
|
True or False: Rod-shaped molecules have more surface area than spherical molecules, so their boiling points are slightly higher.
|
True.
|
|
|
What functional group is RH?
|
Anything with RH is not considered to have a functional group. These are known as "alkanes"
|
|

Name the functional group (in blue).
|
The carbon/carbon double bond makes this an "alkene".
|
|
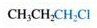
Name the functional group (in blue).
|
The carbon/halogen bond makes this an "alkyl halide".
|
|
|
The ___________ is the lowest-energy orbital.
|
The 1s orbital is the lowest-energy orbital.
|
|
|
What is a "node" in terms of describing orbitals?
|
A region where the value of the wave function equals zero. (Indicating that electrons spend no time there)
|
|
|
Orbitals with the same energy are termed _____________.
|
Degenerate.
|
|
|
What is the "Pauli Exclusion Principle"?
|
The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that no 2 electrons can have all four quantum numbers the same.
|
|
|
What is "Hund's Rule"?
|
Every orbital in a subshell is singly occupied with one electron before any one orbital is doubly occupied, and all electrons in singly occupied orbitals have the same spin.
|
|
|
True or False: The 1s orbital must be full before electrons begin to fill the p orbitals.
|
True. Subshell 2 is the lowest energy subshell with p orbitals. Subshell 1 must fill up before electrons begin to fill 2s and 2p orbitals.
|
|
|
The _____________ states that no 2 electrons can have all four quantum numbers the same.
|
Pauli Exclusion Principle
|
|
|
True or False: The s orbitals must be full before electrons begin to occupy p orbitals, and p must fill up before electrons begin to occupy d orbitals.
|
False. Hund's Rule states that orbitals in each subshell (subshell 1, subshell 2, subshell 3, etc) get one electron before the other degenerate orbitals fill up. (A full orbital having 2 electrons).
|

