![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Iron |
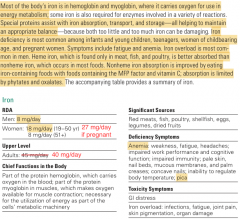
1. MFP factor: a peptide released during the digestion of meat, fish, and poultry that enhances nonheme iron absorption. 2. Hemosiderin: an iron-storage protein primarily made in times of iron overload (liver). 3. Hemosiderosis: Accumulation of too much hemosiderin. Causes liver damage. 4. Pica: a craving for and consumption of nonfood substances. 5. Heme Iron: Animal cells - 25% absorption. Helps increase absorption of non-heme iron. 6. Non-heme Iron: Non-animal sources. 2-20% absorption 7. Free Iron: Acts as a Free Radical. Causes soft tissue damage. 8. Transportation in body: (In SI cell) Mucosal Ferritin > mucosal transferin > (in blood) blood transferrin > either to bones/tissues or to liver > (in liver) held as ferritin or hemosiderin when in excess. 9. Involved in: protein, hormones, CNS, TCA cycle, ETC |
|
|
Zinc |

1.Involved in: Protein synth, clotting cascade, growth. 2. Absorption: 12-40% 3. Competes with: Iron & Copper 4. Held in call as Metalothionein (copper competion). Post cell, held in blood transferrin (iron competiton) or albumin.
|
|
|
Iodine |
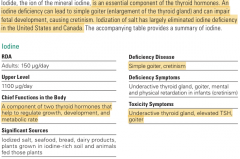
Thyroid-stimulation Hormon (TSH): is a pituitary hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine (T4), and then triiodothyronine (T3) which stimulates the metabolism of almost every tissue in the body. 2. Higher concentrations in coastal regions.
|
|
|
Selenium |
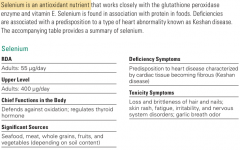
**I don't think I was paying attention when we went over selenium. **My notes say it works well with Vit C. The book says Vit E. **I also wrote that it was organic - this goes against most other minerals?? |
|
|
Copper |

1. Stored in muscle, liver, kidneys, and bones. 2. Toxicity: Diarrhea, vomiting. 3. Deficiency: Menkes disease can cause deficiency. Menkes blocks absorption in SI. Injections can correct this. 4. Wilson's Disease: opper accumulates in the liver and brain, creating a life-threatening toxicity. |
|
|
Manganese |
Manganese-dependent enzymes are involved in bone formation and various metabolic processes such as the urea cycle (breaking down of amino acids) and the conversion of pyruvate to a TCA cycle compound. Because manganese is widespread in plant foods, deficiencies are rare, although regular use of calcium and iron supplements may limit manganese absorption. Also acts an an antioxidant protecting against lipid oxidation. |
|
|
Fluoride |
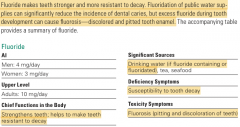
During the mineralization of bones and teeth, calcium and phosphorus form crystals called hydroxyapatite. Then fluoride replaces the hydroxyl (OH) portions of the hydroxyapatite crystal, forming fluorapatite, which makes the teeth stronger and more resistant to decay. |
|
|
Chromium |

|
|
|
Molybdenum |
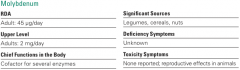
***I literally wrote nothing for this trace mineral... so the books says: Molybdenum is found in a variety of foods and participates in several metabolic reactions. |

