![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
64 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is being overweight mean? |
Being too heavy for one's height |
|
|
What does being obese mean? |
Having more than the amount needed for your body fat |
|
|
What is the BMI for a overweight person? |
25-29.9 kg/m^2 |
|
|
What is the BMI for a obese person? |
30 kg/m^2 or more |
|
|
Why are Americans eating more? |
Improper portion sizes
Eat more because of appetite, not because they are hunger or need it
Exercising less |
|
|
What is being underweight mean? |
Little fat stored |
|
|
How does having more fat then needed affect your body? |
Mental problems: depression, low self esteem
Lung problems: sleep apnea, asthma
Fatty liver
Gallbladder disease, gallstones
Blood glucose: elevated fasting blood glucose, type 2
Gynecological: abnormal periods, infertility
Arthritis, gout
Gastroesophageal reflux
Heart: cardiovascular diseases, elevated blood triglycerides, LDL cholesterol, low HDL cholesterol, atherosclerosis, hypertension, stroke
Increased risk for breast, colon, uterus, esophagus, pancreas, kidney, thyroid, and thyroid cancers |
|
|
What happens when you are underweight? |
Greater risk of early death |
|
|
BMI for underweight people: |
Under 18.5 kg/m^2 |
|
|
What is BMI? |
Body mass index
Evaluates weight
In relation to height
BMI=kg/(m)^2 Or Lbs/(in)^2 x 703 |
|
|
Is BMI accurate? |
No |
|
|
What is one step on how to eat healthy? |
Adjust intake to your metabolism and body needs |
|
|
Bioelectric Impedance Analysis |
Popular
Fast, easy, painless
Sends painless current through body-> measures how much resistance was between when it was first sent and when it returned-> fat is a poor conductor (less water than lean fat)
Amount of resistance is proportional to body fat
GI tract and bladder have to be empty
Hydration has to be normal
Cannot be taken between 24 hour of hardworking excersise (sweat-> low body water) |
|
|
What is skinfold thickness |
Believes that the amount of fat under skin represents entire body
Thickness of the amount of subcutaneous fat in multiple areas is taken with calipers-> equation estimates amount of body fat
Don't need anything to be put in body & accurate for normal weight
Less accurate for obese or elderly |
|
|
Water and air displacement is: |
Uses underwater weighing
lean tissue is denser than fat
the difference between the weight on land and the weight underwater is used to calculate body volume and density
accurate and non-invasive
Require special equipment can I use it cannot be used for some groups for example small children and frail adults
Another way to measure is using an air filled chamber
accurate and more convenient
expensive and not available easily |
|
|
Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry |
DXA
Uses two x-rays
calculates total body mass, bone, mineral mass and the amount and percentage of body fat
Also tells body composition in specific places & evaluates the amount of visceral fat ( associated with risk of heart disease and other diseases) |
|
|
How does Apple body shapes affect health? |
They are connected to more cardiac problems and diabetes |
|
|
How is a pear-shaped body affects health |
They lose weight quicker than an apple |
|
|
What is the correlation between waist circumference and health risks |
men: BMI of 25 to 34.9 with a waist greater than 40 indicates that there is a visceral fat storage
Woman: BMI of 25 to 34.9 with a waist of greater than 35 inches indicates visceral fat storage |
|
|
What is energy balance |
Energy in = energy out |
|
|
How do you measure the energy content in food |
Put dried food in a chamber, outside the chamber is water-> you burn the food -> the amounts of heat raises the temperature of the water-> The amount of the temperature of the water that increases is calculated any correlates with the amount of heat that is given off by food |
|
|
What is basal metabolic rate |
BMR
Amount of energy use during resting time
it's measurements are given when the subject :
is in a warm room in the morning ( before they wake up)
at least 12 hours after the last food or activity |
|
|
Energy requirements of a sedentary person |
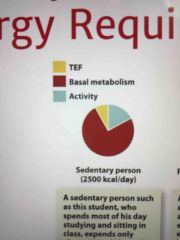
2500 kcal |
|
|
Energy requirements for physically active person |
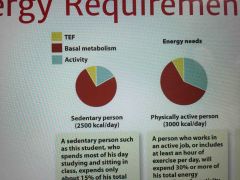
3000 kcal |
|
|
Energy requirements of a very active person |
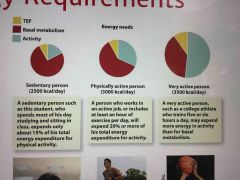
|
|
|
Feasting is: |
Energy in is greater than energy out |
|
|
Fasting is: |
Energy in it is less than energy out |
|
|
Hierarchy of Body Energy Use |

|
|
|
Do genes or environment determine body shape? |
Yes |
|
|
Pima Indians |
Two groups of the same genetic tribe (genetically susceptible to being more fat than average) were living in two different lifestyles-> those who lived in the USA had a higher average BMI
|
|
|
Regulation of Energy Balance |
Set Point
Satiety |
|
|
Set Point |
Point at which you cannot gain extra weight |
|
|
Satiety |
Feeling of being full and satisfied |
|
|
What are the 2 hormones that regulate body weight? |
Ghrelin and Leptin |
|
|
Contributing Factors for Obesity |
Inheriting metabolism
Adaptive Thermogenesis: Changes in amount of energy used due to things like changes in temperature or food intake
Futile cycle: two opposing reaction occur and in the end wastes energy
Brown Adipose Tissue: burns in food quicker. More metabolically active
Differences in Energy Expenditure during Physical Activity |
|
|
Leptin |
Amount produced and secreted is determined by insulin levels
Produced by adipocytes and is in hypothalamus
Fatter= more Leptin released
Inhibits food intake and weight gain, increases energy usage |
|
|
How to determine who should lose weight |
measure height & weight ( see if they are in healthy BMI range)-> assess for obesity related problems that increase risks-> make recommendations for weight loss (obese or overweight with one or more obesity related condition) |
|
|
Weight Cycling |
When you keep going on a diet and then coming off and then going back to your original bad habits. Then you get determined and start dieting again. Goes over and over.
More toxic for your body, compared to not dieting. |
|
|
How to manage your weight: |
Balance intake and output
Decrease calories
Don't get too hungry
Increase activity |
|
|
Physical Activity |
Good for weight management
Adults: minimum 150 min/ week |
|
|
Behavior Management |
Good for weight management
Steps:
A) antecedents: find what causes the problem ( TV)
B) Behavior: what is the problem ( eating too many chips)
C) Consequences: what will you do due to the behavior ( get upset and fat)
Fixing the problem:
A) TV
B) eating fruits
C) happy and healthy |
|
|
Suggestion for weight gain |
Find the clinical reason for weight loss
Increase energy dense foods
Eat more frequently
Replace water w/ milk and juice
Strength chaining |
|
|
A healthy diet: |

Too many changes leads to failure |
|
|
Diet plans: |
Weight watchers
Jenny Craig
SlimFast
HMR
Paleo
Body Reset
Flat Belly diet
Zone
Dukan/ Atkins diet
Biggest loser
NutriSystem
Glycemic index diet
South Beach diet |
|
|
A bad diet : |

|
|
|
Diet plans: |
Weight watchers
Jenny Craig
SlimFast
HMR
Paleo
Body Reset
Flat Belly diet
Zone
Dukan/ Atkins diet
Biggest loser
NutriSystem
Glycemic index diet
South Beach diet |
|
|
Weight Watchers |
Low calorie; social support
Pro: cheap, flexible
Con: N/A |
|
|
Jenny Craig |
Low calorie, prepackaged, weekly counseling
Pro: convenient
Con: expensive, needs purchase of special foods |
|
|
SlimFast |
Low cal, liquid formula, 2 meals/ day
Pro: convenient
Con: needs special food purchase, no social support |
|
|
HMR |
Health Management Resources
Meal replacement
Pro: Rapid Weight loss
Con: severe cal restriction (at the beginning), not flexible for eating out |
|
|
Paleo |
Low carb
Pro: simple to follow
Con: eliminates some food groups, no social support |
|
|
Body Reset |
Train your body to burn cal faster
Pro: rapid weight loss
Con: has unsound science, difficult to follow, no social support |
|
|
Flat Belly diet |
High mono- fat, specific foods for certain time
Pro: safe, nutritious
Con: complicated to follow, no social support |
|
|
Zone |
Controlling blood sugar controls weight
Pro: cheap, flexible
Con: questionable principle, no social support |
|
|
Dukan diet |
High protein
Pro:promotes quick weight loss Con: lots of specific rules, no social support |
|
|
Biggest loser |
Healthy food and regular excercise Pro: safe, easy, effective (short term) Con: bad for long term |
|
|
NutriSystem |
Prepackaged meals Pro: Rapid weight loss Con: no social support, doesn't promote long-term behavior change |
|
|
Glycemic Index Diet |
Promotes good carbs Pro: inexpensive con: poor guidance (mainly carbs), no social support |
|
|
Atkins diet |
very low carb Pro: cheap, rapid weight loss initialy Con: not good for long tem, no social support |
|
|
South Beach diet |
Low carb pro: cheap, good for heart con: you lose mainly water at first, no social support |
|
|
Bariatric surgery |
Recommended sometimes for people with a BMI of 35 or more comes in three ways: gastric banding, gastric sleeve or gastric bypass |
|
|
Gastric banding |
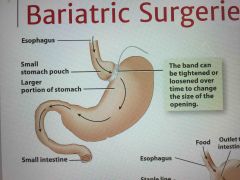
Adjustable band that's around the stomach |
|
|
Gastric sleeve |
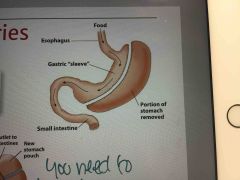
Removal of part of the stomach |
|
|
Gastric bypass |
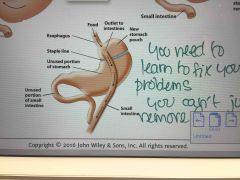
Restricts the size of the stomach and bypasses part of the small intestine |

