![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Private label
brands/generics |
Grocery/farm store/largeformat
retailer Often local/regional manufacturer Less emphasis on ingredient quality & QC Market emphasis - low cost! (from Dr.Hammond lecture #1) Lower quality ingredients: Mineral content up Digestibility down E.g. Private label - Rachel Ray or Paul Newman brand chow |
|
|
Grocery Brands
|
Grocery store/large-format
retailer National manufacturers + Specific purpose foods Market emphasis is palatability Example of grocery brand would be Pedigree |
|
|
Pet store/vet clinic/largeformat
retailer |
- National manufacturers
- + Specific purpose/special needs foods - Market emphasis: ingredients & “optimal nutrition” |
|
|
Veterinary Medical Foods
|
Foods for therapy
Foods for prevention Foods for diagnosis |
|
|
Forms of doggie chow?
|
Dry foods
Semi-moist foods Soft-dry foods Moist foods |
|
|
lower wet fecal weight found in?
|
high quality pet food
prescription diet |
|
|
Dry Matter % =
|
100% - % moisture
Dry Matter (DM) = CHO + Protein + Fats + Minerals + Vitamins |
|
|
Dry Weight % =
|
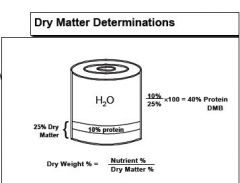
Nutrient % / DM%
|
|
|
Supplements: not necessary if
|
feeding balanced diets to
normal dogs and cats |
|
|
amino acid essential to cats
|
argenine, taurine (antioxidant properties)
|
|
|
carnitine
|
aminovitamin necessary for fat metabolism
|
|
|
AAFCO role in pet food
|
food label regulation and dev. and implementation of dog and cat nutrient profiles
promote uniform pet food regulations and establish dog and cat food nutrient profiles. |
|
|
AAFCO stands for
|
Association of American Feed Control Officials
|
|
|
principle display panel shows
|
product identity (manufacturer’s name, brand name, product name), designator, net weight display, product vignette, nutrition statement, bursts and flags.
|
|
|
• Information panel:
|
nutritional adequacy statement, ingredient list, guaranteed analysis, manufacturer/packer/distributer name and address, feeding directions, universal product code. Statement of calorie content: voluntary, ME, Kcal/kg, feeding trail or calculated
|
|
|
4. Know and understand concept of “percentage” rules used in pet food labels, so as to be able to analyze relative composition of commercial products and make accurate recommendations to owners.
|
•Beef = at least 70% total product
•Beef dinner = at least 10% (canned) or 25% (dry) total product •With beef = at least 3% total product •Beef flavor = recognizable by pet |
|
|
"light or lean" on principle display label, means CF% must be what in wet food (>65% H2O)?
in dry food (<20% h2O) |
<4% CF (<5% for feline)
<9% CF |
|
|
Usage of term "organic" regulated by?
|
USDA, animal given no antibiotics. hormones
food growth with pesticides |
|
|
Where is nutritional adequacy statement found ?
|
on information panel
|
|
|
Name to nutritional adequency determined? (done by cat food manufactures to put NAS on label)?
|
Formulation method: done via computer analysis
>so NAS will say "Formulated to meet the AAFCO dog food nutrient profile for….” Feeding trail protocol method: safer method, covers growth, gestation/lactation, adult maintenance. Statement will read, "Substantiated by feeding tests ….” AAFCO maintenance feeding trail: minimum of 8 dogs (> 1 year old), sole source of nutrition, fed minimum 26 weeks, exam and beginning and end, body weight weekly, hgb, PCV, SAP and albumin. |
|
|
how is order is determined on the ingredient list ?
|
Ingredients are listed in descending order by weight. Each ingredient must be shown. Listed on “As is” basis, official names and definitions.
|
|
|
Purported benefits of raw food diet
|
- improved skin / coat
- elimination of odor - improved health/immune system -reduced disease incidence |
|
|
BARF stands for ?
Idea behind BARF? |
Biologically Appropriate Raw Food
(or Bones and Raw Food) 60% raw bones Suppose to emulate diet wild dog wud eat |
|
|
Volhard Diet
|
AM: cereal, molasses, oil, egg, yogurt, vitamins, etc
PM: raw meat, kelp, garlic, yeast Recommends fasting once weekly |
|
|
Risk associated with raw
|
-time consuming
-nutritional imbalances (cats taurine deficient) -gastrointestinal foreign bodies and perforations -dental issues (tooth fractures) -obstipation (Constipation) Food safety concerns e.g. with salmonella! |
|
|
Name some Homemade raw food diets
|
-BARF diet
- Ultimate diet - Volhard diet |
|
|
Ultimate Diet
|
Type of Raw Food Diets
- Recommends a food pyramid - Base of raw meat, organ meats and eggs. No grains or dairy allowed!!! - Next largest portion is raw bones Veggies - w/kelp, alfalfa, EFA and C at top |
|
|
Combination diets
|
Raw meat + commercial supplements (for nutr)
But still have salmonella problem |
|
|
Are preservatives bad?
|
no they are often anti-oxidants, preserve fat from free-radicals
|
|
|
What is "enzyme theory" ?
Argument agianst? |
Supposedly raw food provides extra enzyme needed by pancrease which improves digestability
(update) |
|
|
How to calculate food dose?
|
Dose = energy requirement (kcal/day) / energy density (kcal/can) = can/day
Basically want complete, balanced diet, but only feed waht animal needs! Requirements for non-energy nutritientss are automatically met |
|
|
Concerns with homemade diets
|
food groups
CHO cooked? quality of protein protein source lean or fat? |
|
|
Ad libitum diet?
|
Ad libitum means free choice
|
|
|
Conditions caused by poor diet
|
Obesity
– Progression of renal disease – Developmental orthopedic disease (canine) – FLUTD (feline): Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disorder – Dental disease |
|
|
Conditions caused by poor diet
|
Obesity
– Progression of renal disease – Developmental orthopedic disease/ skeletal disease (canine) – FLUTD (feline): Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disorder – Dental disease |
|
|
Risks with free choice
|
- over-nutrition e.g. too much calcium or vitamin D, orthopedic disease (in dogs)
- obesity |
|
|
Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disorder caused by
|
1. Bladder Stones, AKA Uroliths: These take the form of crystals of struvite or calcium oxalate. Too much ash, or pH of urine too high
2. infection |
|
|
Free choice?
|
-can use as long as only getting what they need
-dry/semidry better |
|
|
RER
|
-“resting energy requirement”
-does not support activity - RER (kcal/day) = 70 (BWtkg)^0.75 *use ideal body weigh 30(BWtkg) + 70* (*when BWt is 2 to 45 kg) |
|
|
food dosage and ambient temperature
|
generally caloric intake higher during winter
In some places burn more calories when really hot, panting |
|
|
DER =
|
daily energy req = RER x factor
DER = 205 kcal/day × 1.8 = 369 kcal/day |
|
|
• All-purpose foods
|
: “womb to tomb,” one product satisfies all nutritional needs in all situations, food consumption is based on caloric needs. Not a valid concept.
|
|
|
• Specific-purpose food
What are some specific purposes? |
- different life stages (growth, adult, geriatric)
-body condition/use (obese-prone adult, athletic/working dog, gestation, lactation) |
|
|
Nutritient
|
Any food constituent that helps support life
|
|
|
Key Nutrient Factor
|
Key nutritional factors (KNF) are the main nutrient requirements for feeding different life stages and purposes. Encompass nutrients of concern and other food characteristics.
They include: 1. energy/fat: energy intake determines growth intensity. Risk of DOD INCREASES in large breeds with energy- dense well balanced foods b/c grow too fast and get abnormal growth. However, some fat important for vit. absorption. 2. Calcium: growing dogs will absorb 90% calcium are fed. DOD is signif. higher in young, giant-breed dogs being fed food containing excess calcium (e.g. 3.3% DMD), regardless of normal phosphorus ratio. Hence, there is danger in feeding these fast growers adult maintenance foods (to decr. energy intake) or calcium supplements, because calcium level will be too high. 3. digestibilty - goal is high quality (digestible), in low density package Others: soluble carbohydrate (reduce Cu abs), Zn, I, Cu, Ph 4. Encompass nutrients of concern and other food characteristics. |
|
|
Energy density units
|
kcal/unit volume
|
|
|
pyramid top to bottom
|
vit, min, lipids, prot, carbs, h2O
|
|
|
Most common analysis done for
nutritional testing What does it measure? |
Proximate Analysis
Crude fat, crude protein, moisture, crude fiber & ash - carb. (NFE) calculated by subtracting all these from 100% Not very accurate |
|
|
More accurate way to determine nutrient components in food?
Most accurate way to determine what animal needs (energy requirements)? |
Average Nutrient Analysis: More accurate than proximate
analysis Calorimetry - measurement of heat |
|
|
1. How does cat maintain blood glucose lvl between meals?
2. Does cat produce glucokinase? |
1. Cat doesnt get big spike in blood glucose level after meal like humans do, b/c can't produce large amounts of active hexokinases (which brk down
Cats maintain blood gluc. betw meals via gluconeogenesis, breakdown of AA and fats from glycerol 2. No (only tiny bit, but not active), but does produce other 3 non-inducible, constitutive hexokinases. From online: "Gluconeogenesis is the production of new glucose in the body from non-sugar sources, mainly proteins. It occurs mainly in the liver and kidneys. It is major body energy source for cats, who lack the glucokinase that let other animals synthesize glucose more rapidly after eating. Cats use another enzyme called hexokinase, which is not very efficient, for processing carbohydrates. Gluconeogenesis happens slowly and steadily, in each cell of the body. cats are able to maintain fasting blood glucose (by converting protein to glucose) even without a meal, but must be eating a high protein diet on a regular basis to be able to do so. An unrelated process, glycogenolysis, releases stored glucose very fast by breaking down glycogen in liver (Glucokinase (GK) is a isozyme of hexokinase, so not the same) |
|
|
identify basics behind gluconeogenesis (challenge question)
|
metabolic pathway that results in generation of glucose from non-CHO source such as lactate, glycerol, and glucogenic amino acids.
one of two main mechanisms many animals use to keep blood glucose levels from dropping too low (hypoglycemia). Other being degradation of glycogen (glycogenolysis). |
|
|
Glucose 6-phosphatase (challenge question)
|
enzyme that hydrolyzes glucose-6-phosphate resulting in creation of phosphate and free glucose.
Glucose is then exported from cell via glucose transporter membrane proteins.[1] This catalysis completes final step in gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis and plays a key role in homeostatic regulation of blood glucose levels. |
|
|
Cats higher ___ vitamins then dogs.
Where foound? Digestibility? what else does do they require as far as vitamins go? |
B-vitamins (B1, B6, 5xNiacin, folate)
Found green beans, vegetable oil, but mostly biologically unavailable A-vitamins - more specifically require retinoic acid, because cant convert B-carotine (vegetable form) to Ret.Acid (animal form) like humans and dogs can. It is found in animal livers! Also require tryptophan and/or Nicotinic Acid (vit B3)(converted into dopamine) - this is niacin Also require vitamin D, cant get from sun. From animal tissue, fat, liver of mice. |
|
|
Mineral requirements for cats?
What to avoid excess of? |
similar to dogs.
need Ca, dont eat bones. Require Cu danger of Mg, causes Struvite (ammonium magnesium phosphate) crystals. readily soluble in acid. Struvite urinary stones and crystals form readily in urine of animals and humans that are infected with ammonia-producing organisms. They are potentiated by alkaline urine and high magnesium excretion (high magnesium/plant-based diets). |
|
|
Ideally when to spay/castrate cat?
What changes afterwards? |
6 months
energy requirements go way down, |
|
|
Vitamin often deficient in cat food, required for good growth?
|
VItamin A!!!!!
|
|
|
Wean dogs _____, wean cats ____.
|
Wean dogs early (can only imprint them when young), wean cats later
|
|
|
More energy dense: carbs or protein?
|
~same?
|
|
|
Food consumption based on _____ not _____
|
energy density of food, not bulk
if u want to lower energy density, increase fiber and decrease fat |
|
|
key nutritional factors • Obese-prone adults
|
only unique are sodium and chloride, antioxidants, food texture
and as usual energy density, protein, fat, fiber, calcium and phosphorus, |
|
|
What to feed cats?
What amino acids do they need? |
more energy dense than dogs, a little more fat, protein!, Ca/Ph about same as dog,
Taurine (esp. pregnant),Cu, Arginine (high in animal protein, also have high sulfur req (Cys + Met) |
|
|
Peak lactation in cat?
Peak in dog? |
at end
in middle |
|
|
EFA
|
linoleic acid 18c n-6
arachidoinc 20c n-6 elcosapenta. 20c, n-3 docosahex. acid 22c n-3 |
|
|
What changes made in older cat diet?
|
kidney function decreases, so
do NOT on all-growth all-life stage diet. Want to keep eye on potassium!!!! If low, can adversely affect kidney, want to keep Ca/Ph, NaCl down Sell Ca stones in older cats, not Mg stones like see in younger cats |
|
|
Is excess protein a threat to growing giant breed dogs?
|
No, but overconsumption and fat/energy dense foods are bad
|
|
|
Why dont u want to give pregnant dog more calcium?
(more information needed) |
There is no scientifically established nutrient profile for older dogs. Assess individual patient’s needs. Avoid nutrient excess.
|
|
|
do cats like MCT (med chain triglycerides)?
|
no, dont tolerate it
|
|
|
_____ and not ______ are able to elongate and desaturate lineolic acid to form arcachidonic acid
|
dogs but NOT cats
|
|
|
n-6 family includes
|
Linoleic acid 18:2(n-6): is a carboxylic acid (all these are) with an 18-C chain and two cis dbl.bonds
γ-LinoleNic acid (aka ω−6 or omega-6) 18:3 (n−6) arachidonic acid (20:4n-6) : precursor to n-6 prostaglandin and other hormones |

