![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Essential Nutrient
|
Cannot be made in the body
|
|
|
Nonessential Nutrient
|
Other chemicals
|
|
|
Example of nonessential nutrient
|
lechithin
|
|
|
6 classes of nutrients
|
1. Carbohydrates (M)
2. Proteins (M) 3. Lipids (M) 4. Water (M) 5. Vitamins (m) 6. Minerals (m) |
|
|
Carbohydrate structure
|
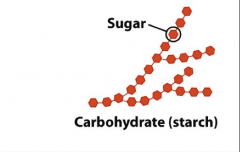
|
|
|
Lipid structure
|
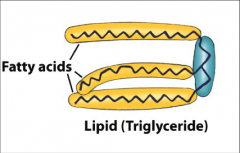
|
|
|
Protein Structure
|
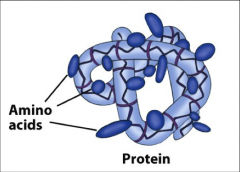
|
|
|
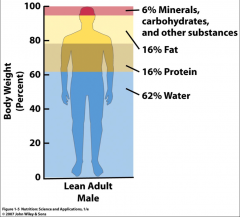
|
|
|
Kilocalorie
|
unit of heat to express the amount of energy produced by food
|
|
|
1 kcal=(description)
|
Amount of heat to raise the temperature of 1 kilogram of water by 1 degree
|
|
|
1 kcal=
|
1000 calories
|
|
|
Carbohydrates provide _____ kcal/gram
|
4 kcal/gram
|
|
|
Carbohydrates composed of these elements
|
C, H, O
(CHO) |
|
|
Simple carbohydrates=
|
Sugars
|
|
|
Complex carbohydrates=
|
Starch
|
|
|
Lipids MADE up of
|
Fatty acids
|
|
|
Lipids MAKE up
|
Cell membranes
|
|
|
Lipids provide _____ kcal/gram
|
9 kcal/gram
|
|
|
Lipids composed of these elements
|
C, H, O, some P
(CHOP) |
|
|
Proteins necessary for...
|
Growth and maintenance of body structures
Regulation of body processes |
|
|
Protein makes up
|
Muscles and connective tissue
|
|
|
Protein MADE up of
|
Amino acids (essential/nonessential)
|
|
|
Protein supplies ______ kcal/gram
|
4 kcal/gram
|
|
|
Protein made up of these elements
|
C, H, N, O
|
|
|
Vitamins/minerals do not provide...
|
Energy
|
|
|
What vitamins/minerals do...
|
Regulate metabolic processes
(bone growth, oxygen transport, tissue growth) |
|
|
Vitamins/minerals necessary for...
|
Energy production
|
|
|
Fortified foods have...
|
added vitamins/minerals
|
|
|
Alcohol supplies...
|
No nutrients
excess sugar/fat |
|
|
Alcohol has ____ kcal/gram
|
7 kcal/gram
|
|
|
Nutrient needs depends on...(4)
|
1. Genetics
2. Lifestyle 3. Health 4. Diet |
|
|
2 components of malnutrition
|
1. Undernutrition
2. Overnutrition |
|
|
Undernutrition
|
Deficiency of energy/nutrients
-Unable to absorb nutrients -Deficient intake (iron, B12) -Dehydration -Starvation |
|
|
Overnutrition
|
Excess nutrient intake
-Toxicity -Obesity |
|
|
Nutrient-related diseases
|
Diabetes
Hypertension Heart Disease Vitamin/mineral deficiencies Toxicities |
|
|
Controllable risk factors for chronic disease
|
-Body weight
-Physical activity -Stress -Lifestyle (smoking, hazards) -Nutrient intake |
|
|
Uncontrollable risk factors for chronic diseases
|
Age
Genetics Gender |
|
|
Factors of a healthy diet
|
-High nutrient density
-Proper energy intake to keep weight in a desired range -Proper types and balance of nutrients -Water -Sufficient, not excessive vitamins and minerals |
|
|
Compensation recommendations for a healthy diet
(Fat, protein, carbs) |
Fat=20-35%
Protein=10-35% Carbohydrates=45-65% |
|
|
American diet _____ compensation recommendations for a healthy diet
|
Meets but is excessive
|
|
|
American diet is....
|
Changing
Used to have home-cooked meals, now lots of fast food |

