![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
American Medical Association (AMA) |
227,000 physicians in the US 27% are a part of the AMA *Very Powerful Lobbyist group |
|
|
American Nursing Association |
3.1-3.5M RN's in US ONLY 10,000 belong to ANA (1/310= 0.027%) |
|
|
Florida (FNA/ FMA) |
295,000 RN's/ 2 lobbyists in Tallahassee 47,000 Physicians (20,000 belong to FMA) 22/23= 45 lobbyists in Tallahassee |
|
|
BSNs affect in hospitals |
Every 5%↑ of BSN's in a facility, there is a significant ↓ in complications for the patients in the hospitals |
|
|
Nursing Science *If nursing doesn't change then nursing will become obsolete |
|
|
|
Theory *Main function of theory is to guide research |
•Definedas a system of ideas presumed to explain a given phenomenon *THEORIES ARE NOT FACTS |
|
|
Practice Discipline |
Field of study that where the performance of a professional role is focused -Not common use until end of 20th century •usefulnesscomes from: •Helpingto interpret phenomenon from unique perspectives •Buildingnew understandings, relationships, and possibilities |
|
|
Metaparadigm |
-Concept that can be superimposed on almost any work in nursing
|
|
|
Conceptual framework |
Group of related ideas, statements, or concepts (ex. Freud's structure of the mind- id, ego and superego) |
|
|
Mid-range nursing theories |
*focus on the exploration of concepts
narrower focus and much more concrete- "More precise & focus on answering precise specific nursing practice questions" Ex.- How mother's and babies bond; Bullying in schools |
|
|
Paradigm |
A pattern of shared understandings and assumptions about reality and the world |
|
|
Nsg, Metaparadigm ( Person) |
Recipient of care *High School Nurse- recipient of care is the High school; Nurse for the Federal Gov't- Recipient of care is the Federal Gov't |
|
|
Nsg, Metaparadigm (Health) |
Goal of nursing "A dynamic state which the developemental and behavioral potential of the individual is realized to the fullest extent possible" |
|
|
Nsg, Metaparadigm (Environment/ situation) |
Conditions affecting the client and the setting in which the health care needs occur *Describe |
|
|
Nsg, Metaparadigm (Nursing) |
is the "Dx and tx of the human responses to actual or potential health problems" |
|
|
Role of Nursing Theory |
|
|
|
Beginning of Nursing Theory |
|
|
|
Nursing Process (Historical perspective) |
Theories guide how to apply/ use the nursing process |
|
|
Florence Nightingale 1820-1910 *1860- Founded School of Nursing at St. Thomas Hospital in London |
|
|
|
Dorethea Orem (1914-2007) |
|
|
|
Dr. Patricia Brenner |
|
|
|
Dr. Jean Watson |
*Developed- Science of Human Caring (described as a philosophy of Nursing/ Caring)
|
|
|
Dr. Madeleine Leininger (a nurse anthropologist) *3 intervention modes: Culture care preservation and maintenance Culture care accomodation, negotiation, or both Culture care restructuring and repatterning |
|
|
|
Jean Watson - 10 clinical caritas |
Human care referred to as carative factors
|
|
|
Critique of Nursing Theory |
|
|
|
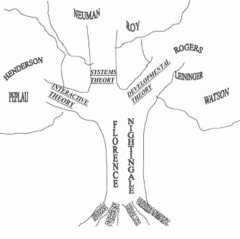
the living tree of nursing theories |
|

