![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Alloantibodies |
An antibody produced following introduction of an alloantigen into the system of an individual of a species lacking that particular antigen. |
|
|
Urticaria |
Multiple eruptions of skin formed by localized edema in the dermis |
|
|
Colloid oncotic pressure (COP) |
The osmotic pressure exerted by colloids in a solution |
|
|
Trocarization |
Using a trocar to penetrate an organ/tissue |
|
|
Gastropexy |
Stomach sutured to abdominal wall/diaphragm |
|
|
Hydrocephalus |
Abnormal expansion of cavities (ventricles) within the brain that is caused by accumulation of CSF |
|
|
Necrosis |
Tissue death |
|
|
Central venous pressure |
The pressure of blood in the right atrium |
|
|
Syncope |
Temporary loss of consciousness and muscle tone secondary to temporary deficiencies in oxygen transport or perfusion to the brain. |
|
|
Pulmonary contusion |
Bruised lung cause by chest trauma as a result of damage to capillaries, blood & other fluids accumulated in the lung tissue |
|
|
Polyphagia |
Excessive hunger |
|
|
Idiopathic |
Disease with no cause |
|
|
Stranguria |
Drip by drip urination |
|
|
Pollakiuria |
Abnormally frequent urination |
|
|
Enophthalmos |
Posterior displacement of the eyeball within the orbit |
|
|
Polydipsia |
Frequent drinking |
|
|
Ptosis |
Drooping of the upper eyelid |
|
|
Iatrogenic |
Due to the activity of a physician |
|
|
Anisocoria |
Pupil asymmetry |
|
|
Hypoxemia |
Insufficient oxygenation of arterial blood necessary to meet metabolic requirements (PaO2 <60-70mmHg) |
|
|
Thrombocytopenia |
Autosomal recessive inherited disorder, causing abnormal platelet signal transduction. Pet will bleed excessively during surgery/ injury |
|
|
Chyme |
Pulpy acidic fluid passing from stomach to small intestine, consists of gastric juice & partially digested food |
|
|
Exogenous |
Developing from external factors |
|
|
Glaucoma |
Elevated intraoccular pressure damages optic nerve = loss of vision |
|
|
Orthotonos |
Rigid posture caused by physiological tetanus infection |
|
|
Polyp |
Abnormal growth of tissue projecting from mucus membrane |
|
|
Ablation |
Procedure for restoring normal heart rhythm |
|
|
Subcutaneous emphysema |
When gas/air is in the layer under the skin |
|
|
Infarction |
Obstruction of the blood apply to an organ/region of tissue causing local death of tissue |
|
|
Erythropoiesis |
Process or RBC production. Detected by decreased O2 in circulation, detected by kidneys which then secrete erythropoietin |
|
|
Canine blood type |
Dog erythrocyte antigen (DEA) (DEA 1.1 positive (most antigenic) or DEA 1.1 negative) - naturally occurring alloantibodies are rare in dogs - reaction rarely seen with 1st transfusion |
|
|
What does Cross matching do? |
Detects the serologic compatibility between the recipient & potential donor - look for presence or absence or alloantibodies |
|
|
Major crossmatch vs. Minor & what to look for? |
Recipient plasma + donor RBC vs. Donor plasma & recipient RBC. Looking for macro/micro agglutination & hemolysis - If we see agglutination, don’t do it! - only 2% of dogs in North America are DEA 4- . DEA 4+ are considered universal donors bc there are no antigens = won’t will trigger alloantibodies |
|
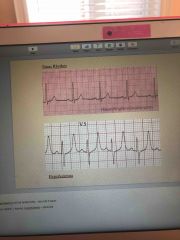
Front (Term) |
Hyperkalemia EKG |
|
|
How to be prepared for CPR? |
1. Well stocked “SHOCK CART” 2. Good knowledge in recognizing signs of CPA 3. Effective CPR |
|
|
Resuscitation centres should be where? |
Centrally located |
|
|
What are some cognitive aids for CPR? |
- drug dosage chart - CPR algorithm - a log sheet |
|
|
Common signs of an impending CPA |
- Changes in pattern & rate of respiration - Hypotension - Bradycardia - Cyanosis |
|
|
Common signs of an impending CPA |
- Changes in pattern & rate of respiration - Hypotension - Bradycardia - Cyanosis |
|
|
ABC = ? |
Airway Breathing Circulation |
|
|
Airway evaluation |
Visual inspection & remove anything obstructive |
|
|
Breathing evaluation |
- Feel/ observe chest movement - agonal breathing is not effective breathing |
|
|
Circulation evaluation |
Palpating pulses & auscultation of the heart |
|
|
For patients that are unresponsive & apneic, should pulse palpation should be done? |
No, it will delay CPR/ decrease the patient’s survival rate |
|
|
How long should ABC take and what should follow it? |
It should take 10-15 seconds followed by basic life support |
|
|
What’s BLS & what does it consist of? |
Basic life support: Airway management Ventilation support Chest compressions |
|
|
What is the goal of CPR? |
Achieve the return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) so that oxygen is delivered to the vital organs |
|
|
Why is ABC done in animals but CAB done in humans? |
Resp. arrest dominates in dogs and cats compared to cardiac arrest in humans |
|
|
What comes first: airway establishment or chest compressions? |
Neither, begin simultaneously |
|
|
What do chest compressions do? |
Replace the function of the ventricles to pump blood to the lungs for gas exchange and restore organs |
|
|
What position can flat chested dogs be in for CPR? Why? |
Dorsal recumbency. Optimizes forward bloodflow better. Position of the compressor: behind |
|
|
How many compressions per min? |
100-120 for dog and cat regardless of the size |
|
|
Why should you not pump faster than the recommended compression? |
Higher rate prevents full recoil of the chest & decreases the amount of forward blood flow |
|
|
What’s the compression depth? |
1/3-1/2 deep |
|
|
Why should you not lean into the animal during compressions? |
It affects the recoil of the chest wall / affects the blood flow |
|
|
What is one of the determinants of ETCO2? |
The amount of blood returning from the tissues to the lungs, which is directly related to the cardiac output. Therefore, the ETCO2 value can be used to evaluate the quality of chest compressions during CPR |
|
|
ETCO2 of less than 15mmHg is associated with what? |
Poor survival outcome |
|
|
A sudden increase of ETCO2 above 30mmHg is an indication of what? |
Good ROSC |
|
|
A sudden increase of ETCO2 above 30mmHg is an indication of what? |
Good ROSC |
|
|
Once the patient is intubated, what should begin? |
Positive pressure ventilation with 100% oxygen with the ambu bag |
|
|
For intubated patients, how many breaths per min? |
10; or 1 breath every 6 compressions |
|
|
What should the tidal volume be for intubated patients? |
10mL/kg |
|
|
For non-intubated patients (mouth-snout), how many breaths? |
2 breaths/30 chest compressions |
|
|
What’s ALS & what does it include? |
Advanced life support. Drug therapy, fluid therapy, defibrillation |
|
|
What is needed in order to proceed ALS? |
ALS is performed based on the type of EKG arrest rhythm diagnosed during BLS |
|
|
Excessive fluid administered to euvolemic or hypervolemic patients may result in what? |
Decreased coronary perfusion/ negatively affect ROSC |
|
|
What are the two shockable arrest rhythms? |
Pulseless ventricular tachycardia 2. Ventricular fibrillation |
|
|
Electrical defibrillation - how does it work? |
Electrical current is applied to the myocardium to depolarize the heart muscle, terminate the arrhythmia, and allow the heart to reestablish a regular sinus rhythm pacing from the SA node |
|
|
Defibrillation joules |
4-6J/kg for monophasic 2-4J/kg for biphasic Don’t exceed 10 |
|
|
How to verify ET tube placement for anesthesia patients ? |
Direct visualization Cough reflex Fogging in tube Hair test Palpation - only one fi tube structure should be felt ETCO2 |
|
|
Verifying tube placement for CPR patients ? |
Direct visualization Proper chest movement (chest should rise in each breath given by ambu bag, of rises in abdomen, improper placement) Palpation ETCO2 |
|
|
Special considerations for intubation |
- over stimulation of the larynx can invoke vagal responses leading to bradycardia, hypotension - head should not be elevated for severely hypotensive patients bc = a decrease in cerebral blood flow = cardiopulmonary arrest. Intubate in dorsal or lateral recumbency |
|
|
Dog maintenance fluids rate |
60ml/kg/day |

