![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Identify the 2 types of viscera in the abdomen. Which of these percuss tympany?
|
Solid viscera
Hollow viscera => Percusses tympany |
|
|
Identify the quadrants in the abdomen.
|
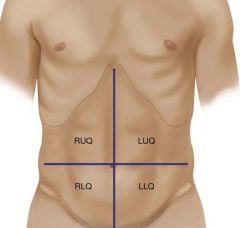
RUQ
LUQ RLQ LLQ |
|
|
Identify and describe the 3 regions of the abdomen.
|
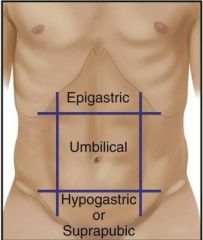
Epigastric - above belly button
Umbilicus - around belly button area Hypogastric/Suprapubic - below belly button, above pubic region |
|
|
Identify the nationalities that have increased risk for lactose intolerance at birth.
|
African Americans, Native Americans, Asians, and Mediterranean groups
|
|
|
abdomen
|
large oval cavity extending from diaphragm down to the brim of the pelvis
|
|
|
Identify what organs/structures are in the RUQ.
|
liver, gallbladder, duodenum, head of pancreas, R kidney
and adrenal, hepatic, flexure of colon, part of ascending and transverse
colon
|
|
|
Identify what organs/structures are in the LUQ
|
stomach, spleen, L lobe of liver, body of pancreas, L kidney and
adrenal, splenic flexure of colon, part of transverse and descending colon
|
|
|
Identify what organs/structures are in the LLQ.
|
part of descending colon, sigmoid, colon, L ovary and tube, L
ureter, L spermatic cord
|
|
|
Identify what organs/structures are in the RLQ.
|
cecum, appendix, R ovary and tube, R ureter, R spermatic cord
|
|
|
Identify the common chief complaint for abdomen.
|
Abdominal pain, unspecific
|
|
|
Identify the normal range in frequency for bowel movements.
|
o Frequent 2-3 times per day
o Infrequent as once every 3-5 times days |
|
|
Should feces be floating or sinking?
|
It should be sinking. If it's floating, it means patient is not getting enough fiber.
|
|
|
If a patient is vomiting/having diarrhea more than ______ times a day, you will be concerned about dehydration.
|
five
|
|
|
Why must you auscultate before palpation and percussion?
|
If you percuss or palpate first, you will create gurgles/sounds in the abdomen.
|
|
|
Identify the 4 descriptions of bowel sounds.
|
Normal (normoactive)
Hypoactive Hyperactive Absent |
|
|
What does it mean when you hear a bruit when checking for vascular sounds?
|
It could mean there is an aneurysm.
|
|
|
Identify the 2 types of sound you would hear via percussion.
|
Tympany and dullness
|
|
|
pyelonephritis
|
Inflammation of the kidney and its pelvis, caused by bacterial infection.
|
|
|
organomegaly
|
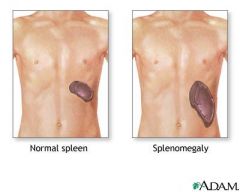
abnormal enlargement of organs
Pic: Spleen enlargement |
|
|
Describe the two types of palpation.
|
Light - 1 cm
Deep - 2-3 inches |
|
|
ascites
|
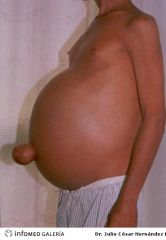
accumulation of serous fluid in the peritoneal cavity
|
|
|
constipation
|
bowels are evacuated at long intervals or with difficulty/straining,
stool is usually very hard
|
|
|
umbilical hernia
|
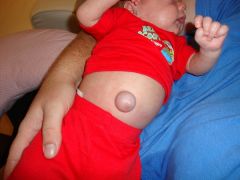
soft skin covered mass which is the protrusion of the intestine
through a weakness or incomplete closure in the umbilical ring
Note: When person is relaxed, you should be able to retract this into belly. |
|
|
hepatitis
|
inflammation and usually enlarged liver
|
|
|
gastroesophageal reflux (GER/GERD)
|
complex of symptoms of
esophagitis, heartburn, usually occurs 30-60 minutes after eating, aggravated by lying down or bending over, (in infants characterized by spitting up/vomiting)
|
|
|
aortic aneurysm
|
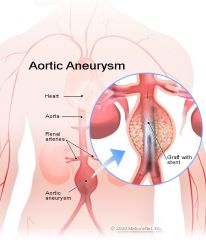
pulsating mass in the upper abdomen just left of midline; positive bruit, decreased femoral pulses
Note: 80% are palpable during routine physical exam |
|
|
Describe pain related to appendicitis.
|
diffuse pain in periumbilical region that later shifts to severe, sharp, persistent pain and tenderness localized in RLQ (McBurney’s point)
|
|
|
Appendicitis pain is aggravated by _________. (2)
It is associated with the following symptoms: __________. (3) |
aggravated by movement, coughing
anorexia, N/V, fever |
|
|
gastroenteritis/gastritis (AGE)
|
diffused generalized abdominal pain with nausea and diarrhea
|
|
|
cholecystitis
|
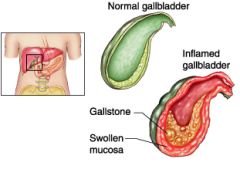
inflammation of the gallbladder
|
|
|
Describe the clinical manifestation of cholecystitis and its causes.
|
Sudden pain in RUQ that may radiate to right or left scapula and which builds over time, lasting 2-4 hours after ingestion of fatty foods, alcohol, or caffeine
|
|
|
Cholecystitis is common in ______.
|
females > 40 years old.
|
|
|
A bruit indicates _________ in _________ vessels.
|
turbulent blood flow
in constricted, abnormally dilated, or tortuous vessels |
|
|
What result confirms rebound tenderness (Blumberg sign)?
|
Pain on release of pressure
|
|
|
Describe how to perform the following test: rebound tenderness. What is normal response?
|
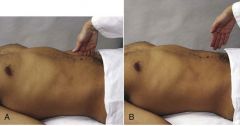
Choose a site away from the painful area. Hold your hand 90 degrees, or perpendicular, to the abdomen. Push down slowly and deeply; then lift up quickly.
A normal, or negative, response is no pain on release of pressure. |
|
|
Describe how to perform the following test: inspiratory arrest (Murphy Sign). What is a normal response?
|
Hold your fingers under the liver border. Ask the person to take a deep breath.
A normal response is to complete the deep breath without pain. |
|
|
Describe how to perform the following test: iliopsoas muscle test.
|
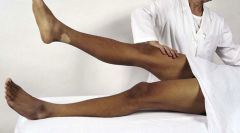
With the person supine, lift the right leg straight up, flexing at the hip (Fig. 21-31); then push down over the lower part of the right thigh as the person tries to hold the leg up.
|
|
|
Identify the 5 locations you would listen for vascular sounds.
|
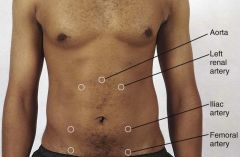
Aorta
L/R renal artery L/R iliac artery L/R femoral artery |
|
|
hepatomegaly
|
enlarged liver
|
|
|
Hypoactive or absent bowel sounds typically follow ___________. (2)
|
abdominal surgery or inflammation of the peritoneum
|
|
|
peritoneum
|
serous membrane lining the cavity of the abdomen and covering the abdominal organs
|
|
|
An individual is 5' 3'' in height and weighs 120 pounds. What is their BMI?
|

21.3
|
|
|
apple shape vs. pear shape
|
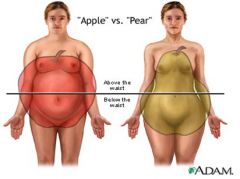
Apple - Wider waist than hips
Pear - Wider hips than waist |
|
|
Which of the following has a higher risk for heart disease: apple shape or pear shape?
|
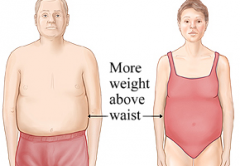
Apple shape
|
|
|
Describe how to calculate waist/hip ratio.
|
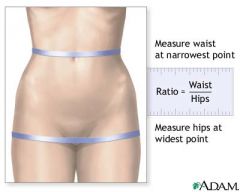
Ratio = Waist/Hips
|
|
|
Identify the formula for BMI using inches and pounds.
|

|
|
|
Perform the iliopsoas muscle test when ________ is suspected.
|
appendicitis
|
|
|
What is the normal result for iliopsoas muscle test?
|
No pain/change
|
|
|
When the iliopsoas muscle is inflamed (which occurs with an inflamed or perforated appendix), pain is felt the ______ quadrant.
|
RLQ
|
|
|
TRUE/FALSE
Evidence shows that the Obturator Test, another technique that stretches the obturator muscle, does not work to diagnose appendicitis. |
True
|
|
|
Sharp pain during CVA tenderness test indicates __________.
|
Sharp pain occurs with inflammation of the kidney or paranephric area.
|
|
|
Describe how to perform the following test: CVA tenderness. What is normal response?
|
To assess the kidney, place one hand over the twelfth rib at the costovertebral angle on the back (Fig. 21-17). Thump that hand with the ulnar edge of your other fist.
Normal response is no pain. |
|
|
Identify the disease/condition the following patient may have.
You feel a pulsating mass in the upper abdomen. You hear a bruit in that region and the pt has decreased femoral pulses. |
Aortic aneurysm
|
|
|
Identify the disease/condition the following patient may have.
Pt has had increasing pain in the RLQ. The pain started in the preumbilical region and has gotten worse and moved to the RLQ. |
Appendicitis
|
|
|
Identify the disease/condition the following patient may have.
Pt has abdominal pain throughout belly. He/She is also experiencing nausea and diarrhea. |
Gastroenteritis/gastritis
|
|
|
Identify the disease/condition the following patient may have.
Pt reports pain lasting ~3 hours after ingesting fatty foods and caffeine. The pain is in the RUQ. |
Cholecystitis
|
|
|
Identify the disease/condition the following patient may have.
Pt feels heartburn ~30 minutes after eating. He said it feels worst after lying down or bending over. |
gastroesophageal reflux (GER/GERD)
|
|
|
Blumberg sign = _______ test
|
rebound tenderness
|
|
|
Murphy sign = _______ test
|
inspiratory arrest
|

