![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is amblyopia, what is its causes and what should be done about it?
|
amblyopia: loss of visual acuity because of disuse.
- baby brain must have equally focused images from both eyes. if not: amblyopia. - MUST CORRECT EARLY (before age 6) or PERMANENT BLINDNESS!!! - most common cause: cross-eyes (heterotrophia) TO DO: screen babies. |
|
|
What are the four most common causes of preventable vision loss?
|
1. amblyopia
2. age related maculopathy 3. glaucoma 4. diabetic retinopathy |
|
|
Macular degeneration is the age related loss of (CENTRAL OR PERIPHERAL) vision. pick one.,
|
central vision
S/S - blurry vision - center blind spot |
|
|
Glaucoma
gradual loss of (CENTRAL OR PERIPHERAL) vision. pick one. |
slow loss of peripheral vision - don't notice it happening - get tunnel vision
|
|
|
What causes glaucoma?
|
Damage to the optic nerve because of increased interocular pressure IOP
|
|
|
What is normal IOP (intra ocular pressure) and how is it measured?
|
Normal IOP is 12 - 20 mmHg
- it is measured by finger pressure or tonometry. FYI: IOP varies during the day. Normally higher in the morning. |
|
|
IF both eyes go glaucoma... is this chronic or acute?
|
Chronic - open angle - 90% of cases
|
|
|
Doctor: "you have glaucoma."
Patient: "nonsense. I have no pain!" Chronic or Acute? |
Chronic - painless - slow "insipid" onset.
|
|
|
A diabetic, over 40 who has severe myopia is more at risk for chronic or acute glaucoma?
|
chronic glaucoma
The acute kind is more dependent on problems with physical structures: small chamber, large lens, small cornea. |
|
|
Name that Eye Disease!
severe, sudden pain halos around lights blurred vision & headaches red eye - pupil dilated nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain |
Acute Glaucoma
Medical Emergency |
|
|
Which glaucoma is caused by an obstruction of aqueous humor flow?
|
chronic - open angle - simple.
- trabecular network blocks flow of humor through the canal of Schlemm (my favorite canal ever!) |
|
|
Which glaucoma is caused by a block of aqueous humor flow or an over production of aqueous humor?
|
acute - congestive - closed angle
- lens/pupil dilation causes this from meds or sympathetic stimulation. |
|
|
So we all know :) that the trabecular network drains the aqueous humor... an channels it through the canal of Schlemm... but where does it go from there?
|
to the general circulation.
I guess that's why you have to be careful giving beta blocker eyedrops. They can get into the bloodstream and do what beta blockers do to the whole body. |
|
|
She mentioned cranial nerves, so lets just take a guess. Which ones are involved with the eye?
|
2, 3, 4, 6
II = optic III = oculomotor IV = troclear VI = abducens |
|
|
Which class of meds will slow the rate of fluid production (aqueous humor)? there are four.
|
1. carbonic anhydrase inhibitors - CAI's for short. These are sulfonamides so be careful about allergies. drops or pills.
2. beta blockers. block epi & norepi - careful they make pulmonary disease worse, decrease HR & BP (and let's not forget cause impotence!) 3. Alpha Agonists -aka adrenergics aka sympathomimetics - vasoconstriction, also decrease production of aqueous humor. and 4. combination durgs (beta blockers and alpha agonists or beta blocker and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors |
|
|
What classes of medications increase drainage of aqueous humor? there are 4
|
1. Cholinergic drugs - stimulate eye muscles to work; open drainage channels. include Miotics: opens drainage angle
2. Prostaglandin Analogs: side effects - change eye color, grow eye lashes! 3. alpha agonists aka adrenergics - 4. Combination drugs - do both. beta blocker + alpha agonist or beta blocker + carbonic anhydrase inhibitor CAI |
|
|
What do most people call these three conditions?
conjunctivitis blepharitis hardoleum |
conjunctivitis = pink eye
blepharitis = inflammation of eyelid hardoleum = stye (infection of sebaceous gland/hair follicle) |
|
|
What is chalazion and what would you do about it?
|
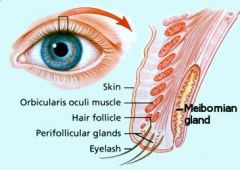
chalazion = inflammation of the meibomian gland in the upper or lower lid due to obstruction. Need I&D surgery (incision & drainage)
|
|
|
What is keratitis, how do you know you have it and what are ya gonna do about it?
|
Keratitis = cornea inflammation
S/S SEVERE eye pain photophobia blepharospasms opacity of cornea with loss of vision. TX:steroids to lessen inflammation, antibiotics, antiviral, anticholinergics to rest eye. |
|
|
Do you know the Uveal Tract?
Then what is uveitis? Would you be upset if you got it? |
Uveal Tract = iris, ciliary body, choroid - provides blood supply to retina.
Hell yea, I'd be upset. - can cause blindness. - secondary to acute/chronic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. - TX: steroids to lessen inflammation, anticholinergics to rest eye, dark glasses. |
|
|
What do mydriatic medications do to the eye?
What class of drug does the opposite? |
mydriatics - dilate pupils.
by contracting the radial muscle. opposite miotics - contract the pupil |
|
|
What do the cycloplegic drugs do to the eye?
|
cycloplegics - also dilate pupils (like mydriatics) but also paralyze the ciliary body. Lens will not be able to adjust = blurry vision
|
|
|
What should the nurse do if someone is getting an IV with Fluorescein?
|
Fluorescein is a dye that outlines damaged issue. it can be given by drops or IV.
- for IV, ask about dye allergies; get informed consent. After; give fluids to get rid of dye. The urine may be bright green! I want some of that - Christmasy! |
|
|
What are characteristics of legally blind?
|
worse than 20/200 vision and less than 20 degree visual field.
|
|
|
If you can't read the Snellen chart, what are some other ways to test vision?
|
E chart: children or illiterates
CF: counts fingers at 3 feet HM: sees hand movements LP: light perception |
|
|
Define strabismus
|
strabismus aka heterotropia
- muscles not balanced - hold object 12 inches away, cover one eye, observe movement of other eye |
|
|
What's the test for color blindness called?
|
Ishihara plates. by the way, the first plate is just for practice- all people should be able to read it.. Diagnoses red/green color blindness. mostly men.
|
|
|
What a pupil's normal diameter?
|
3 - 5 mm
|
|
|
Why are cataracts yellow?
|
- reduction in oxygen uptake
- initial increase in water content, then dehydration - protein turns yellow |
|
|
What eye problem is this?
- gradual vision loss - blurry - decreased color perception ** unique - halos, photophobia - maybe diplopia - vision better in low light (late sign) - opaque lens (late sign) |
YES!!! CATARACTS!!!
- must remove lens. remember the video?? ew! |
|
|
Name some Post Op concerns with cataract removal
(5) |
1. secondary glaucoma
2. infections 3. hemorrhage 4. retinal detachment 5. TASS: toxic anterior segment syndrome. an acute postoperative inflammatory reaction in which a noninfectious substance enters the anterior segment and induces toxic damage to the intraocular tissues. Almost all cases occurred after uneventful cataract surgery |
|
|
What diseases can cause cataracts?
(there are 5 listed here) |
diabetes mellitus
maternal rubella severe myopia UV light exposure (wear your sunglasses!) meds (eg steroids) |
|
|
Client education/nursing actions after cataract surgery includes...
|
1. avoid eye strain
2. don't rub 3. don't raise intraocular pressure (straining, vomiting, sneezing, coughing) 4. EYE SHIELD at bed 5. eye drops 2-4 weeks 6. turn to good side, elevate HOB 30-45 degrees, use side rails. |
|
|
What the heck is aphakia? What do you do about it - three things.
|

Aphakia - is absence of a lens in an eye.
Can correct by 1. glasses - heavy/thick. distort distance (objects appear closer). only give you central vision. 2. contact lenses 3. lens implants (still need glasses because lens will not accommodate) |
|
|
Diagnose me!
- sudden, painless - floating spots, recurrent flashes - shadow or curtain like *** unique |
Retinal Detachment because of fluid accumulation, tumor or trauma. retina pulls away, layers separate; loses blood supply... avascular necrosis develops. can take hours or years.
|
|
|
What are some risk factors for Retinal Detachment?
|
- chronic illness such as diabetes mellitus
- cataract extraction - trauma - aging |
|
|
Nursing actions for retinal detachment?
|
- positioning (how depends on location of detachment.
- cover both eyes - prep for surgery |
|
|
Post op, Retinal Repair
|
- eye patch
- monitor for hemorrhage - prevent N/V - report sudden, sharp eye pain - NO coughing, sudden head movements, NO increase IOP by lifting, squinting, constipation - limit reading for 3-5 weeks. |

