![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
5 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Nucleic Acids |
•DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) •RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) DNA codes for sequence of amino acids in proteins RNA is used in Protein Synthesis Proteins determine all characteristics of organisms |
|
|
|
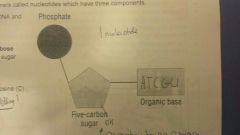
Nucleic Acid Structure |
Monomers: Nucleotides (Which have 3 Components) ●Phosphate Group ●Deoxyribose (Pentos Sugar) ●Nitrogen containing bases: ADENINE & THYMINE GUANINE & CYTOSINE |
|
|
|
Complementary Base pair rule |
Adenine has 2 HYDROGEN BONDS with Thymine Guanine has 3 HYDROGEN BONDS with cytosine |
|
|
|
RNA Structure |
●Phosphate Group ●Ribose (Pentose Sugar) ●Nitrogen containing Base: ADENINE with 2 Hydrogen bonds to URACIL GUANINE with 3 Hydrogen Bonds with Cytosine |
|
|
|
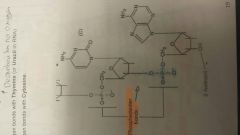
Formation Of Nucleic Acids |
Nucleotides link together to form POLYNUCLEOTIDES through condesation reaction ●Covalent bond formed between C3 OF 1 Nucleotide and the phosphate of another,Bond is called Phosphodiester Bond ●This Bonding forms the SUGAR-PHOSPHATE BACKBONE |
|

