![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are some strategies to promote health?
|
1)Teaching Patients to Stay Well
2)Motivate patients to change unhealthy behaviors. 3)Propose strategies for behavior change. 4)Show patients how to care for themselves more effectively. 5)Teaching Patients to Stay Well 6)Build on patients’ strengths. 7)Help patients find and use available resources. 8)Provide support through telephone, individual and group counseling, and continuing education. |
|
|
What are some factors that affect health?
|
1)Supports
2)Psychological state 3)Motivational level 4)Access to health care 5)Factors Affecting 6)Access to Health Care 7)Finances 8)Location 9)Age 10)Ethnicity or religion 11)Rationing of health care 12)Insurance 13)Transportation 14)Gender -Men deter from going to the doctor 15)Healthy Behaviors 16)Rest and sleep -look at cercatian rythm 17)Exercise -why won't excersize 18)Stress -what is a stress influence Safety/injury prevention |
|
|
What is the definition of nutrition?
|
o Nutrition is the state of balance between nutrient intake and physiological requirements for growth and physical activity.
|
|
|
What is malnuttrition?
|
1) Undernutrition
2) "bad nutrition" 3) Nutrition deficet |
|
|
What is overnutrition?
|
Consumption of nutrients especially calories, sodium, and fat in excess of body needs.
|
|
|
What is the primary nutrients?
|
1) Carbohydrates (50-60%)
2) Proteins (10-20%) 3) Fats (20-30%) 4) Vitamins (b-vits, Vit c ect) 5) Minerals 6) Water |
|
|
What are the effects of nutritional deficiency
|
stage 1) Primary & secondary malnutrition
stage 2) tissue reseve decrease stage 3) Biochemical lesions stage 4) Clinical lesions |
|
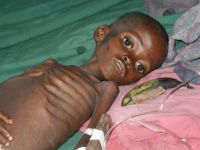
What is this Marasmus
|
Diet contains almost all carbohydratesMuscle waisting
|
|
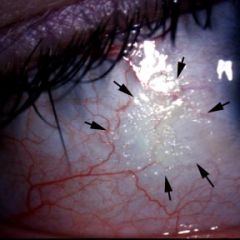
What are Bitit's spots
|
A fomy lesion of the cornea
Vitamin A diffitiency |
|
|
Who are at nutritional risk?
|
People who are severly sick are at risk
|
|
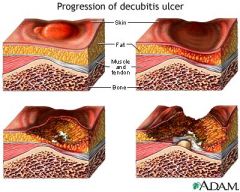
What can add to forming a decubitus ulcer?
|
Person has great vitamin needs
|
|
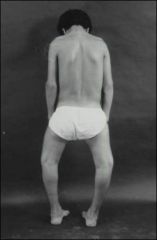
What is rickets?
|
Vitamin D difitiency
|
|
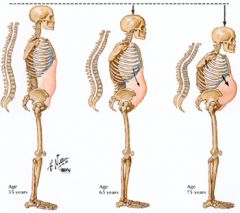
What is osteoporosis?
|
Los of bone matrix
Insufitient calcium and Vit D intake |
|
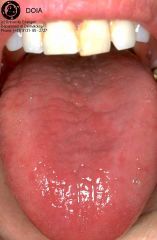
What is glossitis?
|
Disorders such as iron deficiency anemia, pernicious anemia and other B-vitamin deficiencies
|
|
|
What are so nutritional considerations for Infants?
|
1)High metabolic rate
2)Increased protein needs 3)Fat is critical to developing CNS 4)Fetal iron stores deplete around 4-6 months |
|
|
What are some nutrtional needs of Childeren?
|
1)Weight doubles in first years by age 6
2)Breakfast important 3)Calcium and Phosphorus critical to skeletal development 4)Calories 2000/day |
|
|
What are some nutritional considerations of adolecents?
|
1)Growth is erratic, Occurs in spurts
2) Sex hormones influence growth factors 3) Boys need more calories, zinc, and iron needs for sexual maturation. |
|
|
What are some nutritional needs of ?pregnant women?
|
1)Folic acid,
2) vit C, 3)Iron, 4)Calcium, 5) Fluoride 6)Zinc 7)300 more calories |
|
|
What are some nutritional needs of the older adult?
|
1)Decreased taste
2)Dec gastric acidity 3)Less vit D 4)Loss urinary sphincter muscle tone |
|
|
What is a comprehensive nutritional history?
|
1)24-hour recall: record everything one ate and drank in the past 24 hours
2)Food intake Diaries: quantitative listing of all foods and fluids consumed within a designated time period, 3–5 days 3)Direct Observation of Eating Habits |
|
|
What is the triceps skin fold?
|
1)Use individuals dominant arm
2)Also a way of measuring foat skin and adibose tissue |
|
|
What is the mid-arm circumference?
|
1)Estimate muscle mass
2)Used as a backup of trceps 3)Can also do a measurement of individual dominant arm, and calf right below the knee in cm and the difference should not be more than 1 cm |
|
|
What is the purpose of the physical assesment?
|
1)Provides an objective data base
2)Identifies actual/potential health problems 3)Identifies patients’ strengths 4)Validates history data |
|
|
What are the two types of physical assessment?
|
Fucussed aand complete
|
|
|
What are the components of a physical?
|
1)General survey
2)Measurements oVital signs oAnthropometric 3)Measurements oHead-to-toe, including all systems 4)Weighing patients oWeigh patient at the same time and the same scale oPatient should be wearing as little clothing as possible |
|
|
What are the tools one would useto assess?
|
o Eyes
o Ears o Nose o Hands |
|
|
What is the purpose of the penlight?
|
oUsed to assess eyes and hard to see places such as the mouth, throat, and nose
|
|
|
What is the use of the Thermometer?
|
Temperatures
oOral: 98.6(F) or 37 degrees Centigrade oRectal: 99.5 (F) for 37.5© oTympanic (99.5(F) 37.5© oAxillary (97.6(F), 36.5 © oForehead (94(F), 34.4 © |
|
|
What are the convertions of temp?
|
F →C : (F – 32) X 5/9 = ____C
C →F: ( C x 9/5) + 32 = _____F |
|
|
What is a pulcse?
|
The force of the heart contracting
oReflects the stroke volume oNote rate and rhythm oNewborn: 125 beats/min oAge 4: 100 beats/min oAdolescence : 80 -100 BPM |
|
|
What are the respiratory rates?
|
oNote rate, rhythm and depth
oCount for 1 minute: oFull inspiration and full expiration cycle oAbnormal/Normal oRespiratory Rates oEupnea (Normal) oTachypnea(Above) oBradypnea (slow) oApnea (No breathing) oDypsnea (Dificulty breathing) |
|
|
What is blood presure?
|
oMeasurement of pressure within the vascular system as the heart contracts (Systole) and relaxes(diastole)
oBlood pressure = cardiac output(CO) x Peripheral Resistance (PVR) |
|
|
What is prehypertensive blood presure?
|
S:120 – 139
D:80 – 89 |
|
|
What is hypertension BP?
|
S: 140-159
D:90-99 |
|
|
What is hypertension stage 2
|
S:>160
D:>100 |
|
|
How is orthostatic(or postural B/P) assessed?
|
Used to see if the person is volume depledet
1) Normal to see the BP to drop only by 10 points |
|
|
What is a doppler?
|
oUsed to detect fetal heart sounds, locate pulses such as pedal pulses that may be difficult to feel
|
|
|
What is a nasoscope?
|
oIlluminates the nostrils to check for swelling, congestion, color, and obstruction
|
|
|
What is the Opthalmascope?
|
oUsed to assess the internal structure of the eye
|
|
|
What is the transilluminator?
|
oUsed to assess for fluid in the sinuses, the fontanels of the newborn, and the male testes.
|
|
|
what is the Goniometer?
|
oUsed during a musculoskeletal examination to assess the range of motion of a joint
|
|
|
what parts of the hand is used for palpation?
|
1)Dorsal aspect
Best for temperature 2)Balls & ulnar surface of hand Best for vibrations 3)Fingertips Best for fine sensations 4)Ballottement Size, shape of free-floating objects |
|
|
What types of precussion is ther?
|
Direct (immediate)
Indirect (mediate) Fist or blunt (Ex: tenderty of the kidneys) |
|
|
What is direct or indirect used to ditect?
|
-Density (air, fluid, solid)
-Size and shape -Tenderness -Deep tendon reflexes |
|
|
What is fist or blunt precussion for?
|
Tenderness
|
|
|
What is the precussion hammer used for?
|
(deap tendon reflex
|
|
|
What is the types of Auscultation?
|
1)Direct: Without a stethescope,
2)indirect: stethoscope |
|
|
What does auscultating assess?
|
1)Heart sounds
2)Lung sounds 3)Bowel sounds 4)Vascular sounds |

