![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
daltons law says that the sum of all partial pressures gives... |
the total pressure for a mixture of gases |
|
|
3 types of muscle |
skeletal cardiac smooth |
|
|
_______________ muscle is attached to bones and used for movement
|
skeletal |
|
|
_____________ and _________ muscle have striations |
skeletal cardiac |
|
|
what do skeletal and cardiac muscle have in common? |
they have striations, and can contract |
|
|
___________ muscle is also known as involuntary muscle |
smooth |
|
|
__________ muscle is found around blood vessels and hollow organs |
smooth |
|
|
The major functional differences in the three muscle typesresult from their differing _______________ _____________ |
electrical properties |
|
|
muscles generate what 3 things |
force movement heat |
|
|
muscles are made up of thousands of _________________ |
muscle fibers |
|
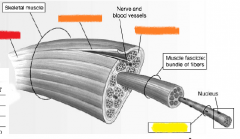
red |
skeletal muscle |
|
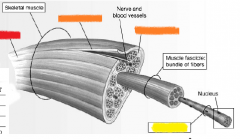
orange |
connective tissue |
|
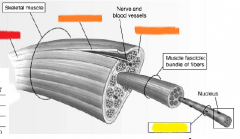
yellow |
muscle fibers |
|
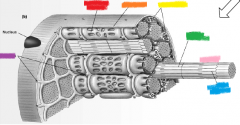
red |
sarcoplasmic reticulum |
|
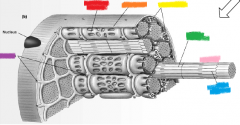
orange |
sarcolemma |
|
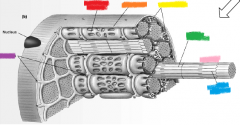
yellow |
mitochondria |
|
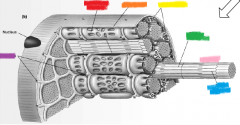
green |
thick filament |
|
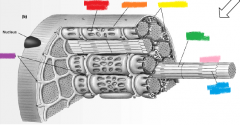
pink |
myofibril |
|
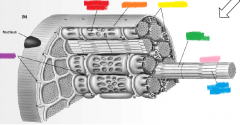
blue |
thin filament |
|
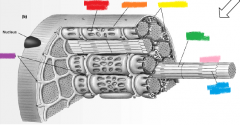
purple |
T-tubules |
|
|
The muscle membrane is called the |
sarcolemma |
|
|
sarcoplasmic reticulum is the muscle equivalent of the .. |
endoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
the thin dark band in sarcomeres is called a ____________ |
Z-line |
|
|
thick filaments are called... |
myosin |
|
|
thin filaments are called... |
actin |
|
|
the filamentous protein of actin is called |
tropomyosin |
|
|
the globular protein of actin is called |
troponin |
|
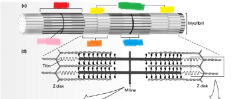
red |
A band |
|
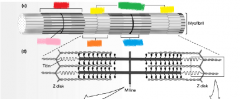
pink |
M line |
|
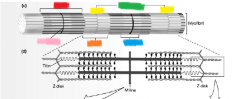
yellow |
Z disk |
|
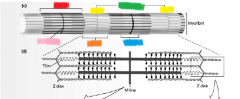
orange |
I band |
|
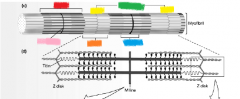
green |
sarcomere |
|
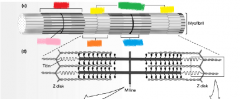
blue |
H zone |
|
|
During muscle contraction, the energy input from_______ and ___________ ________ must equal energy output or work performed and heat released |
ATP creatinine phosphate |
|
|
about how much of the energy in chemical bonds of nutrients is converted to work |
20-25% |
|
|
____-____% of the energy contained by biomolecules consumed during metabolism is released as heat |
75-80% |
|
|
the metabolism of ___________ ______________ is a significant source of body heat. |
skeletal muscle fibers |
|
|
a single __________ ________ will innervate several muscle cells |
=motor neuron |
|
|
a motor unit is the _____________+ the ____________ |
motor neuron muscle cells |
|
|
how does an individual muscle cell contract |
all or none fashion |
|
|
what affects the variations in strength of the contraction of the muscle as a whole |
activation of different numbers of motor units |
|
|
A skeletal muscle cell is innervated by a single contact pointfrom a single motor neuron – called the |
neuromuscular junction |
|
|
A spike in the motor neuron will cause the release of |
acetylcholine |
|
|
what happens after acetylcholine is released after a spike in the motor neuron? |
it diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to a receptor on the muscle |
|
|
the opening of many channels on the muscle membrane causes a _______________ |
depolarization |
|
|
A spike on the muscle surface is conducted to the interiorof the cell by the _____________ ________________ |
transverse tubules |
|
|
=Contained in the T-tubule membrane is a voltagesensitivereceptor called the |
dihydropyridine receptor |
|
|
Depolarization of T-tube causes conformational changeof DHP receptor – which causes |
opening of calcium channel of SR |
|
|
when calcium diffuses out of SR, it raises... |
cytosolic Ca+++levels |
|
|
what does calcium bind to |
troponin |
|
|
after the calcium binds to troponin, it causes ________________ to be displaced |
tropomyosin |
|
|
after tropomyosin is displaced, what is exposed |
a site on the actin molecule |
|
|
the exposure of the actin site allows for the head of the ___________ to bind to it |
myosin molecule |
|
|
what does the cross bridge do |
rotates and pulls theactin molecules towards the center,sliding past the myosin molecule |
|
|
when Z-lines are pulled towards one another, the sarcomere (lenghtens/shortens) |
shortens |
|
|
when myosin head releases the actin at the end pf the power stroke, ____________ is required |
ATP |
|
|
how does rigor mortis work |
animal stops making ATP when it dies calcium is released after SR breaks down myosin cant release actin rigid state in muscle causes rigor mortis |
|
|
what can rigor mortis be used for |
estimating time of death |
|
|
what happens during the latent period? |
Ca++ is released from SR |
|
|
muscles contain an energy storage molecule called |
phosphocreatine / creatine phosphate |
|
|
damaged muscle cells release... |
creatine kinase |
|
|
Blood test for elevated levels of CK can distinguish between cardiac &skeletal muscle damage by the ___________ present in the blood |
isozyme |
|
|
single twitches are only used by _____________ muscle |
cardiac muscle |
|
|
what causes summation in muscles |
higher calcium in the sarcoplasma |
|
|
voluntary movements are produced by controlled _______________ contraction |
tetanic |
|
|
The amount of tension a muscle canproduce is dependent on the amount themuscle... |
stretched |
|
|
______________ contraction occurs when the length of themuscle doesn’t change |
isometric |
|
|
___________ contraction occurs when movement occurs |
isotonic |
|
|
isotonic excercise is for building |
cardiovascular health |
|
|
isometric excercise is for building |
muscle strength |
|
|
how can muscle contraction be driven by anaerobic mechanisms for short periods |
using energy from creatine phosphate breakdown and anaerobic glycolysis |
|
|
type I of skeletal muscle fiber is called |
slow-oxidative |
|
|
how do type I (slow-oxidative) contract ___________ and make ATP at what rate |
slowly at the rate they use it |
|
|
type II muscle fibers are called |
fast-oxidative |
|
|
type IIa (fast-oxidative) contract ____ and make ATP _____ |
fast moderately |
|
|
which muscle fiber type can use ATP faster than they can make it |
type IIa |
|
|
type IIb muscle fibers are called |
fast-glycolic |
|
|
which muscle fiber type contract very rapidly, using ATP much faster than they can produce it |
type IIb |
|
|
what is the end product of anerobic glycolysis that produces the burn of sustained muscle use |
lactic acid |
|
|
_______ muscle cells are smaller than skeletal muscle cells& are spindle shaped |
smooth |
|
|
smooth muscle has a poorly developed |
sarcoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
The contraction rate of SM is much slower because of the |
slower action of its myosin ATPase |
|
|
adjacent fibers are connected by electrical synapses is the arrangement of _____-unit |
single |
|
|
each cell receives own stimulatory input as for skeletal muscle is the arrangement of ____-unit |
multi |
|
|
in smooth muscle, Calcium binds to .. |
calmodulin |
|
|
what does calmodulin activate |
enzyme myosin light chain kinase |
|
|
____________-muscle can maintain tension over very longperiods of time |
smooth |
|
|
smooth muscle that never relax are called |
tonus |
|
|
for smooth muscle, tension is related to |
membrane potential |

