![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Atmosphere |
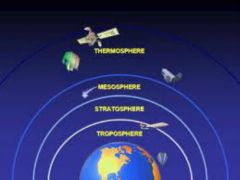
The gases that surround Earth. It has four layers which are the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and the thermosphere. |
|
|
Troposphere |
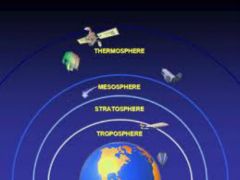
The troposphere is the layer of the atmosphere in which Earth's weather occurs. |
|
|
Stratosphere |
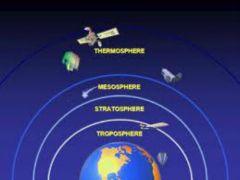
The stratosphere is the second layer of the atmosphere and contains the ozone layer. |
|
|
Mesosphere |
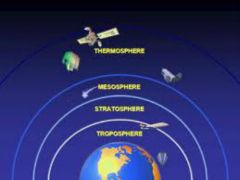
The mesosphere is the layer of the atmosphere that protects Earth's surface from being hit by most meteorites. |
|
|
Thermosphere
|
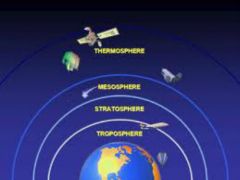
The outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere is the thermosphere. |
|
|
Tropopause |
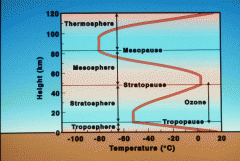
The boundary between the troposphere and the stratosphere. |
|
|
Stratopause
|
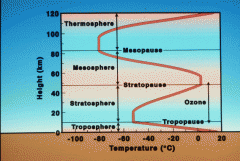
The boundary between the stratosphere and the mesosphere. |
|
|
Mesopause
|
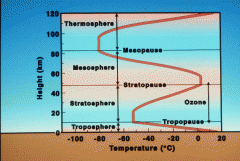
The boundary between the mesosphere and the thermosphere.
|
|
|
Altitude
|
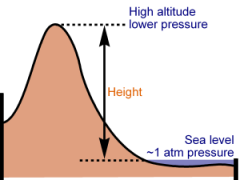
The elevation or distance above sea level. |
|
|
Air Pressure |
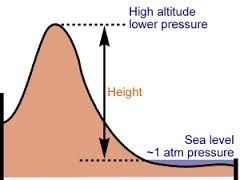
The result of the weight of a column of air pushing down on an area. |

