![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
If iron is low, does it mean the patient has iron deficiency anemia? |
1. No |
|
|
What are the causes of normocytic anemia? |
1. Primary bone marrow dysfunction 2. Anemia secondary to underlying disease 3. Increased RBC loss or destruction |
|
|
What are the anemias due to RBC loss/destruction? |
1. Sickle cell disease 2. Hypersplenism 3. Spherocytes 4. Schistocytes |
|
|
What are the primary causes of decreased RBC destruction in normocytic anemia? |
1. Bone marrow hypoplasia or aplasia 2. Myelpathies 3. Myeloproliferative diseases 4. Pure RBC aplasia |
|
|
What are the 2o causes of decreased RBC production in normocytic anemia? |
1. Chronic kidney failure 2. Liver disease 3. Endocrine deficiency states 4. Anemia of chronic disease |
|
|
What are the MCC of microcytic anemias? |
1. Chronic blood loss-- GI or GU 2. Thalassemias 3. Lead poisoning 4. Fe-deficiency |
|
|
Low ferritin means... |
1. Most like Fe-deficiency |
|
|
What is the first value you should check in microcytic anemia? |
1. Ferritin |
|
|
What is the board typical ethnic group associated with thalassemia? |
1. Greek/mediterranean |
|
|
What are the major iron studies to do in an anemia workup? |
1. Serum iron 2. % saturation 3. TIBC 4. Ferritin level |
|
|
What will the lab values be in Fe-deficiency anemia? |
1. Low % sat 2. High TIBC 3. Low ferritin 4. Low Fe |
|
|
What will the lab values be in anemia of chronic disease? |
1. Low Fe 2. Low % sat 3. Normal or low TIBC 4. High ferritin |
|
|
In what disorders is ferritin increased? |
1. Iron overload 2. Acute inflammatory states 3. Hemochromatosis 4. Chronic hepatitis |
|
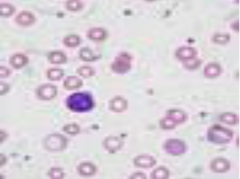
|
1. Microcytic--- Fe-deficiency |
|
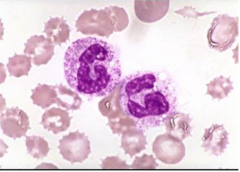
|
1. Crenation |
|
|
What is creation usually indicative of? |
1. Chronic kidney disease |
|
|
What can sickle cell do to the spleen? |
1. Autosplenecotmy--- becomes nonfunctional 2. Increases rate of platelet dysfunction |
|
|
What type of infections is an autosplenic patient susceptible to? |
1. Streptococcus 2. Haemophilus 3. Neisseria |
|
|
What does an increased reticulocyte count indicate? |
1. Adequate bone marrow function 2. RBC destruction |
|
|
In what types of anemia will ferritin be high? |
1. Normocytic 2. Hemolytic 3. Chronic disease |
|
|
What leads to anemia in anemia of chronic kidney disease? |
1. Decreased EPO |

