![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anatomical planes |
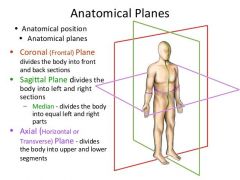
coronal - dorsal/ventral or anterior/posterior Sagittal - left/right axial or transverse - superior/inferior |
|
|
On a chest X ray what do the different colours show? |
Bone = white Air = black Everything else = various shades of grey |
|
|
Is an X-ray a negative or positive image? |
Negative image NB dense objects block beam therefore reduce exposure and look white or radiopaque eg bone less dense objects allow the beam through therefore look dark or radiolucent eg air |
|
|
What are the advantages of plain x-ray? |
quick easy cheap good for bones involves radiation |
|
|
Pros and cons of ultrasounds? |
Pros = cheap, good to look at organs, no radiation, multi-modal-duplex- pictures and flow operator-dependent difficult to evaluate still images |
|
|
Pros and cons of computed tomography? |
Pros Good all-rounder Especially for bones/organs Enhanced by contrast dyes Rapid acquisition Compatible w/ metal implants Cons - Involves radiation |
|
|
Pros and cons of magnetic resonance imaging? |
Pros Excellent tissue definition Especially for soft tissue/ligaments No radiation Can use smart contrast agents Cons Much slower acquisition Incompatible w/ metal implants |
|
|
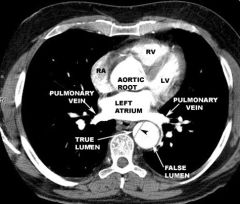
Normal aorta on CT |
|
|
|
Features of abdominal aortic aneurysm |
Dilatation > 3 cm - intervene when dilatation > 5.5 cm Usually infra-renal Asymptomatic when intact Often incidental diagnosis Rupture = 80-90% fatal |
|
|
Risk factors for abdominal aortic aneurysm |
4x more common in males But rupture 4x common in females Highest prevalence in >75 years Rupture risk at least doubled in current smokers Hypertension Hypercholesterolaemia Family history of AAA Diabetes Statin use Large baseline diameter |
|
|
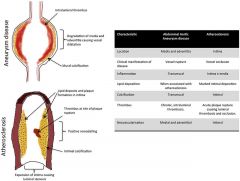
Pathobiological features of AAA vs atherosclerosis |
|
|
|
Differential diagnoses for sudden onset severe abdominal pain |
Perforation – peptic ulcer, large bowel – cancer,diverticular, small bowel – meckel’s diverticula Ischaemia – mesenteric/intestinal, solid organ Infection/Inflammation – pancreatitis,appendicitis, cholecystitis, cholangitis, diverticulitis Colic – biliary, renal colic, intestinalobstructionOther – Atypical MI/ LRTI, referred pain, gynae,DKA |
|
|
What is a FAST Scan |
Focussed Assessement with ultraSonography for Trauma It demonstrates free intra-abdominal fluid - likely ruptured AAA |
|
|
What are the two options if a FAST scan demonstrates free intra-abdominal fluid? |
If unstable - proceed with no further imaging If stable - CT angiogram |
|
|
The use of a CT angiogram? |
use of intravenous contrast to demonstrate vessel lumen on CT Timed in appropriate phase to capture contrast in arterial system Excellent for demonstrating significant haemorhage (slow bleeding may not be captured) |
|
|
Treatment of ruptured AAA |
Open surgery EVAR - endovascular aneurysm repair |
|
|
Challenges in AAA management |
Often asymptomatic - many patients still present w/ rupture Unpredicatable disease - staccato growth pattern, may rupture at small diameters High risk patients = typical elderly, mulltiple co-morbidities, difficult to estimate risk:benefit of surgery |
|
|
Name two types of molecular imaging and two types of biomechanical imaging that can help overcome the challanges in AAA management |
Molecular imaging - MRI, PET-CT Biomechanical imaging - stress maps, 3D contouring |
|
|
What does molecular imaging require? |
Biological target Target specific probe Imaging modaility with adequate spatial resolution Safe and available agent for imaging |
|
|
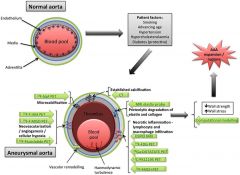
Potential molecular imaging targets in AAA |
|
|
|
Name two specialised imaging modalities? |
Positron emission tomography (PET-CT) Wall stress maps |
|
|
What is positron emission tomography ? |
Produces functional/biological information Involves radiation and radioactive tracer Slow acquisition time |
|
|
What are wall stress maps? |
Can produce gradation of biomechanical wall stress require specialised equipment/expertise |

