![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
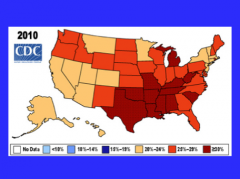
What is nonalcoholic FLD associated with the epidemic of in the US?
|

Obesity |
|
|
What two conditions are associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease? |

|
|
|
What is the clinical definition of obesity? How do you calculate BMI? |

|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|
What percent of normal individuals have fatty liver? What percent of obese?
What percent of normal have NASH? What percent of morbidly obese have NASH?
|

BMI > 35 = morbidly obese only if there is another associated disease BMI > 40 = morbidly obese if no other associated disease |
|

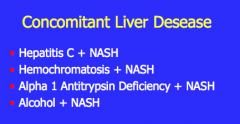
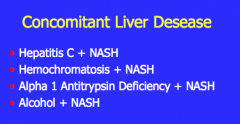
Guess what these are all associated with... |
NAFLD |
|
|
Which race has highest rates of NAFLD? Race with lowest?
Which sex?
|

|
|
|
What is the leading cause of pediatric liver disease?
Median age?
|

|
|
|
What are some nutritional abnormalities and metabolic disease that can cause NAFLD? |

|
|
|
What are some drugs that can cause NAFLD? |

Don't have to memorize these medications! |
|
|
Two surgeries that can cause NAFLD? |

|
|
|
What is an increasing cause of hepatocellular carcinoma? |

|
|
|
What is the pathogenesis of NAFLD? Use trigylcerides, chylomicrons, lymphatics, free fatty acids, mitochondria
What is a result of disturbed balance (more lipogenesis and increased FFA)? |

|
|
|
Insulin resistance: Insulin promotes the uptake of _____ |
Insulin resistance: Insulin promotes the uptake of glucose |
|
|
How does obesity affect the synthesis of FFA? How does it affect the oxidation of FFA?
How does insulin effect adipose tissue lipolysis? This leads to increased or decreased FFA? |

|
|
|
What does an increase in FFA lead to in the liver? Increased or decreased oxidative stress? |

|
|
|
What is the two hit hypothesis of NAFLD? |

|
|
|
Draw the pathway of insulin resistance: |

|
|
|
|
|
|
What are the clinical signs or symptoms of NAFLD? What is one nonspecific symptom? |

|
|
|
What are the four signs on physical exam for NALD? |

|
|
|
What percent of patients with NASH have elevated liver enzymes?
Is AST 2x ALT like in alcoholic fatty liver disease? What is the alkaline phosphatase level? |

|
|
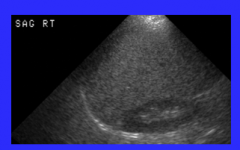
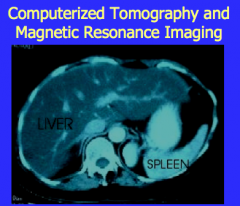
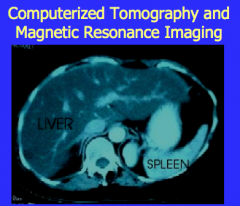
What is shown on ultrasound? |
US: homogeneously fatty infiltrated liver, increased echogenicity throughout |
|
|
|
|
|
Does a fatty appearance on ultrasound or CT make the diagnosis?
What is the only way to DEFINITELY diagnose and stage the disease? |
Nope
Biopsy (controversial) |
|
|
What is macrovesicular fat? |
Steatosis |
|
|
Inflammation, hepatocyte degeneration, ballooning, and Mallory bodies on histology. What is it? |
Steatohepatitis |
|
|
Pericellular then bridging on histology. Diagnosis? |
Fibrosis
|
|
|
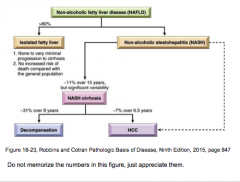
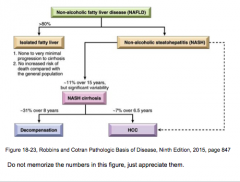
NAFLD: What percent of patients in 10 years will develop cirrhosis? |
20% |
|
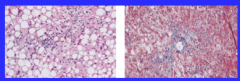
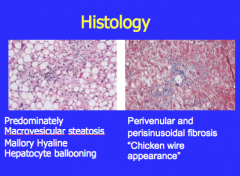
Which shows perivunular and perisinusoidal fibrosis "chicken wire appearance"?
Which shows macro vesicular steatosis, Mallory hyaline, and hepatocyte ballooning?
|
|
|
|
What is the number one lifestyle change for NAFLD?
|

|
|

|

|
|
|
What is felt to be a major cause of cryptogenic cirrhosis?
What are two increasing causes of cirrhosis and HCC? |

|
|

|

|
|
|
What are the five components metabolic disease (which is strongly associated with NAFLD)? Diabetes mellitus Hypertension Dyslipidemia Central obesity Microalbuminuria |
Diabetes mellitus Hypertension Dyslipidemia Central obesity Microalbuminuria |
|
|
What are the two major forms of NAFLD?
What is the subset of NAFLD with over clinical features of liver injury, such as elevated serum transminases, and histologic features of hepatocyte injury?
What disease contributes to the progression of other liver disease such as HCV and HBV?
What increases the risk for hepatocellular carcinoma in the absence of significant scarring unlike chronic viral hepatitis and alcoholic liver disease |
Steatotis Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
NASH
NAFLD
NAFLD |
|
|
Hepatic steatosis, like obesity in general, arises from an overabundance of _____, diminished exercise, and genetic/epigenetic mechanisms. Individuals with NAFLD eat more fast food and exercise less. _____, a nearly ubiquitous, inexpensive sweetener in manufactured foods, also appears to promote insulin resistance. |
Hepatic steatosis, like obesity in general, arises from an overabundance of calorie rich food, diminished exercise, and genetic/epigenetic mechanisms. Individuals with NAFLD eat more fast food and exercise less. High fructose corn syrup, a nearly ubiquitous, inexpensive sweetener in manufactured foods, also appears to promote insulin resistance. |
|
|
In individuals with established insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome, the visceral adipose tissue not only _____, but also becomes dysfunctional, with reduced production of the _____ hormone, adiponectin, and increased production of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and _____. These changes in turn promote hepatocyte apoptosis. Fat laden cells are highly sensitive to lipid _____ products generated by oxidative stress which can damage mitochondrial and plasma membranes, causing apoptosis. Diminished autophagy also contributes to mitochondrial injury and formation of _____ bodies. |
In individuals with established insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome, the visceral adipose tissue not only increases, but also becomes dysfunctional, with reduced production of the lipid hormone, adiponectin, and increased production of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6. These changes in turn promote hepatocyte apoptosis. Fat laden cells are highly sensitive to lipid peroxidation products generated by oxidative stress which can damage mitochondrial and plasma membranes, causing apoptosis. Diminished autophagy also contributes to mitochondrial injury and formation of Mallory-Denk bodies. |
|
|
Kupffer cell production of ___ and ____ activate stellate cells directly leading to deposition of scar tissue. Stellate cell activation also occurs through the _____ signaling pathway in part through natural killer T-cell activation. In fact, the level of _____ pathway activity correlates with stage of fibrosis in NAFLD. |
Kupffer cell production of TNF-α and TGF-β activate stellate cells directly leading to deposition of scar tissue. Stellate cell activation also occurs through the hedgehog signaling pathway in part through natural killer T-cell activation. In fact, the level of hedgehog pathway activity correlates with stage of fibrosis in NAFLD. |
|
|
True or false:
NASH almost completely overlaps in its histologic features with alcoholic hepatitis. |
TRUE |
|
|
At the most clinically benign end of the spectrum, there is no appreciable hepatic inflammation, hepatocyte death, or scarring, despite persistent elevation of serum liver enzymes. In NASH, compared with alcoholic hepatitis, _____ cells may be more prominent than neutrophils and _____ bodies are often less prominent.
Steatofibrosis in NAFLD shows precisely the same features and progression as it does in alcoholic liver disease, although _____ may be more prominent. Cirrhosis may develop, is often subclinical for years, and, when established, the steatosis or steatohepatitis may be ___ or ___. |
At the most clinically benign end of the spectrum, there is no appreciable hepatic inflammation, hepatocyte death, or scarring, despite persistent elevation of serum liver enzymes. In NASH, compared with alcoholic hepatitis, mononuclear cells may be more prominent than neutrophis and Mallory-Denk bodies are often less prominent.
Steatofibrosis in NAFLD shows precisely the same features and progression as it does in alcoholic liver disease, although portal fibrosis may be more prominent.
Cirrhosis may develop, is often subclinical for years, and, when established, the steatosis or steatohepatitis may be reduced or absent. |
|
|
What is 90% of previously described "cryptogenic cirrhosis" now thought to represent?
How does pediatric NALD differ from that in adults? (steatosis, portal vs. central, and mononuclear vs. parenchymal)? |

|
|
|
Is NAFLD a diagnosis of exclusion? |
Yes! |
|
|
Individuals with simple steatosis are generally _____ (symptomatic or asymptomatic). Imaging studies may reveal ___ accumulation in the liver. _____ is the most reliable diagnostic tool for NAFLD and NASH, and for assessment of scarring. NAFLD is a diagnosis of exclusion! Viral, autoimmune and other metabolic diseases of the liver must be excluded before the diagnosis can be made. Serum AST and ALT are _____ in about 90% of patients with NASH. Despite the enzyme elevations, patients may be _____. Others have general symptoms such as fatigue or _____-sided abdominal discomfort caused by hepatomegaly. Because of the association between NASH and the metabolic syndrome, _____ disease is a frequent cause of death in patients with NASH. |
Individuals with simple steatosis are generally asymptomatic. Imaging studies may reveal fat accumulation in the liver. Liver biopsy is the most reliable diagnostic tool for NAFLD and NASH, and for assessment of scarring. NAFLD is a diagnosis of exclusion! Viral, autoimmune and other metabolic diseases of the liver must be excluded before the diagnosis can be made. Serum AST and ALT are elevated in about 90% of patients with NASH. Despite the enzyme elevations, patients may be asymptomatic. Others have general symptoms such as fatigue or right-sided abdominal discomfort caused by hepatomegaly. Because of the association between NASH and the metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease is a frequent cause of death in patients with NASH |
|
|
|

