![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
1. In which radopharmaceutical is Tc99m left in the valence state of +7?
a. sulfur colloid b. macroaggregated albumin c. MAG3 d. sestamibi |
a
|
|
|
|
2. A technologist receives a request for a patient to receive Sm 153 for palliation of pain from bone metastases. The patient has a leukocyte count of 3500 and 40,000 platelets. What should happen next?
a. the order should be changed to Sr89 b. the therapy should be delayed until the platelet count is at least 60,000 c. the therapy should be delayed until the leukocyte count is below 2400 d. the Sm153 dose should be ordered |
b
|
|
|
|
3. A sulfur colloid kit requires the addition of 1-3 ml containing no more than 500 mCi of Tc99m pertechnetate. In addition, 1.5 ml of Solution A must be added before boiling, and 1.5 ml of solution B must be added after cooling. If the kit is correctly prepared, what is the maximum concentration of Tc99m is could contain?
a. 83 mCi/ml b. 125 mCi/ml c. 167 mCi/ml d. 500 mCi/ml |
b
|
|
|
|
4. A Hine-Duley phantom is useful for testing the spatial resolution and spatial linearity with only one image.
a. true b. false |
b
|
|
|
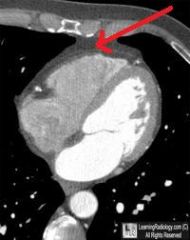
The wall of the heart indicated by the arrow in the image is the:
a. septal b. lateral c. inferior d. anterior |
d
|
|
|
|
6. The advantages of a lung ventilation scan performed with Xe133 is:
a. the ability to match perfusion and ventilation positioning b. the ability to detect delayed washout c. the ability to perform the exam at the patient's bedside d. the ability to perform perfusion before ventilation without increasing the dose given for the ventilation study |
b
|
|
|
|
7. A diphosphonate kit contains 180 mCi of Tc99m in 30 ml when it is prepared at 8am. Immediately, a 20 mCi dose is withdrawn for a bone scan. If a patient arrives late at 9:30, and half the volume is accidently discharged, how much from the kit must now be added to the syringe to correct the dose to 20 mCi? (no other doses have been withdrawn meanwhile, and the decay factor for 1.5 hours is 0.841.)
a. 1.5 ml b. 2.0 ml c. 2.3 ml d. 2.5 ml e. 2.7 ml |
c
|
|
|
|
8. A whole body bone scan film shows a good posterior image, but the anterior view appears diffuse and with greater soft tissue activity. What is the probable cause?
a. wrong collimator used for the anterior b. increased patient to detector distance on the anterior relative to the posterior c. low tagging efficiency of the radiopharmaceutical d. patient was not sufficiently hydrated e. none of the above |
b
|
|
|
|
9. Which of the following will not reduce the probablity of contamination from perspiration and saliva of a therapy patient?
a. disposing eating utensils b. plastic covering over the mattress c. covering the telephone receiver with plastic d. collecting the patient's waste and storing until decayed to background |
d
|
|
|
|
10. Why would an image of the brain be obtained during a lung perfusion scan using Tc99m MAA?
a. to rule out brain metastases b. to detect low tagging efficiency c. to detect a right to left cardiac shunt d. to see if pulmonary emboli have traveled into the cerebral vessels |
c
|
|
|
|
11. Bone marrow imaging is performed using:
a. Tc99m MDP b. Tc99m HDP c. Tc99m Sulfur Colloid d. Gd 153 e. both a and b |
c
|
|
|
|
12. All of the following have an effect on the concentration of eluate obtained from a wet generator except:
a. time since last elution b. volume of saline added to charging port c. size of collection vial d. amount of Mo99 activity present on the alumina column |
b
|
|
|
|
13. A Mo99m/Tc99m generator has an elution efficiency of 89%. If 1.1 Ci of Tc99m are present on the column, what is the estimated activity of eluate that will be obtained?
a. 97.9 Ci b. 979 mCi c. 979 uCi d. 97.9 mCi |
b
|
|
|
|
14. Tc99m DTPA has been used for all of the following except:
a. aerosol lung scanning b. renal flow study c. brain flow study d. shunt patency e. spleen scanning |
e
|
|
|
|
15. Which of the following is not used as an anticoagulant?
a. heparin b. EDTA c. ascorbic acid d. ACD solution |
b
|
|
|
|
16. If concentration of a solution desired is 2 uCi/ml and the 325 uCi of solute is contained in a volume of 2.5 ml, how much water should be added to create the solution?
a. 160.0 ml b. 162.5 ml c. 650.0 ml d. 125.0 ml |
b
|
|
|
|
17. The inferior wall of the heart is supplied by the:
a. left anterior descending branch b. left circumflex artery c. right coronary artery d. left coronary artery |
c
|
|
|
|
18. The uptake of F-18 FDG by tumors is based on:
a. a blood brain barrier breakdown b. the higher glycolytic rate of tumors relative to normal tissue c. active transport d. antibody-antigen reations e. receptor binding |
b
|
|
|
|
19. In111 delivers a lower radiation dose to the patient than Ga67 because it has only one gamma emission whereas Ga67 has four.
a. true b. false |
b
|
|
|
|
20. If dipyridamole is supplied in a 50 ml vial containing 250 mg, and a patient weighs 205 pounds, how much volume will need to be withdrawn from the vial to prepare his dose of 0.56 mg/kg?
a. 5.6 b. 10.4 c. 15.9 d. 22.6 |
b
|
|
|
|
21. If 450 mCi of Tc99m eluted from a generator contains 200 uCi of Mo99, is the eluate within the standards of radioactive purity set forth by the NRC?
a. yes b. no c. the NRC does not regulate radionuclidic activity d. this is an example of radiochemical impurity rather than radionuclidic impurity. |
b
|
|
|
|
22. If SPECT images taken with 360 deg rotation, 32 stops for 15/sec/stop and a matrix of 64 x 64 have significant star artifact, which imaging parameter would be best to change to correct the image?
a. change the rotation to 180 deg b. change the number of stops to 64 c. change the time/stop to 20 sec d. change the matrix to 128 x 128 e. none of the above |
b
|
|
|
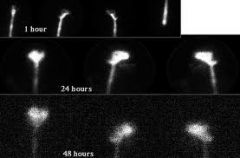
23. The above image was taken following the intrathecal injection of radiopharmaceutical. These images are from a:
a. Leveen shunt study b. cisternogram c. esophageal transit study d. CSFshunt patency study e. radionuclide venogram |
b
|
|
|
|
24) Which radiopharmaceutical is best to use for renal scanning if a determination of effective renal plasma flow is also desired?
a. 99mTc MAG3 b. 99mTC GH c. 99mTc DMSA d. 99mTc DTPA |
a
|
|
|
|
25) Calculate the 6 hour thyroid uptake from the data given below. The six hour decay factor for 1231 is 0.730.
Pre-administration I-123 capsule 1,157,259 Neck 278,941 Thigh 2836 a. 17.4 % b. 23.9 % c. 32.7 % d. 33.4 % e. none of the above |
c
|
|
|
|
26) Which of the following cannot be studied with a MUGA study?
a. left ventricular ejection fraction b. regional wall perfusion c. stroke volume d. regional wall motion |
b
|
|
|
|
27) Free 99mTc pertechnetate in a bone scan kit will result in activity in the:
a. breasts b. thyroid c. gastric mucosa d. lungs e. b and c |
e
|
|
|
|
28) A superscan is the result of:
a. renal insufficiency b. diffuse skeletal metastases c. chemotherapy response d. Paget's disease e. none of the above |
b
|
|
|
|
29) Which of the following is not true regarding 99mTc HMPAO?
a. it crosses the intact blood brain barrier b. distribution of 99mTc HMPAO follows cerebral flow c. it is also known as exametazime d. it does not significantly redistribute in the brain e. none of the above . |
e
|
|
|
|
30) Which of the following may cause a false positive hepatobiliary scan?
a. if the patient has recently eaten b. if the patient has been fasting for an extended period (> 24 hours) c. use of sincalide d. a and b e. b and c |
d
|
|
|
|
31) Phagocytosis of 99mTc albumin colloid is performed by the:
a. liver parenchymal cells b. Kupffer cells c. hepatocytes d. red blood cells . |
b
|
|
|
|
32) Which will perfuse last following an intravenous injection of 99mTc DTPA?
a. lungs b. left ventricle c. kidney d. liver |
d
|
|
|
|
33) A patient undergoes renography followed by captopril renography and the GFR from the second exam is lower than the first. What does this mean?
a. the patient is rejecting a transplanted kidney b. the patient has renovascular hypertension c. the patient has an obstruction in the collecting system d. the patient has high blood pressure e. none of the above |
b
|
|
|
|
34) The left and right lobes of the thyroid are connected by the:
a. pyramidal lobe b. major calyx c. isthmus d. loop of Henle |
c
|
|
|
|
35) The exposure rate at the surface of a package to be shipped is 50 mrem/hr. What label is required?
a. DOT Radioactive White I b. DOT Radioactive Yellow II c. DOT Radioactive Yellow III d. no radioactive label is required . |
b
|
|
|
|
36) If the exposure rate at 5 meters from a source is 75 mR/hr, what will it be at 2 meters?
a. 12 mR/hr b. 36 mR/hr c. 245 mR/hr d. 469 mR/hr |
d
|
|
|
|
37) If a patient has persistent activity in the renal pelvis during renography, furosemide administration may:
a. assist in diagnosis of renovascular hypertension b. help rule out mechanical obstruction c. cause a transplant to be rejected d. decrease the radiation burden on the bladder e. none of the above |
b
|
|
|
|
38) The NRC requires the use of tongs for moving vials between shields and the dose calibrator.
a. true b. false |
b
|
|
|
|
39) Which of the following may be used for thyroid uptake and scanning?
a. 99mTc pertechnetate b. 1-131 sodium iodide c. 201TI chloride d. 99mTc sestamibi e. all of the above . |
b
|
|
|
|
40) The lowest point on a time activity curve generated over the cardiac cycle of a patient following a gated blood pool study represents:
a. end systole b. end diastole c. injection point d. stroke volume e. the QRS complex |
a
|
|
|
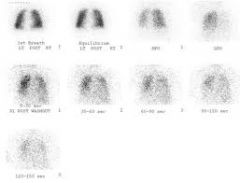
41) The images in above figure were obtained during a ventilation scan taken with the use of-
a. 99mTc MAA b. 133 Xe gas c. 81m Kr gas d. 99mTc DTPA aerosol |
b
|
|
|
|
42) Pinhole collimation is not commonly used during:
a. scrotal scans b. bone scans for AVN c. thyroid imaging d. renal imaging |
d
|
|
|
|
43) A sentinel node is:
a. the first draining lymph node from a primary cancer b. the node containing cancer which is most distant from the primary tumor site c. the common iliac node d. always ipsilateral to the tumor |
a
|
|
|
|
44) Which method of data collection allows the greatest flexibility for manipulation of data after collection?
a. frame mode b. list mode c. there is no difference between the two methods concerning data manipulation |
b
|
|
|
|
45) The second phase in a four phase bone scan takes place:
a. a few minutes after injection b. 2-4 hours after injection c. 6 hours after injection d. 24 hours after injection |
a
|
|
|
|
46) The NRC recommends but does not require the use of syringe shields during preparation and administration of radiopharmaceuticals.
a. true b. false |
b
|
|
|
|
47) Which of the following is true regarding albumin colloid?
a. it is less expensive than sulfur colloid b. the particle size is smaller than that of sulfur colloid c. a lower dose is required for liver imaging d. it must be boiled during preparation |
b
|
|
|
|
48) For a patient with intermittent gastrointestinal bleeding, the best radiopharmaceutical to locate the bleed is:
a. 99mTc sulfur colloid b. 99mTc denatured RBCs c. 99mTc WBCs d. 99mTc DTPA e. none of the above |
e
|
|
|
|
49) Which is not a beta emitter?
a. 32 P b. 131-I c. 81m Kr d. 89 Sr |
c
|
|
|
|
50) Which are used for the imaging of neoplasms?
a. 201T1 chloride b. I-131 MIBG c. 99mTc sestamibi d. all of the above e. a and b only |
d
|
|
|
|
51) Constancy of a dose calibrator must be performed:
a. daily b. weekly c. monthly d. yearly e. at installation and following repair |
a
|
|
|
|
52) The valence state of 99mTc is usually reduced when preparing kits through the use of:
a. nitrate b. oxygen c. stannous ions d. alumina |
c
|
|
|
|
53) First pass cardiac studies require:
a. a compact bolus of radiopharmaceutical b. gating c. multiple crystal imaging system d. extended imaging time e. all of the above |
a
|
|
|
|
54) Most of the thyroid hormone in the circulation is:
a. T3 b. T4 c. TSH d. TRF |
b
|
|
|
|
55) Which of the following guidelines apply to positioning a patient for a flow study of native kidneys?
a. center the detector over the iliac fossa of interest b. iliac crests should be centered over the detector face c. sternal notch should beat the top of the field of view d. xiphoid process should be over the upper part of the detector face |
d
|
|
|
|
56) 133Xe gas may be used:
a. in rooms that are held at a positive pressure to surrounding areas b. in patient rooms if they are private c. in imaging rooms that have a ceiling vent d. in rooms that are held at a negative pressure to surrounding areas e. in all of the above as long as oxygen is not in use |
d
|
|
|
|
57) Given the following data, calculate the left ventricle ejection fraction.
Net counts, end systole 20,582 Net counts, end diastole 44,653 a. 18.5% b. 46.1 % c. 53.9 % d. 68.5 % |
c
|
|
|
|
58) Calculation of gallbladder ejection fraction requires:
a. cholecystokinin b. cimetidine c. pentagastrin d. 99mTc mebrofenin e. a and d |
a
|
|
|
|
59) Which study does not require any fasting before the examination?
a. esophageal transit b. gastroesophageal reflux c. Schilling test d. hepatobiliary scan e. Meckel's diverticulum . |
e
|
|
|
|
60) The usual adult dose for hepatobiliary imaging with 99mTc iminodiacetic acid is:
a. 2-4mCi b. 5-8mCi c. 10-12 mCi d. 15-20 mCi . |
b
|
|
|
|
61) What is the effective half life of a radiopharmaceutical with a physical half life of 6 hours and a biologic half life of 10 hours?
a. 2.6 hours b. 3.8 hours c. 4.3 hours d. 5.2 hours |
b
|
|
|
|
62) If a technologist absorbs a dose rate of 2.5 mrem/hr while working 3 feet from a therapy patient, what distance will need to be maintained in order to absorb only 2 mrem/hr?
a. 2.5 feet b. 3.4 feet c. 4.0 feet d. 4.2 feet |
b
|
|
|
|
63) At least thirty million counts should be obtained when assessing the uniformity of a planar imaging system.
a. true b. false |
b
|
|
|
|
64) Records of dose calibrator linearity must be kept for:
a. one year b. three years c. five years d. ten years e. until license expiration |
b
|
|
|
|
65) Transport index refers to:
a. the type of packaging required for a shipment of radioactive material b. the type of labeling required for a shipment of radioactive material c. the exposure rate measured at one meter from the package d. the NRC isotope group label . |
c
|
|
|
|
66) If a vial of 131-I contains 100 mCi on December 1, approximately how much activity will it contain on December 17 provided none is withdrawn?
a. 6.25 mCi b. 12.5 mCi c. 25 mCi d. 50 mCi |
c
|
|
|
|
67) Which of the following is an example of radiochemical impurity? a. presence of 99Mo in 99mTc eluate
b. presence of free pertechnetate in 99mTc HDP c. presence of Al" in 99mTc d. presence of pyrogens in reconstituted kits |
b
|
|
|
|
68) What does dyspnea mean?
a. increased urine production b. difficulty walking c. temporary cessation of breathing d. labored breathing e. paradoxical wall motion |
d
|
|
|
|
69) Which of the following is not used to image the heart?
a. 201T1 chloride b. 99mTc sestamibi c. 99mTc diphosphonate d. 99mTc RBCs |
c
|
|
|
|
70) Arrhythmia filtering rejects cardiac cycles:
a. that have an R-R interval outside the preset limits b. that have too short an S-T segment c. that have too high a QRS complex d. all of the above e. a and b only |
a
|
|
|
|
71) If a SPECT is being performed involving 64 projections, and 52,000 counts are collected during each 20 second stop, what are the total counts for the study and the total acquisition time?
a. 1 million counts, 20 minutes b. 1.1 million counts, 21 minutes c. 3.3 million counts, 21 minutes d. 3.3 million counts, 25 minutes |
c
|
|
|
|
72) A SPECT study is required to consist of 2 million counts. If there are 64 stops, and the count rate is 65,000 cpm, how many seconds should each stop last?
a. 13 seconds b. 21 seconds c. 29 seconds d. 31 seconds e. 48 seconds |
c
|
|
|
|
73) If a MDP kit contains 230 mCi of 99mTc in 9 ml at 7:00 a. m., how much will have to be withdrawn for a 20 mCi dose at 1:00 p.m.?
a. 0.6 ml b. 0.8 ml c. 1.6 ml d. 1.9 ml e. 2.1 ml |
c
|
|
|
|
74) In 20 ml of 99mTc eluate, there are 30 ug of Al 3+ present. Can this eluate be used for reconstituting kits for patient injection?
a. yes b. no |
a
|
|
|
|
75) If 800 mCi of 99mTc is eluted from a 99Mo/99mTc generator, what is the maximum amount of 99Mo allowed in the eluate by the NRC?
a. 8 µCi b. 12 µCi c. 80 µCi d. 120 µCi e. 200 µCi |
d
|
|
|
|
76) If a technologist stands 2 feet from a radioactive source, and receives 1 mrem/hr from it, what will he or she absorb by stepping one foot closer to the source?
a. 0.25 mrem/hr b. 1.5 mrem/hr c. 2.0 mrem/hr d. 4.0 mrem/hr |
d
|
|
|
|
77) A locked storage closet next to the radiopharmacy containing phantoms and sealed sources has a measured exposure rate of 3 mR/hr. It should be posted with a sign reading:
a. Caution: Radioactive Materials b. Caution: Radioactive Area c. Caution: High Radiation Area d. Grave Danger: Very High Radiation Area e. no sign is necessary |
a
|
|
|
|
78) A technologist is preparing an HDP kit at 8:00 a. m. If the schedule of doses required is as follows, and the eluate available has 7 mCi/ml, what is the minimum volume of 99m Tc pertechnetate that should be added?
9:00 Bone Scan 20 mCi 10:00 Bone Scan 20 mCi 11:00 Bone Scan 20 mCi a. 8.6 ml b. 10.8 ml c. 60.0 ml d. 75.9 ml |
b
|
|
|
|
79) When injecting 99mTc MAA, which of the following are true?
a. it is best not to withdraw blood into the syringe before injection b. the patient should be supine c. the radiopharmaceutical should be gently agitated before injection d. all of the above e. a and b only |
d
|
|
|
|
80) Following a spill of 50 mCi of 99m Tc mebrofenin in the nuclear medicine department the first priority is to:
a. notify the NRC b. notify the RSO and/or chief technologist c. perform an area survey to determine exposure rate in the area d. contain the spill by covering it and restricting access to the area e. collect glass pieces |
d
|
|
|
|
81) The annual TEDE limit for a technologist's hands is:
a. 5 mrem b. 5 rem c. 15 mrem d. 50 mrem e. 50 rem |
e
|
|
|
|
82) Center of rotation must be determined for:
a. each collimator used b. each matrix used c. each zoom factor used d. all of the above |
d
|
|
|
|
83) If the HVL of lead for I-131 is 3 mm and a lead vial shield holding the iodine is 6 mm thick, what percentage of the original exposure rate will remain?
a. 75% b. 50% c. 25% d. 12.5% |
c
|
|
|
|
84) One ml of a liquid is assayed and contains 206 mCi. If it is diluted with 9 ml and subsequently is assayed at 180 mCi, what is the geometric correction factor?
a. 0.75 b. 0.87 c. 0.96 d. 1.14 e. 1.20 |
d
|
|
|
|
85) Increasing the matrix size of a SPECT acquisition:
a. decreases the imaging time b. decreases the storage space needed c. increases spatial resolution d. increases count density e. all of the above |
c
|
|
|
|
86) An MAA kit has an average of 900,000 particles. If 50 mCi of 99m Tc pertechnetate in 7 ml are added, how many particles will a patient who gets a 3 mCi dose receive?
a. 72,000 b. 129,000 c. 240,000 d. 514,000 |
a
|
actual answer is 54,000 which is not included in the answers in the book
|
|
|
87) To minimize oxidation of stannous chloride, which of the following may be added to radiopharmaceutical kits?
a. oxygen b. water c. bacteriostatic saline d. nitrogen |
d
|
|
|
|
88) On an intrinsic field uniformity image, the area of increased activity around the image is called:
a. halo effect b. edge packing c. flare phenomenon d. septal penetration |
b
|
|
|
|
89) The photomultiplier tube functions to:
a. convert light to electrical signal b. emit light in response to a gamma ray c. filter radiation not originating perpendicular to the detector face d. discard signal from background radiation |
a
|
|
|
|
90) Film badges should be worn:
a. between shoulder and waist b. except while doing paperwork c. only during preparation and administration of radiopharmaceuticals d. all of the above |
a
|
|

