![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
75 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A new patient enters your office complaining of muscular spasms involving the muscles on the right side of their neck. Spasmotic contractions which follow voluntary contractions (i.e. head turning) last, on average, about 30 – 45 seconds. Contractions are associated with increased electromyographic activity. Nerve conduction velocities in nerves supplying the involved muscles are normal, and direct electrical stimulation of the affected muscles produces normal contraction without spasm. This patient is most likely suffering from...
|
Torticollis dystonia
|
|
|
The reason why an action potential arriving at a neuromuscular junction causes only one action potential to be generated in the muscle cell membrane is because...
|
Ach is destroyed by Ach-ase before a second muscle cell action potential can be produced
|
|
|
The proportion of nuclear bag fibers to nuclear chain fibers would be expected to be the highest in...
|
muscles of the distal extremities
|
|
|
A patient complains of a progressive "loss of feeling" in his fingers and toes. Sensory
testing reveals a rather curious loss of pain and temperature sense particularly in the cooler regions of all four extremities. Conscious proprioception and vibration sense are unremarkable. This patient most likely is suffering from... |
leprosy
|
|
|
A patient you have been seeing for complaints of radiating mid-scapular pain has begun to experience severe muscle weakness involving his extremities, in particular. However, strength improves somewhat with repetitive attempts to perform certain movements. Nerve conduction velocities are normal and direct electrical stimulation of affected muscles produces normal contraction. Upon examination of the patients' x-rays, you note a radio-opacity in the upper left quadrant of the right lung field. Of the following, this
patient is most likely suffering from... |
Eaton-Lambert syndrome
|
|
|
Electrical stimulation of motor nerves produces normal action potentials in the nerves, but leads to muscle contractions which last far beyond the period of nerve stimulation. During this prolonged contraction, action potentials are found to be occurring in the muscle membranes However, direct stimulation of the muscle results in normal action potential generation and contraction. Barring any additional diagnostic information, the patient could be suffering from...
|
dystonia
|
|
|
In which of the following disorders or conditions would direct electrical stimulation of muscle lead to deficient muscle contraction?
|
- hyperkalemia
- upper limb girdle form of muscular dystrophy - Becker's dystrophy |
|
|
In reference to question #17 (above), if increasing the intensity of the voltage utilized for direct muscle stimulation reveals a "threshold effect" (in other words, as the applied voltage is increased, at some point normal patterns of muscle cell action potentials are finally produced) then the most likely diagnosis would be...
|
hyperkalemia
|
|
|
An elderly chronic back pain patient of yours has begun to complain of noticeable episodes of weakness, numbness, and tingling sensations particularly involving her hands and fingers, bilaterally. Nerve and muscle testing reveal the following: electrical stimulation of affected muscles directly produces normal contractions. However, you determine that nerve conduction velocities in nerves innervating the affected muscles are significantly reduced. Elevation of the arms quickly reproduces the symptoms. Sensory loss is specific to type II modalities. Of the following, this patient most likely is suffering from...
|
diabetic neuropathy
|
|
|
Loss of the elasticity of the lens of the eye results in ...
|
presbyopia
|
|
|
The most common etiology for the syndrome, tic doloreaux is...
|
bacterial
|
|
|
In the disease, retinitis pigmentosa, blurring of vision is caused primarily by...
|
abherant reflection of light due to the build up rod and cone disc membranes
|
|
|
Following a rather severe bout of the flu, a chronic low back pain patient of yours has begun to develop noticeable weakness, particularly of his extremities. Muscle weakness appears to follow a "myotomal pattern." Nerve and muscle testing reveal the following: Stimulation of affected muscles directly produces normal contractions. However, you determine that nerve conduction velocities in nerves innervating the affected muscles are significantly reduced. Of the following, this patient most likely has...
|
post-infectious polyradiculitis
|
|
|
The neurological manifestation particularly indicative of hypoparathyroidism is...
|
nerve and muscle membrane instability
|
|
|
With respect to the prevention of skeletal muscle fatigue, the sustained production of ATP primarily serves the purpose of...
|
maintaining low P04 concentrations (by its reincorporation with ADP) thus preventing its interference with G-actin-myosin club head interactions
|
|
|
The "spasticity" of upper motor neuron disease is due to...
|
the tonic inhibitory influence of the cerebral cortex on gamma motor neurons supplying antigravity muscles is reduced
|
|
|
One of your patients has suffered an attack of severe weakness involving both his upper and lower extremity musculature on the left. He also complains of blurred vision on conjugal gaze to the left. Of the following, this patient has most likely suffered a vascular infarct (TIA) involving his...
|
right cerebral peduncle
|
|
|
Touching the cornea of the left eye elicits no blink response in either eye. Touching the cornea in the right eye elicits blink responses in both eyes. This indicates dysfunction of the...
|
left trigeminal nerve
|
|
|
A low back pain patient of yours has recently begun to exhibit weakness, numbness, and intermittent pins and needles sensations involving his right leg and foot. Cranial nerve testing is unremarkable, as are sensory, motor, and reflex testing of the upper extremities. However, neurological testing of the right lower extremity reveals significant deficits in position and vibratory appreciation involving the right foot and toes. Achilles reflex is a bit exaggerated on the right, and is associated with significant paresis involving the muscles of the right foot and leg. Babinski's test is plantar-extensor on the right. Pain and temperature testing are unremarkable except for the fact that the patient appears to have difficulty precisely localizing these stimuli when applied to the right lower extremity. Of the following, these signs and symptoms are most likely due to...
|
thrombus-anterior cerebral artery-left
|
|
|
A new patient presents in your office with complaints of neck stiffness and pain involving his neck musculature. During the course of your physical exam, you note severe weakness of trapezius and sterno-cleido-mastoid muscles on the left. There is significant atrophy of these muscles on the left as well, and electromyographic testing reveals fibrillation potentials in various locations throughout those muscles. Sensory testing is unremarkable in all extremities, and deep tendon reflexes involving the extremities are within the normal expected range. You would suspect...
|
tumor - posterior cranial fossa - left
|
|
|
A patient of yours has recently experienced the rather sudden onset of muscle weakness on the left side of their face, left upper extremity, and left lower extremity. Motor testing of the extremities reveals wrist and ankle clonus on the left. Babinski's sign is planter extensor on the left. Facial paresis is exhibited below the level of the eye. Forehead musculature and blink responses are preserved bilaterally. Sensory testing is unremarkable. This patient has most likely suffered a vascular infarct involving...
|
internal capsule - right lenticulostriate a. branches
|
|
|
A patient complains of stiff neck and intermittent cramping of the muscles of her hands and fingers. Electrical stimulation of motor nerves produces normal action potentials in the nerves supplying the affected muscles, but leads to muscle contractions (spasms) which last far beyond the period of nerve stimulation. During this prolonged contraction, action potentials are found to be occurring in the muscle membranes. Direct stimulation of the affected muscles results in a similar prolonged action potential generation and contraction, both of which far outlast the period of direct stimulation. The problem is probably due to...
|
hypocalcemia
|
|
|
A lesion involving the ventral horn of the spinal cord at L-5 on one side would be expected to produce...
|
Flaccid paralysis and fasiculations of skeletal muscles of the L-5 myotome ipsilateral to the side of the lesion
|
|
|
Which of the following can cause osteomalacia?
|
- vit. D deficiency
- low calcium intake (dietary) - high phosphate intake |
|
|
The reason action potentials cannot repropagate into the membranes of sensory receptors is that...
|
The proteins lining Na+ and K+ channels are not voltage sensitive in sensory nerve endings
|
|
|
Following a severe bout of the flu, a patient complains of severe general weakness and G.I. distress. Needle EMG reveals severe hyperpolarization of muscle membranes. You also note that the knuckles, elbows, and crease lines of the palms of the hands have a dirty hyperpigmented appearance. Blood pressure is 80/50. Of the following, you would suspect...
|
Hashimoto's autoimmune adrenalitis
|
|
|
One of your patients has suffered an attack of severe weakness involving both his upper and lower extremity musculature on the right. He also complains of blurred vision on conjugal gaze to the left. Of the following, this patient has most likely suffered a vascular infarct (TIA) involving his...
|
left pons
|
|
|
A patient has developed significant weakness involving their right arm flexors, forearm flexors, and wrist extensors. What named syndrome describes this patient's pattern of weakness?
|
Erb's palsy
|
|
|
Botulinum toxin is currently used for the management of...
|
dystonia
|
|
|
When light strikes the retina...
|
- rods are hyperpolarized
- ganglion cells are depolarized - bipolar cells are hyperpolarized |
|
|
An individual with 20:50 vision...
|
can just see at 20 feet, two lines separated by a distance of 50 microns
|
|
|
A patient presents with severe atrophy and weakness of the muscles of the legs and feet. Plantar flexion reflexes are also depressed bilaterally. Good muscle girth of quadriceps and hamstring muscles leads to a "stork like" appearance of the lower extremities. Of the following, this patient most likely is suffering from...
|
hereditary motor neuropathy
|
|
|
It is known that a single CNS transmitter can cause excitation of some and inhibition of other post-synaptic cells. The explanation for this phenomenon is that...
|
the receptors for a particular transmitter are associated with different ionic channels
|
|
|
A patient complains of progressive weakness involving primarily the extraoccular muscles, facial muscles and muscles of the proximal extremities. Motor strength is found to deteriorate significantly with repetitive muscular contractions. Nerve conduction velocities are normal, and direct electrical stimulation of affected muscles produces normal contractions. You happen to note the presence of a large irregular mass involving the thymus gland on examination of the x-ray. Of the following, this patient is most likely suffering from...
|
myasthenia gravis
|
|
|
A new patient enters your office complaining of muscular spasms involving the muscles on the right side of their neck. Spasmotic contractions are most severe following passive rotatory movements of the head to the right. "Distractional" tests are negative. Spasms are associated with increased electrical activity in nerves supplying those muscles. Nerve conduction velocities in nerves supplying the involved muscles are normal, and direct electrical stimulation of the affected muscles produces normal contraction without spasm. This patient is most likely suffering from...
|
"mechanical" torticollis
|
|
|
In which of the following disorders or conditions would there be evidence of increased action potential generation in motor nerves?
|
- tetanus toxin poisoning
- hypocalcemia - strychnine poisoning |
|
|
The factor which ultimately determines whether a neurotransmitter will be inhibitory or excitatory is...
|
the type of ionic channel with which the post-synaptic receptor is associated
|
|
|
A patient presents with complaints of intermittent muscle "cramps." Electrical stimulation
of motor nerves produces normal action potentials in the nerves, but leads to muscle contractions which last far beyond the period of nerve stimulation. During this period prolonged contraction, action potentials are found to be occurring in the muscle membranes. Direct stimulation of the muscle results in a similar prolonged action potential generation and contraction, both of which far outlast the period of direct stimulation. The problem is probably due to... |
- instability of muscle cell membranes
- instability of motor nerve membranes |
|
|
In reference to the question above, given these signs and symptoms, you would suspect...
|
hypocalcemia
|
|
|
The concentration of Ach in CNS nerve terminals is maintained primarily by...
|
re-uptake of Ach from the synaptic cleft
|
|
|
A patient has noticed progressive weakness and "numbness" of the lower extremities bilaterally. Neurologic testing reveals significant bilateral paresis with ankle clonus. Babinski's test is plantar-extensor, bilaterally. In addition, there is severe loss of vibratory and position sense in both lower extremities. However pain and temperature sense are normal except for poor localization of these applied stimuli. Upper extremity and cranial nerve testing are unremarkable. Of the following, this patient is most likely suffering from...
|
tumor - falx cerebri
|
|
|
A chronic neck pain patient of yours complains of new symptoms. These include the progressive onset of right axillary pain, together with paresthesia and hypoesthesia of the ring and little finger and along the medial aspect of the right arm and forearm. In addition, the patient exhibits rather severe weakness of the finger flexors and interossei muscles of the right hand. Also, you notice mild ptosis, a narrowed pupillary aperture, and noticeable dryness (scalyness) of the skin on the right side of the face. You would suspect...
|
C-8, T-l spinal nerve compression
|
|
|
Following a rather severe bout of the flu, a chronic back pain patient or yours has developed severe weakness of his proximal musculature, with early fatigue on upward gaze and bilateral ptosis. Electrical stimulation of the affected muscles produces normal contractions and nerve conduction velocities are also normal. Pupillary light reflexes are normal, bilaterally. Muscle strength is found to deteriorate significantly with repetitive attempts to perform movements. You would suspect...
|
myasthenic syndrome
|
|
|
Following an extremely severe bout of the flu, a mechanical low back pain patient of yours has begun to complain of extremity weakness. Your neurological evaluation reveals selective paresis involving the dorsi-flexors of the right foot. It also reveals a rather selective weakness involving the interossei muscles of the left hand, and the wrist flexors and forearm extensors of the right upper extremity. Cranial nerve function and sensory perception are unremarkable. Of the following, this patient is most likely suffering from...
|
Guillain-Barr'e disease
|
|
|
A patient suffers from intermittent tingling and numbness involving the lateral aspect of their right foot and little toe. You also observe that they have difficulty supporting their body weight when attempting to stand up on their toes. Which disc and root level combination would you suspect?
|
L5 disc - S-1 roots
|
|
|
A patient complains of difficulty chewing and swallowing. Speech is slurred. Upon protrusion, the tongue deviates markedly to the right. These findings indicate dysfunction related to the...
|
right hypoglossal nerve
|
|
|
Which of the following is (are) pathognomic for lower motor neuron disease?
|
fibrillation potentials
|
|
|
A new patient presents in your office exhibiting severe weakness involving his chest, back, and shoulder musculature. Direct electrical stimulation of affected muscles produces subnormal action potential generation and contraction of these muscles. This is the case at all intensities of muscle stimulation. You would suspect...
|
muscular dystrophy (regional form)
|
|
|
A patient suddenly experiences severe weakness and tingling sensations involving the left side of her face and left arm and hand. Sensory testing reveals loss of vibration sense on the left side of the face and in the left hand and fingers. Pain and temperature sense are normal. Weakness of the left facial muscles is exhibited below the level of the eye. Blink responses are normal. Stretch reflexes are hyperactive in the left upper extremity. This patient has most likely suffered a lesion involving which vascular territory?
|
middle cerebral a. - right
|
|
|
A patient has developed significant weakness involving their left finger flexors and interossi muscles. Which named syndrome describes this patient's pattern of weakness?
|
Klumpke's palsy
|
|
|
A patient presents in your office with headaches accompanied by neck stiffness, and intermittent muscle cramps involving the hands, fingers, feet and toes. During your blood pressure exam, with compression of the brachial artery, the muscles of the forearm suddenly go into spasm, resulting in a rather characteristic extension of the thumb and flexion of the wrist and fingers. You would suspect...
|
parathyroid disease
|
|
|
A patient presents in your office exhibiting severe paresis of the muscles on the left side of her face and on the right side of her body. Facial weakness includes the forehead musculature on the left. Touching the cornea on the right or left elicits a blink response only on the right. Neurological examination also confirms severe paresis involving both the upper and lower extremities on the right. Babinski's test is plantar extensor on the right, and passive dorsiflexion of the right foot elicits mild clonic contractions. This patient most likely has suffered a lesion involving...
|
base pons-left
|
|
|
A patient enters your office with complaints of blurred vision and episodes of dizziness. On
lateral gaze to the left, there is no evidence of diplopia. However, upon downward gaze from that position, a significant diplopia is ellicited. A red glass placed over the left eye causes the upper image to turn red, whereas a red glass placed over the right eye causes the lower of the two images to turn red. If due to neurovascular compression, you would suspect involvement of the... |
right trochlear nerve
|
|
|
A patient is referred to you by another chiropractor. The patient complains that he has suffered from the progressive onset of weakness, numbness, and pain involving his left leg and foot for over a year now. Cranial nerve testing is unremarkable, as are sensory, motor, and reflex testing of the upper extremities as well as the right lower extremity. However, neurological testing of the left lower extremity reveals significant deficits in position and vibratory appreciation involving the left foot and toes. Achilles reflex is depressed on the left, and is associated with significant paresis involving the muscles of the left foot and leg. Babinski's test is plantar -flexor, bilaterally, although difficult to elicit on the left. Pain and temperature sense are intact, and if anything, are a bit exaggerated in the left lower extremity. These signs and symptoms could be due to...
|
tumor - spinal canal - involving lumbosacral roots (cauda equina) - left
|
|
|
A patient complains of the progressive onset of severe muscle weakness involving his distal extremity musculature, in particular. Muscle strength is found to improve significantly with repetitive contraction. Nerve conduction velocities are normal, and direct electrical stimulation of affected muscles produces normal contraction. Of the following, this patient is most likely suffering from...
|
Eaton - Lambert disease
|
|
|
A patient complains of progressive weakness involving primarily the extraoccuiar muscles and muscles of the proximal extremities. Nerve conduction velocities are normal, and direct electrical stimulation of affected muscles produces normal contractions. Muscle strength is observed to deteriorate significantly with repetitive movements. You happen to note the presence of a diffusely enlarged thymus gland on examination of the x-ray. Of the following, this patient is most likely suffering from...
|
myasthenic syndrome
|
|
|
In primary hypoaldosteronism, the severe muscle weakness is caused by...
|
- hyperpolarization of muscle cell membranes
- an increase of intracellular K+ |
|
|
An "ill" appearing patient presents in your office with complaints of blurred vision and severe weakness involving his facial muscles. The patient relates that he has been suffering from extreme nausea, chills and fever over the past couple of days. Occular testing reveals severe ptosis and severe diplopia (double images) in all fields of conjugal gaze. Pupillary light reflexes are markedly slowed in one eye, absent in the other. Of the following, your patient is most likely suffering from...
|
botulism
|
|
|
The mechanism of pre-synaptic inhibition involves...
|
- depolarization of the pre-synaptic membrane
OR - hyperpolarization of the pre-synaptic membrane depending on the action of the released neurotransmitter |
|
|
The reason why patient's with hypoparathyroidism exhibit severe muscle stiffness (spasticity) is that...
|
sodium channel proteins in nerve and muscle membranes become unstable
|
|
|
Muscle tone could be decreased by which of the following...
|
- an increase in Ib afferent action potential generation
- a decrease in gamma motor neuron activity - a decrease in alpha motor neuron activity |
|
|
A patient presents in your office exhibiting severe paresis of the muscles of the left side of her face. Facial weakness includes the forehead musculature (which has an "ironed out" appearance) on the left. Touching the cornea on the right or left elicits a blink response only on the right. Neurological examination also reveals severe paresis involving the upper and lower extremities on the right. Babinski's test is plantar extensor on the right, and passive dorsiflexion of the right foot elicits mild clonic plantar flexion contractions. This patient most likely has suffered a lesion involving...
|
base pons-left
|
|
|
A chronic low back pain patient of yours presents in your office 2-3 weeks following a period of fever and severe sore throat. The patient complains of continued difficulty swallowing, even though the pain had subsided a week earlier. Speech has a nasal quality and the patient complains of blurred vision. Of the following, you would suspect...
|
post-diptheria syndrome
|
|
|
In which of the following disorders or conditions would there be evidence of weakness due to inadequate release of Ach by motor nerves by each action potential arriving at the terminal?
|
- Eaton-Lambert syndrome
- botulinum toxin poisoning |
|
|
In general, most (85%) of the ATP in skeletal muscle is utilized in order to...
|
Supply the energy necessary for the active transport of Ca++ into the sarcoplasmic reticulum thus preventing the interaction of G-actin with myosin club heads
|
|
|
A patient complains of intermittent tingling and numbness along the dorsal surface of their left foot and big toe. Additionally, they have difficulty supporting their body weight standing back on their heels with their toes held up in the air. Which disc and root level combination would you suspect?
|
L-4 disc - L-5 roots
|
|
|
A patient presents with weakness and severe muscle "cramps" exhibited in all extremities and most noticeable following exertion. However, there are no detectable action potentials being generated in the affected muscles during periods of abnormal contraction. Of the following, the patient could have...
|
- myotonic dystrophy
- glycogen storage disease |
|
|
set a limit on cell A's ability to inhibit cell C
|
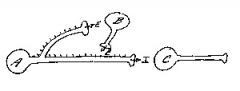
Cell A's effect on cell C is one of inhibition. At higher action potential frequencies, cell A begins to excite cell B, causing it to fire. This would serve to ...
|
|
|
A patient you have been treating for pain exhibited in their low back and buttock region enters your clinic with new complaints of urinary incontinence. Neurologic testing reveals flaccidity of the anal and urethral external sphincters. Sensory and motor testing of the lower extremities are unremarkable, except for a small perianal area of hypoesthesia. Of the following, you would suspect...
|
tumor - filum terminali
|
|
|
A low back pain patient of yours has an attack of severe weakness and tingling sensations in his right lower extremity. Sensory testing reveals loss of position sense and vibratory detection. However, pain and temperature sensations are preserved. Babinski's sign is planter-extensor on the right and dorsiflexion of the right foot elicits mild clonic contractions. Sensory and motor testing are unremarkable in the left leg and foot, and in both upper extremities and face. This patient has most likely suffered a vascular infarct involving the...
|
cerebral cortex - territory of anterior cerebral a. - left
|
|
|
In which of the following disorders or conditions would there be evidence of spasticity or muscle "cramping" due to excessive release of Ach by motor nerves by each action potential arriving at the terminal?
|
blepharospasm
|
|
|
Decreased curvature of the lens of the eye results in...
|
"far sightedness"
|
|
|
Which of the following can cause hypocalcemia?
|
parathyroid disease
|
|
|
A farmer enters your clinic following a day spent spraying for grasshoppers. He complains of headache, nausea, and extreme muscle stiffness. Clinical testing shows no abnormality in the amount of action potentials in the nerves supplying the skeletal muscles. Muscle stiffness is associated with an increased number of action potentials being produced in the muscle cell membranes following nerve stimulation. However, direct electrical stimulation of muscle produces normal action potentials and contractions...
|
- the agent responsible for the described symptoms may have been an anticholinesterase
- the site of the defect is probably at neuromuscular junctions |
|
|
The primary role(s) of lactic acid secreted by skeletal muscle is (are)...
|
- to facilitate a lactate-induced reduction in local hemoglobin oxygen affinity in conditions of increased oxygen demand
- to facilitate a lactate-induced increase in respiratory rate and depth in conditions of increased oxygen demand |

