![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
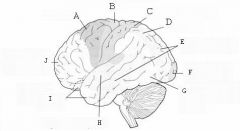
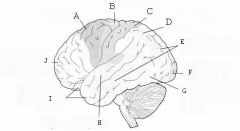
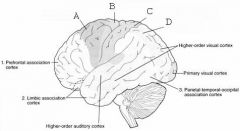
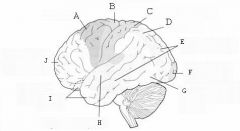
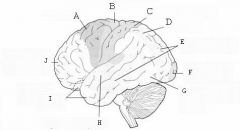
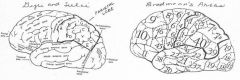
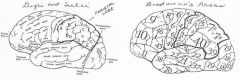
image016 identify the primary sensory and primary motor, higher-order sensory or motor association, or multimodal association area: A
|
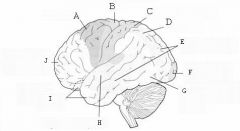
Premotor complex
|
|
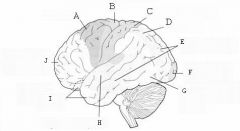
image016 identify the primary sensory and primary motor, higher-order sensory or motor association, or multimodal association area: B
|
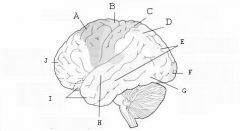
Primary motor complex
|
|
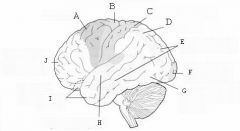
image016 identify the primary sensory and primary motor, higher-order sensory or motor association, or multimodal association area: C
|
Primary somatic sensory cortex
|
|

image016 identify the primary sensory and primary motor, higher-order sensory or motor association, or multimodal association area: D
|
Posterior parietal cortex
|
|
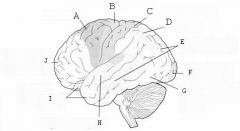
image016 identify the primary sensory and primary motor, higher-order sensory or motor association, or multimodal association area: E
|
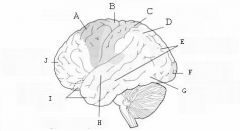
higher order visual cortex
|
|
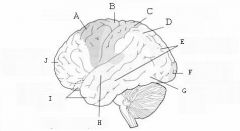
image016 identify the primary sensory and primary motor, higher-order sensory or motor association, or multimodal association area: F
|
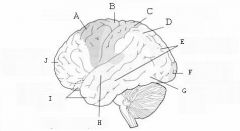
Primary visual cortex
|
|
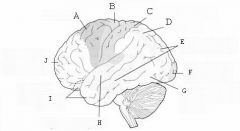
image016 identify the primary sensory and primary motor, higher-order sensory or motor association, or multimodal association area: G
|
Parietal-temporal-occipital association complex
|
|
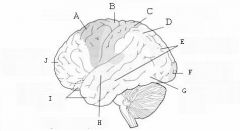
image016 identify the primary sensory and primary motor, higher-order sensory or motor association, or multimodal association area: H
|
Higher order auditory complex
|
|
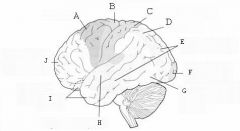
image016 identify the primary sensory and primary motor, higher-order sensory or motor association, or multimodal association area:I
|
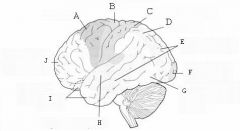
Limbic association cortex
|
|
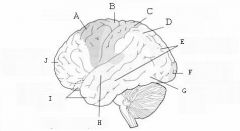
image016 identify the primary sensory and primary motor, higher-order sensory or motor association, or multimodal association area: J
|
Prefrontal association cortex
|
|
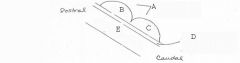
image026 identify the midbrain structure: A
|
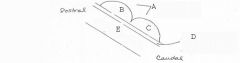
Tectum
|
|
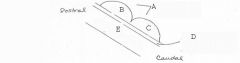
image026 identify the midbrain structure: B
|
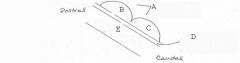
Superior Colliculus
|
|
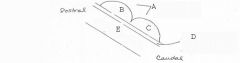
image026 identify the midbrain structure: C
|
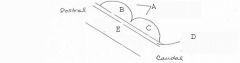
Inferior Colliculus
|
|
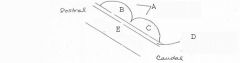
image026 identify the midbrain structure: D
|
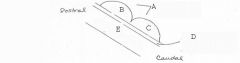
Cerebral aqueduct of sylvius
|
|
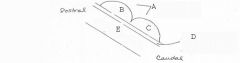
image026 identify the midbrain structure:E
|
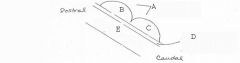
Tegmentum
|
|
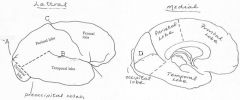
image028 identify the sulcus or fissure: A
|
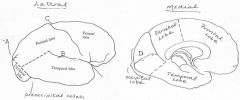
Parieto-occipital sulcus
|
|
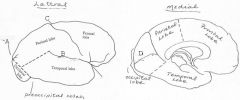
image028 identify the sulcus or fissure: B
|
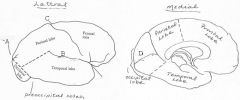
Sylvian fissure
|
|
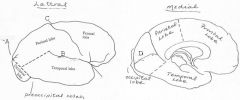
image028 identify the sulcus or fissure: C
|
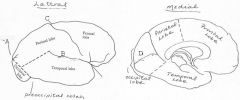
Central sulcus of Rolando
|
|
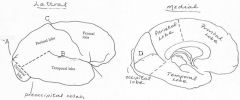
image028 identify the sulcus or fissure: D
|
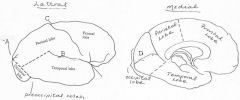
Calcarine Fissure
|
|
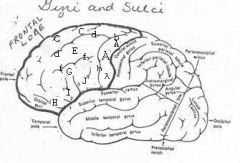
image030 identify the gyrus or sulcus/fissure: A
|
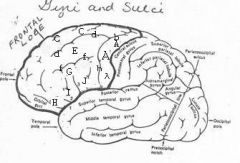
Precentral gyrus, primary motor cortex, Area 4
|
|
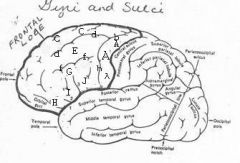
image030 identify the gyrus or sulcus/fissure: B
|
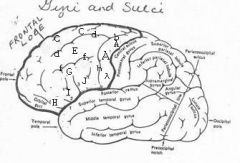
Precentral sulcus
|
|
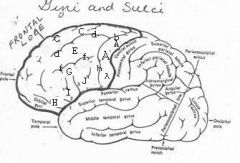
image030 identify the gyrus or sulcus/fissure: C
|
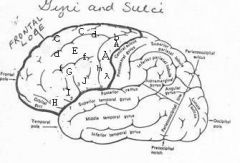
superior frontal gyrus
|
|
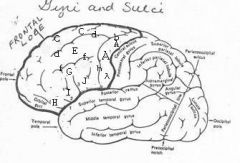
image030 identify the gyrus or sulcus/fissure: D
|
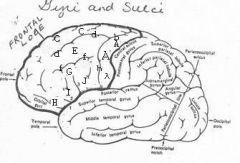
superior frontal sulcus
|
|
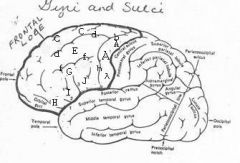
image030 identify the gyrus or sulcus/fissure: E
|
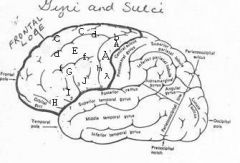
Middle frontal gyrus
|
|
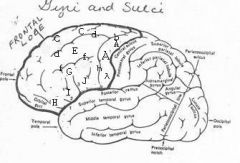
image030 identify the gyrus or sulcus/fissure: F
|
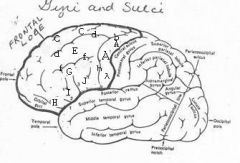
Inferior frontal sulcus
|
|
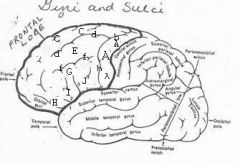
image030 identify the gyrus or sulcus/fissure: G
|
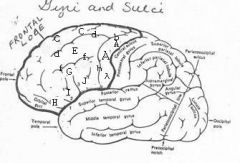
Inferior frontal gyrus
|
|
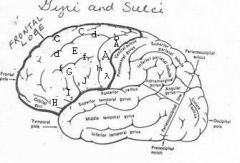
image030 identify the gyrus or sulcus/fissure: H
|
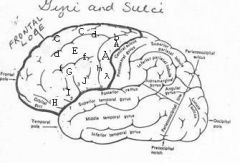
orbitalis
|
|
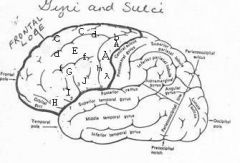
image030 identify the gyrus or sulcus/fissure: I
|
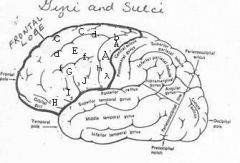
pars triangularis
|
|
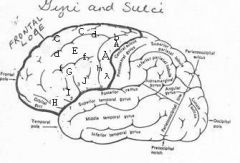
image030 identify the gyrus or sulcus/fissure: J
|
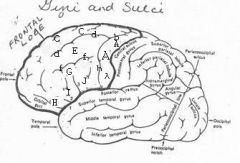
pars operularis
|
|
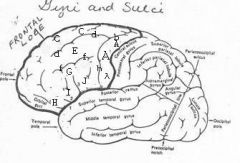
image030 what is the significance of regions I and J
|
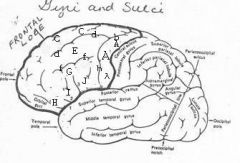
pars triangularis and pars operularis (areas 44 and 45) comprise Broca’s area
|
|
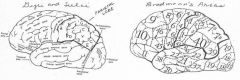
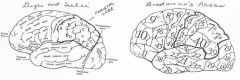
image034 identity, function, area of the gyrus or sulcus/fissure: A
|
postcentral gyrus, Areas 3, 1, 2; primary somatosensory cortex
|
|
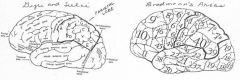
image034 identify the gyrus or sulcus/fissure: B
|
postcenral sulcus
|
|
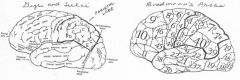
image034 identify the gyrus or sulcus/fissure:C (includes D and E)
|
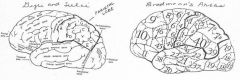
inferior parietal lobule
|
|
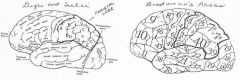
image034 identity, area, function of the gyrus or sulcus/fissure: D
|
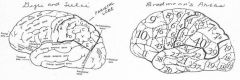
supramarginal gyrus, Area 40, in dominant hemisphere important in perception of and interpretation of written language
|
|
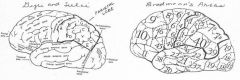
image034 identify the gyrus or sulcus/fissure: E
|
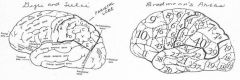
angular gyrus, Area 39, in dominant hemisphere important in perception of and interpretation of written language
|
|
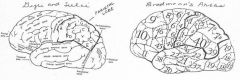
image034 identify the gyrus or sulcus/fissure: F
|
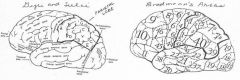
Intraparietal sulcus
|
|
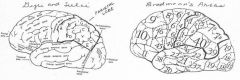
image034 identify the gyrus or sulcus/fissure: G
|
superior parietal gyrus
|
|
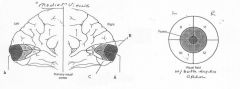
image040 identify A
|
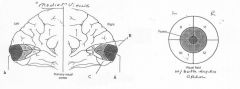
Calcarine fissure
|
|
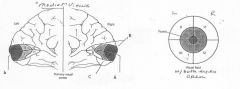
image040 identify B
|
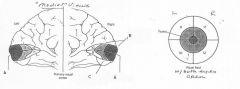
Cuneus
|
|
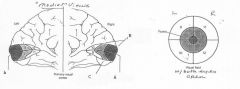
image040 identify C
|
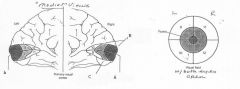
Lingual Gyrus
|
|
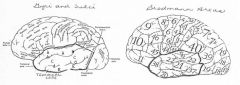
image042 identify A
|
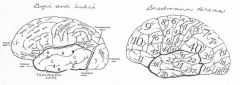
Superior temporal gyrus
|
|
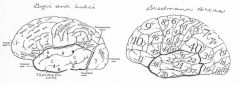
image042 identify B
|
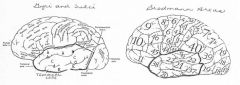
superior temporal sulcus
|
|
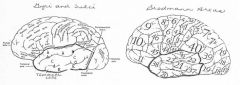
image042 identify C
|
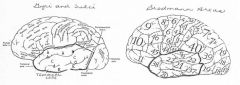
middle temporal gyrus
|
|
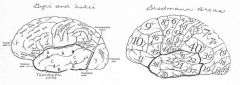
image042 identify D
|
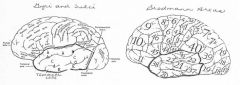
inferior temporal sulcus
|
|
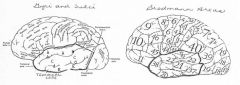
image042 identify E
|

inferior temporal gyrus
|

