![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Adenosine
Mechanism of action: |
Acts on presynaptic terminals to inhibit the release of catecholamines.
Caffeine blocks Adenosine, works as an Antagonist and a competitive inhibitor |
|
|
MDMA
|
Binds to the serotonin re-uptake transporter
Also enters the serotonergic neuron via the serotonergic reuptake inhibitor, causing excessive release of serotonin. Also causes the relase of dopamine, to a lesser extent. |
|
|
Ketamine
|
Dissociative Anesthetic; distorts perceptions of light and sound, affects the NMDA (glutumate receptor )
|
|
|
Cocaine
|
– Cocaine binds to dopamine re-uptake
transporters on the pre-synaptic membranes of dopaminergic neurons. This inhibits the removal of dopamine from the synaptic cleft and its subsequent degradaton by monoamine oxidase in the nerve terminal – Also blocks re-uptake transporters for serotonin and norepinephrine |
|
|
Rohypnol
|
Also known Benzodiazepine
It acts onat the GABAa Receptor |
|
|
GHB
|
Acts as a CNS depressant and is used to treat narcolepsy, its a metabolite of GABA.
Exists naturally in the naturally in the brain, but at low levels. Acts on GABAb receptor and specific GHB binding site. |
|
|
Alcohol
|
Mechanism of action:
Blcocks Glutumate recepto. Impairs memory Acts on GABA receptors to make them more inhibitory. Incresass the release of dopamine from the nuecleus accumbens. |
|
|
Tobacco
|
Ncotine is the msajor ingredient.
Acts on cholingernic receptors in CNS. Makes the receptors more senitive to nicotine and acetylcholine. Stimulates the release of dopamine from the nucles accumbens. |
|
|
Factors that determine the effect of a drug on an individual
|
Age
Weight Setting in which the drug is used Tolerance Time of day that its consumed |
|
|
Seven steps in neurotransmitter action
|
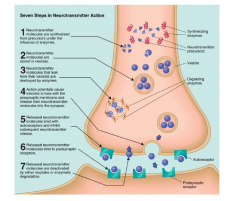
Neirotransmitter molecules are synthezied from precurosrs under the influence of enzymes
Neurotransmitter molecules are stored in vesicles. Neurotransmitter molecules that leak from the vesicles are destroyed by enzymes. Action portentials cause vesicles to fuse with the presynaptic membrane and release their neurotransmitter molecules into a synapse Released neortranmitter molcecules bind with autoreceptors and inhibit the subsequent neurotransmitter release. Released neurotransmitter molecules bind to postsynaptic molecules Released neurotransmitter molecules are deactivated by either uptale or enzymatic degradation.. |
|
|
Opiates
|
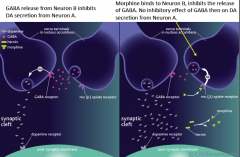
Heroin is converted to morphine once it crosses the blood-brain barrier.
Morphine is a powerful agonist at the mu opiod receptor. Inhibits the release of GABA, inhibits its inhibitory and the increased activation of dopaminergic neurons |
|
|
Drug Tolerance
|
Decreased Sensitivity to a drug, due to repeated exposure
|
|
|
Cross-Tolerance
|
Exposure to one drug can product tolerance to similar drugs (Alcohol and Benzodiazepines
|
|
|
Sensitization
|
Increased effect of a drug following repeated usuage
|
|
|
Metabolic tolearnace
|
Less of the drug is getting to the site of the action
|
|
|
Functional tolerance
|
Decreased responsiveness fewer receptors, decreased efficiency of binding at receptors , receptors less resoinsive
|
|
|
Drug withdrawal/Physical Dependence
|
Seen when the drug has been terminated
Body has made changes to compensate for drug's presence Severity varies with drug and pattern use |
|
|
Relpase
|
Stress: You use alcohol and cigarettes to cope after a bad day.
Priming You've been sober for a while, so thinking that just one drink is okay Environmental cue: You are around people and places associated with drug use. |
|
|
Incentive-sensitization thoery
|
Positiveincentive value- the anticipated pleasure of the drug associated with the action
Hedonic value: Liking- actual pleasure experienced. With drug use, the postive incentive value increases due to memory of pleasure early drug experience; the hedonic value decreases due to drug tolerance Addicts crave drugs more and enjoy them less |
|
|
Addiction
|
Continues to use drug despite adversive effects
|
|
|
Conditioned drug tolerance
|
Tolerance effects are maximized when the drug is taken in the same environment as previously taken.
|
|
|
Physical-dependence theory
|
Biopschological theory of addiction that doesnt explain why addists relapse after detoxification, indivudals begin using drugs, Addictions develop to drugs that do not produce severe withdrawal symptoms
|

