![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name and described the function of a neuron structure? |
Dendrites- receptor Axon hillock- joins the soma at a cone shaped elevation Axon- narrow tube that Carrus nerve signals to target Axon collaterals- arise from axon, called axon terminals in fine processes Synaptic bulb- contains neurotransmitters which realease when AP arrives |
|
|
Name and describe the neuroglia in CNS? |
Astrocytes- wrap around brain capillaries to form blood brain barrier and governs what passes from blood to interstitial fluid.
Microglia- small phagocytic immune cells.
Ependymal cells - line the central fluid filled cavities of the brain and spine. Circulate CSF Oligodendrocytes- wrap around axon to form myelin sheath. Insulated axon and allows saltatory conduction = takes place in gaps between oligodendrocytes (nodes of Ranvier) |
|
|
Name and describe the 2 neuroglia in the PNS? |
Schwann cells- same as oligodendrocytes and regenerate neurons by forming tube to allow axons to pass. Also in non myelated axons. Satellite cells - surround cell bodies with ganglia of sensory and autonomic systems. |
|
|
What pathway does the afferent division of the nervous system take? |
It carries info from sensory receptors to the CNS |
|
|
What pathway does the efferent division of the nervous system take? |
It carries information away from the CNS to muscles and glands |
|
|
What does the integration centre in the nervous system layout do? |
It receives ,modifies and acts of information in the brain and spinal cord |
|
|
How many spinal nerves are there? |
31 |
|
|
What two divisions is the PNS functionally split into? |
The somatic nervous system (afferent voluntary- initiates skeletal muscle) and the autonomic nervous system (efferent involuntary , controls cardiac muscle, smooth muscle and glands, sympathetic and parasympathetic) |
|
|
What two areas of the nervous system act as antagonists and what do the each control? |
Parasympathetic system and the sympathetic system. Para= rest or digest Sympathetic= fight or flight |
|
|
Do we have a PNS in the head? |
Yes the 12 crainal nerves |
|
|
How many hemispheres does the cerebral cortex have? |
2, right and left |
|
|
How many lobes does the cerebral cortex have ? |
4 frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal |
|
|
Within the cerebral cortex where does sensory information come from? |
The primary somatic cortex and the somatic sensory cortex. These are in the postcentral gyrus in the right hemisphere. |
|
|
Where does motor information come from in the cerebral cortex? |
The primary motor cortex and the premotor area in the precentral sulcus area of the left hemisphere |
|
|
What does the white matter contain in the brain? |
Myelin ( nerve cables) |
|
|
What does grey matter in the brain contain? |
Nerve body cells (synapses) |
|
|
3 nerve bundles in white matter that connects info to and from grey matter ? |
Commissural fibres - connects matter between 2 hemispheres
Association fibres connects areas within same hemisphere
Projection fibres - connects lower and upper brain for afferent and efferent information. |
|
|
What is the gateway to the cerebral cortex? |
The thalamus |
|
|
What does the diencephalon contain? |
The thalamus, hypothalamus and epithalamus |
|
|
What are the components of the diencephalon and thier functions? |

|
|
|
What does the midbrain do? |
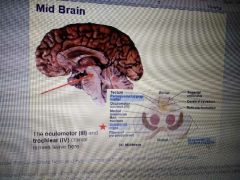
-Its involved in pain suppression ( periaqueductal grey matter)
- it coordinates head and eye movements (copora quadrigemina)
- supports dopamine and menalin precursor ( substantia Nigra) |
|
|
What does the pons do? |
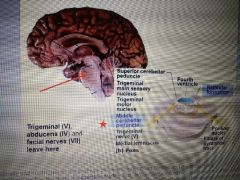
Control respiration with the medullary respiratory centre. Helps ascending pathways to cortex and connects pons to cerebellum |
|
|
What does the medulla oblongata do? |
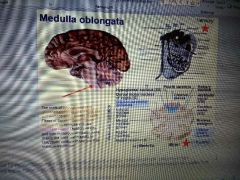
Contains cardiac centre, vasomotor centre (vasodilation) also contains central priaminds where motor cortex crosses over and touch information decussates here. |
|
|
Is the sensory neural pathway anterior or dorsal? |
Dorsal |
|
|
Is the motor neural pathway anterior or dorsal? |
Anterior |
|
|
Which cranial nerves fissure is the superior obital fissure? |
3,4,5,6 |
|
|
Which cranial nerves fissure is the auditory meatus ? |
7 ,8 |
|
|
Which cranial nerves fissure is the jugular foramen? |
9,10,11 |
|
|
What are the 3 main meninges of the brain? |
Dura, ( strong) arachnoid (separated from Dura with fluid layer and also fluid layer called subarachnoid space containing brain blood vessles) pia (delicate connective tissue clings to brain) |
|
|
Where is CSF formed? |
Choroid plexus |
|
|
What two arteries supply the brain with blood? |
Internal carotid arteries ( supply's anterior 2/3 of cerebral hemispheres)
Vertebral arteries ( right and left form basilar artery and supply medial regions of hemispheres e.g diencephalon, brainstem, cerebellum and cervical spinal cord) Both form the circle of willis |
|
|
Whats the names for components of the venous cerebral drainage? |
Superficial cerebral veins and the deep cerebral veins. ( They don't have veins and drain into the internal jugular vein) |

