![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|

|
|
|
What are the non-depolarizing agents (isoquinoline derivatives)? |
Atracurium Cisatracuium |
|
|
What are the non-depolarizing agents (steroid derivatives)? |
Pancuronium Rocuronium Vecuronium |
|
|
What is the depolarizing agent? |
Succinlycholine |
|
|
What are the reversal agents? |
Edrophonium Pyridostigmine Neostigmine
Sugammedex (steroidal only) |
|
|
When are the reversal agents given and why? |
Given post-procedurally to reverse the residual effects of the paralytic agents and restore normal neuromuscular activity and tone. |
|
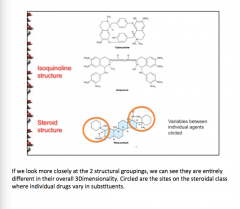
|
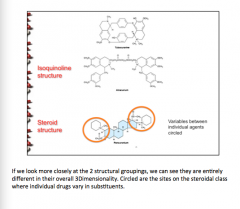
|
|
|
Draw the pathway of cholinergic signaling: |
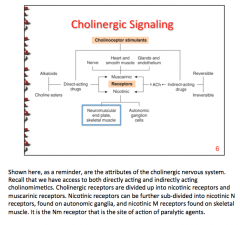
|
|
|
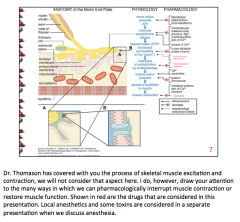
What are the two types of nicotinic receptors? Where is each found? Which receptor is the site of a cation of paralytic agents? |
Nicotinic N = autonomic ganglia
Nicotinic M = skeletal muscle (site of action of paralytic agents) |
|
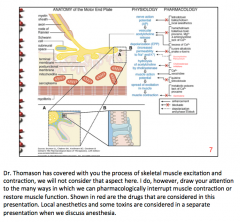
|
|
|
|
What type of receptor is the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor? How many molecules needed to bind to activate? |

Multimeric ligan-gated ion channel => gates for sodium influx into cell => depolarization
Two molecules of Ach |
|
|
What is the difference between a non-depolarizing blocker (rocuronium) and a depolarizing blocker (succinylcholine) in terms of action on the channel? |
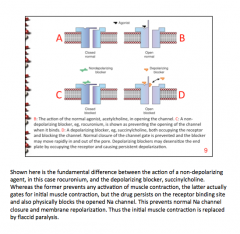
Non-depolarizing prevents opening, depolarizing occupies receptor and blocks the channel (normal closure prevented) => flaccid paralysis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
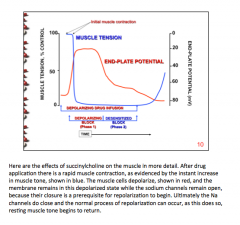
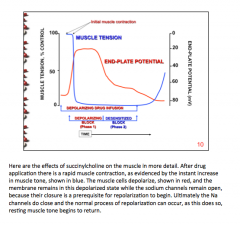
How does strength/contraction change with addition of non-depolarizer or depolarizing block? |

|
|
|
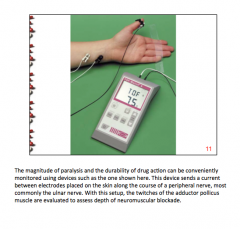
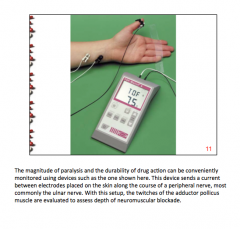
Patients given a depolarizing blocker show brief __________ before paralysis. |
Twitching |
|
|
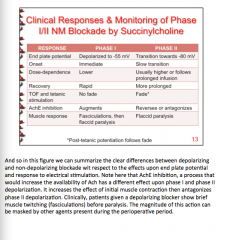
True or false: The durability of effect closely correlates with drug half-life, indicating that the binding kinetics to the nicotinic receptor are short lived and effects are dependent upon local tissue concentration. |
True |
|
|
Non-depolarizing:
Rapid or slow distribution, rapid or slow elimination How are they eliminated? Are they highly ionized? Do they bind protein? |

|
|
|
How is atracrium metabolized and eliminated? What product is produced related to seizures?
Which drug replaced it? |

|
|
|
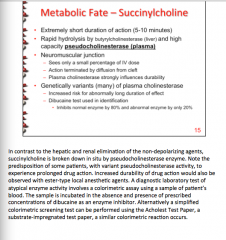
Succinylcholine:
Short or long duration of action What is it rapidly hydrolyzed by? Where? Broken down into what?
|
|
|
|
Of the three isoquinolones, which has the longest duration? |
Tubucurarine |
|
|
Which drug has the shortest duration? Which drugs have the highest potency? |
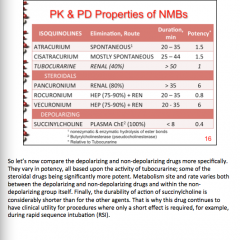
|
|
|
Which drugs cause block of ganglia block and histamine release?
Which drug causes cardiac M receptor block?
Which drug causes ganglia stimulation, cardiac M receptor stimulation, and slight histamine release? |

|
|
|
Which drug exhibits significantly expanded series of adverse effects when compared to the non-depolarizing agents? What are some of these AEs? |

Succinylcholine:
Hemodynamic changes Hyperkalemia Prolonged neuromuscular blockade Increase in pressures Malignant hyperthermia |
|
|
How is malignant hyperthermia produced? |
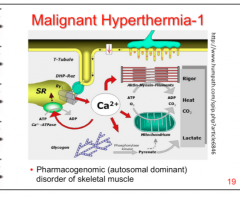
Drugs cause an uncontrolled release of calcium from the SR => symptoms indicated in image |
|
|
What drug is commonly associated with malignant hyperthermia? Other drugs?
What is the treatment (4 things)? |
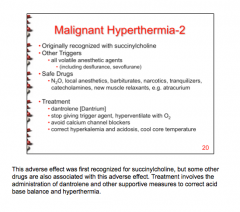
|
|
|
What drug interactions can occur with volatine anesthetics? (Isoflurane, sevoflurane, desflurane, and halothane, N20) |
Malignant hyperthermia = Ca2+ release from SR, administer dantrolene |
|
|
What drug interactions can occur with antibiotics (amino glycosides)? |
Enhancement of blockade (pre-junctional P-type Ca2+ channels), depressed Ach release similar to that caused by magnesium |
|
|
What drug interactions with local anesthetics? |
Can depress via pre-junctional neural effect Block in large doses |
|
|
What drug interactions with other neuromuscular blocking drugs? (succinylcholine) |
Depolarizing effect of succinyl choline => antagonized by administering a small dose of a non-depolarizing blocker |
|
|
What are two ways to reverse blockade and restore muscle tone and function? |
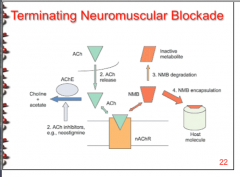
1. Increase levels of Ach by prevention metabolism of endogenous ligand by AchE, AchE => outcompete paralytic and restore activity
2. The future... |
|
|
What are the three AchE inhibitors? Do they cross the BB? Which has the longest duration? Shortest? Anticholinergic of each? |
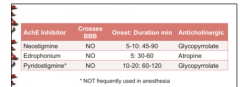
|
|
|
Atropine, Scopolamine, Glycopyrrolate
Which causes tachycardia, which causes bronchodilation, sedation, antisialogogue |
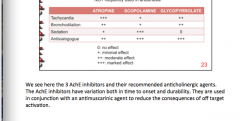
|
|
|
What are some of the off target actions of AchE inhibitors? (think about increase parasympathetic activity). |

|
|
|
What is the alternative approach to reverse NMB?
Which drug used in Europe does this? What drugs is it active against? |

Remove the blocking drug from the equation
Steroidals |
|
|
What is the mechanism of sugammadex? |
Pore structure into which NMB inserts, preventing blocker from being capable of accessing the binding site on the Ach nicotinic receptor |
|
|
What are some therapeutic uses of NMBs? How are they administered? |
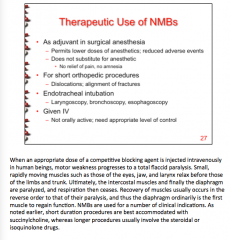
Surgical anesthesia Short orthopedic procedures Endotrachel intubation
Administed IV |
|

|

|

