![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
687 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
tactile sensation anterior 2/3 of tongue
|
trigeminal nerve |
|
|
taste posterior 1/3 of tongue
|
glossopharyngeal nerve |
|
|
parasympathetics to head/neck
|
superior salivatory nucleus |
|
|
motor nuclei to pharyngeal/laryngeal muscles
|
nucleus ambiguous |
|
|
innervation to parotid gland by the glossopharyngeal nerve
|
inferior salivatory nucleus |
|
|
nuclei for taste sensation
|
rostral nuclei solitarius |
|
|
nuclei for baroreceptor reflex
|
caudal nuclei solitariu |
|
|
nuclei for parasympathetic output to chest
|
dorsal motor nucleus of vagus |
|
|
corneal reflex
|
afferent: V efferent: VII |
|
|
gag reflex
|
efferent: vagus |
|
|
fourth nerve palsy
|
contralateral head tilt |
|
|
cocaine eye drops
|
confirmation of Horners (no change in size of Horners pupil/unaffected side dilates) |
|
|
Hydroxyamphetamine eye drops
|
Horner's pupil dilates, first or second order (if it doesn't dilate then it is a third order lesion) |
|
|
Aproclonidine
|
alpha-agonist-Horners pupil is supersensitive 2/2 down regulation of recptors and thus there is constriction of the Horners pupil and reversal of the anisocoria |
|
|
trochlear nerve
|
exits dorsally, innervates the superior oblique which depresses and intorts the eye, head tilt c/l
|
|
|
INO |
impaired adduction of the affected side and nystagmus in the nl eye
|
|
|
b/l INO
|
2/2 b/l MLF which will cause extropia (known as "wall-eyed bilateral INO" |
|
|
One and a half syndrome
|
lesion to both the ipsilateral abducens nucleus or PPRF and ipsilateral MLF (results in loss of all horizontal eye movements on that side and abduction of the c/l eye is the only lateral eye movement retained) |
|
|
APD combined with c/l hemianopia
|
optic tract lesion |
|
|
Nystagmus in BPPV
|
slow drift of the eyes toward the affected side and away from the unaffected side followed by a fast cortical correction to the opposite side (toward the unaffected side)---nystagmus is c/l |
|
|
otolithic organs
|
saccule and utricle (hair cells overlain by otolithic membrane covered by calcium carbonate particles); detect linear movement |
|
|
semicircular canals |
contain endolymph and an ampulla (contains sensory hair cells which are embedded in a gelatinous cap termed the cupula ---w/o otoconia); angular motions
|
|
|
anterior belly of the digastric, medial and lateral pterygoids, masseter, deep temporal, mylohyoid, tensor veli palatine and tensor typani
|
trigeminal nerve |
|
|
only muscle innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve |
stylopharyngeus muscle |
|
|
facial nerve course |
motor + nervus intermedius>geniculate ganglion>lacrimal and mucosal glands>chorda tympani nerve (causes hyperacusis if injured)>anterior 2/3 of tongue |
|
|
cornea sensory innervation |
V2: lower half of cornea |
|
|
Hypoglossal nerve injury
|
LMN: I/l tongue deviation |
|
|
I/l third nerve palsy and c/l hemiplegia
|
Weber's syndrome (midbrain) |
|
|
I/l third nerve and c/l involuntary movements
|
Benedikt's syndrome (ventral portion of mesencephalic tegmentum involving the red nucleus) |
|
|
I/l third nerve and c/l ataxia/tremor
|
Claude's syndrome (dorsal portion of mesencephalic tegmentum) |
|
|
I/l sixth and seventh nerve palsies with c/l hemiplegia
|
|
|
|
limited upward gaze, convergence retraction nystagmus, light near dissociation, lid retraction and skew deviation
|
Parinaud's (quadrigeminal plate)
|
|
|
Gerstmann's
|
finger agnosia, r/l disorientation, agraphia and acalculia |
|
|
recurrent artery of heubner
|
deep branch of ACA that supplies anterior limb of internal capsule , inferior part of head of the caudate and anterior GP |
|
|
clumsy hand dysarthria
|
c/l paramedian pons or posterior limb of internal capsule |
|
|
ataxic hemiparesis
|
pons, midbrain, internal capsule |
|
|
dilated thin-walled vessels with no smooth muscle or elastic fibers and no intervening brain parenchyma |
cavernous malformation |
|
|
thin-walled venous structure with normal intervening brain tissue |
venous angioma
|
|
|
abnormally dilated capillaries, normal intervening brain tissue
|
capillary telangiectasia |
|
|
hypertensive hemorrhage
|
putamen, caudate, thalamus, pons, cerebellum and deep white matter |
|
|
retinal artery origin
|
ICA>ophthalmic artery>retinal artery |
|
|
anterior choroidal artery
|
ICA origin, supplies internal segment of the GP and posterior limb of the internal capsule |
|
|
BP with tPA
|
<185/110 |
|
|
surgery with tPA |
major surgery w/in the prior 14days
|
|
|
nl CT with ASPECTs |
10 |
|
|
symptomatic stenosis 50-69%
|
benefit from CEA with greater impact in men vs women |
|
|
cavernous sinus drainage |
superior and inferior petrosal sinuses>sigmoid sinus |
|
|
MRI hemorrhage |
1-3d-iso T1 hypo T2 3-7d-hyper T1 hypo T2 1w-1mn-hyper on T1 and T2 afterward hypo T1 and hypo T2 |
|
|
Wave form with ICP
|
; 5-20 minutes with high amplitude 50-100mmHg |
|
|
Apneustic breathing
|
pontine lesion (respiratory pause at full inspiration |
|
|
decorticate posture |
flexion of the upper extremities and exension of the lower extremities |
|
|
decerebrate posture |
|
|
|
hyperventilation
|
hypocapnia leads to vasoconstriction; goal of 30mmHg of PCO2 |
|
|
serum osm goal with mannitol
|
320mOsm/L |
|
|
hypertonic saline goal
|
150mmol/L |
|
|
maximal cerebral edema
|
2-5 days post stroke |
|
|
sodium nitroprusside
|
continuous infusion can lead to cyanide and thiocyanate toxicity (causing anxiety, confusion, pupillary constriction, tinnitus, hallucinations and seizures); Tx dialysis |
|
|
epidural hematoma
|
middle meningeal artery; foramen spinosum |
|
|
nimodipine s/p SAH
|
60mg q4hrs for 21 days has been shown to improve outcomes (as has pravastatin) |
|
|
Indications for ventilation with GBS
|
VC<15-20mL/kg or reduction of >30% from baseline OR NIF less than 30 |
|
|
critical illness polyneuropathy |
nl latency and conduction velocity; reduced CMAP and SNAP with myopathic motor unit potentials; myosin loss on path |
|
|
best predictor of prognosis after cardiac arrest |
N20 SSEP (also with absent pupillary response at 24-72hrs or no corneal/eye movement in 72hrs) |
|
|
apnea test |
Must have temp >32 and SBP>90 |
|
|
MAP
|
CPP=MAP-ICP (most effective 60-159mm Hg)
|
|
|
bilateral trigeminal neuralgia
|
MS, sarcoid, lyme |
|
|
CADASIL |
AD, chrom 19, NOTCH3 |
|
|
FHM1 |
nystagmus, coma or hemiplegia |
|
|
FHM2 |
coma, long lasting hemiplegia, sz, MR (NOT associated with ataxia) |
|
|
FHM3
|
AD, chrom 2q4, SCN1A, defective pre- and post-synaptic voltage gate sodium channels |
|
|
tension HA
|
30min-7d; bilateral, pressure/tightening; mild-mod pain not worse with physical activity; no n/v no more than one of photo/phono |
|
|
migraine pathophys
|
spreading depression>activatin of central generator>ion homostasis disrupted>blood vessel dilation >vasoactive neuropeptide lead to inflammation>worsen vasodilation>pain signals to trigeminal nuceus caudalis |
|
|
triptan receptors
|
5HT-1B (constricts the vessels) and 5HT-1D (inhibits trigeminal peptide release) |
|
|
New Persistent Daily HA
|
daily, unremitting for >3mnths, with 2 of 4 of; b/l location pressure/tightening mild-mod intensity not worse with activity |
|
|
cluster HA time
|
15-180min |
|
|
paroxysmal hemcrania
|
2-30 min of severe unilateral pain; Tx: indomethacin |
|
|
Chiari I
|
>4mm of tonsillar decent in those 30-80yrs |
|
|
low CSF pressure
|
HA w/in 15 min of sitting/standing with at least one of; CSF leak on conventional myelogram, CT myelograpy o CSF OP<60mm in a sitting posiio |
|
|
frovatriptan
|
1/2 life f 26hrs (but slower onset of action) |
|
|
Doose syndrome
|
myoclonic astatic epilepsy; 1-5 yrs; irregular 2- to 3-Hz spike and wave |
|
|
Dravet syndrome
|
severe myoclonic epilepsy of infancy; typical initial presentation is with febrile seizures; DD is a rule; multiple seizure types
|
|
|
Otahara syndrome
|
early infantile epileptic encephalopathy; 1d-3mnths; tonic spasms with an EEG with burst suppresion |
|
|
West syndrome
|
|
|
|
Landau-Kleffner syndrome
|
epilepsy with multiple seizure types and acquired aphasia |
|
|
EPM1
|
Unverricht Lundborg syndrome |
|
|
Cystatin B
|
Unverricht Lundborg syndrome |
|
|
EPM2A
|
Lafora body disease |
|
|
PME and cherry red spot
|
Sialidosis |
|
|
PME and mitochondrial disease
|
Myoclonic epilepsy with ragged red fibers |
|
|
Glutamate-3 receptor antibodies
|
Rasmussen's |
|
|
alpha
|
8-13Hz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Narcolepsy
|
low hypocretin |
|
|
Febrile seizures |
5mnth-5yr (3-5% of children), Simple <15min w/o focality
|
|
|
Absence epilepsy |
Peaks around 6yrs, girls>boys |
|
|
Benign childhood epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes |
2-13yrs; 70% of sz in sleep; independent b/l broad centrotemporal spikes; AD with variable penetrance |
|
|
Hypsarrhythmia |
interictal high-amplitude slow waves on a background of irregular multifocal spikes (will disappear ictally during a cluster or during REM) |
|
|
Adding valproate to lamictal
|
may necessitate an immediate 50% dosage reduction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
OCPs and AEDs
|
increase lamictal clearance |
|
|
Aicardi syndrome
|
X-linked dominant; infantile spasm, chorioretinal lacunae and agenesis of the corpus callosum |
|
|
Benign myoclonic epilepsy of infancy
|
female predominance, 4mn-3yrs, myoclonic sz that are easily treatable |
|
|
benign neonatal sz
|
around the 5th day of life, EEG is usually normal, resolve around 4 to 6wks; KCNQ channel is implicated |
|
|
Panayiotopoulos
|
1- 3-Hz high voltage occipital spikes which disappear with eye opening and reappear with eye closure or darkness; sz with visual manifestations |
|
|
ESES
|
1-12yrs, psychomotor retardation and multiple seizure types, status epilepticus during sleep for >85% of slow wave sleep |
|
|
Unverricht Lunborg syndrome
|
EPM1 cystatin |
|
|
Sialidosis
|
myoclonic epilepsy, cherry red spot, AR with defect in NEU1 gene |
|
|
Lafora bodies
|
AR disease with EPM2A mutation Sz of varioius tpes including myoclonus, dysarthria, ataxia and cognitive decline |
|
|
Drug absorption in the elderly
|
decreased lean body mass (volume of distribution of hydrophilic drugs is smaller) fat decreases |
|
|
triphasic waves
|
small negative (upward) wave, prominent positive (downward) wave and final negative wave |
|
|
circadian pacemaker
|
suprachiasmatic nucleus in the anterior hypothalamus |
|
|
sleep terrors
|
non-REM parasomnia, occur in the first 1/3 of the night |
|
|
Arousal d/o
|
confusional arousals, sleepwalking and sleep terrors (non-REM parasomnia) arising from SWS or stage III
|
|
|
Kleine-Levin syndrome
|
recurrent episodes of hypersomnia occurring weeks to months apart (lasting days to weeks) |
|
|
Direct pathway |
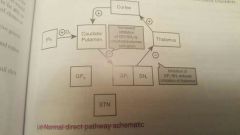
Overall excitatory |
|
|
Indirect pathway |
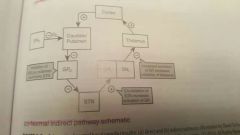
Overall inhibitory
|
|
|
Hyperkinetic movement d/o |
Reduced activity of the indirect pathway (reduced activity of the indirect pathway which disinhibits the thalamus leading to increased activity) |
|
|
Hypokinetic movement d/o
|
reduced activity of the direct pathway (SNc degenerates in PD reducing activity which leads to a reduced excitation of the direct pathway and reduced inhibition of the indirect pathway)
|
|
|
MOA of ropinirole and pramipexole
|
dopamine agonist at D2 and D3
|
|
|
MOA of dopamine
|
dopamine precursor converted into dopamine by dopa-decarboxylase
|
|
|
Most common gene mutated in herediatory PD
|
leucine-rick repeat kinase 2 (LLRK2)
|
|
|
neuroacanthocytosis |
tongue-protrusion dystonia, chorea, acanthocytes on wet mount
|
|
|
HD
|
chrom 4, CAG expansion
|
|
|
Torsin A mutation
|
primary generalized dystonia, AD, chrom 9, DYT1 dystonia
|
|
|
Filipino with dysonia and PD
|
DYT3, lubag, X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism
|
|
|
DRD genetics
|
AD, GTP cyclohydrolase 1 on chrom 14
|
|
|
Episodes of ataxia and facial twitching; diagnosis/gene/triggers/treatment
|
Myokymia on EMG |
|
|
Episodes of ataxia with nystagmus and dysarthria
|
Episodic ataxia type II, CACN1A4, Triggers: EtOH, stress and fatigue, Tx: acetazolamide |
|
|
Neurotransmitter in hyperekplexia
|
Glycine |
|
|
Antibodies in stiff person syndrome
|
GAD and anti-amphiphysin (paraneoplastic)
|
|
|
High arched feet, scoliosis, neuropathy, ataxia, cardiomegaly
|
Friedreich's ataxia, GAA repeat in frataxin gene on Chrom 9; AR |
|
|
Telangiectasia, ataxia, oculomotor abnormalities, immunodeficiency, hematologic malignancy
|
ataxia-telangiectasia, AR, ATM gene on chrom 11, impaired DNA repair |
|
|
Ataxia with high serum alpha-fetoprotein
|
ataxia-telangiectasia and ataxia with oculomotor apraxia type 2 |
|
|
SCA-3 (Machado-Joseph disease)
|
CAG repeat expansion, AD, ataxia, spasticity, neuropathy |
|
|
Ataxia, parkinsonism in grandfather of a boy with fragile X syndrome
|
Fragile X-tremor-ataxia syndrome (FXTAS) from permutation in CGG in FMR1 on chrom X, T2 hyperintensities in cerebellum and inferior cerebellar peduncle |
|
|
ataxia, cataracts, tendon xanthomas |
cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis, serum cholestanol |
|
|
"Eye of the tiger"
|
hyperintensity surrounded by hypointensity in the basal ganglia, seen in PKAN (pantothnate-kinase-associated neurodegeneration) |
|
|
medication that improves cardiomyopathy in Friedreich's ataxia
|
Idebenone, a coenzyme Q10 analogue |
|
|
striatum |
caudate and putamen |
|
|
lentiform nucleus |
putamen and globus pallidus |
|
|
Dopamine receptors in the pituitary gland
|
D2 receptors (activity inhibits prolactin release and thus hyperprolactinemia is seen in pts taking antipsychotics) |
|
|
PET in PD
|
hypometabolism in the putamen |
|
|
iPD tremor |
lips, chin and jaw |
|
|
iPD rigidity
|
striatal toe (extension of the big toe with flexion of the other toes), camptocormia, striatal hand (ulnar deviation of the wrist with flexion at the MCP joints and extension in the interphalangeal joints) |
|
|
PD pathophysiology
|
Results from the degeneration of the dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta |
|
|
PARK2
|
AR parkinson's with juvenile onset |
|
|
PARK1
|
AD, young onset |
|
|
amantadine
|
anti-glutamatergic effects, increases presynaptic dopamine release |
|
|
Selegiline |
MOAB inhibitor which is metabolized to methamphetamine and can lead to insomnia (unlike resagaline which does not have amphetamine like properties)
|
|
|
DBS target sites |
STN, GPi and ventral intermediate
|
|
|
Synucleopathies |
MSA Lewy "PML" |
|
|
hot crossed buns signs |
MSA, due to loss of pontine neuron and pontocerebellar tracts with intact corticospinal tracts |
|
|
vascular parkinsons |
most often from multiple lacunes in the basall ganglia (classically affects the lower extremities more than the upper extremities and tremor is not a prominent feature)
|
|
|
Maganese toxicity
|
seen in welders, miners, chronic liver disease patients and those on total parenteral nutrition; psychiatric symptoms, parkinsonism (usually w/o tremor) and typical gait with toe walking with elbow flexion "cock walking" |
|
|
ET
|
4-8Hz postural tremor with or without a kinetic component |
|
|
Rubral tremor
|
low-frequency tremor typically presenting at rest with posture and with action; from lesions in the dentate nucleus or cerebellum and/or superior cerebellar peduncle (often seen in MS patients) |
|
|
Tourette's
|
at least one motor and one phonic tic beginning prior to the age of 18 |
|
|
Wilson's disease
|
Wing beating tremor, characteristic grin |
|
|
MRI in Wilsons
|
increased signal on T2 weighted images of the caudate and putamen as well as midbrain sparing the red nucleus "double panda sign" and thalamus |
|
|
Huntington's clinical features
|
motor impersistence (inability to sustain tongue protrusion), impaired saccades and pursuits with insuppressible head movements during eye movements |
|
|
Sydenham's disease Tx
|
anti-dopamingergic therapies |
|
|
Benign hereditary chorea |
AD, with chorea and mild gait ataxia (mutation in thyroid transcription factor gene) |
|
|
Neuroacanthocytosis |
AD, XLR and sporadic forms have been reported |
|
|
Lesch-Nyhan |
Hyperuricemia (nephrolithiasis), self mutilating behavior, neuropsychiatric symptoms and chorea, athestosis and rigidity |
|
|
PKAN
|
AR d/o with dystonia, abnl movements and cognitive decline |
|
|
Tx of tardive dyskinesia
|
Clozapine, tetrabenazine or resperpine (deplete dopamine), levodopa, VPA and clonazepam |
|
|
Primary generalized dystonia
|
AD, mutation in torsin A (usually begins in childhood with action-induced limb dystonia that later spreads to involve trunk and other limbs) |
|
|
Lance-Adams syndrome
|
action myoclonus manifesting after HI injury
|
|
|
palatal myoclonus
|
Can see hypertrophy of the inferior olive on MRI |
|
|
Paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesias
|
Tx AEDs (CBZ) |
|
|
Paroxysmal nonkinesigenic dyskinesia
|
2min-several hours sometimes with no clear precipitant (though sometimes EtOH or stress can precipitate the d/o); doesn't respond well to AEDs |
|
|
Paroxysmal exertional dyskinesias
|
triggered by prolonged exercise; last 5-30 min |
|
|
episodic ataxia II |
Tx acetazolamide |
|
|
episodic ataxia IV
|
ataxia episodes are associated with ocular motion abnormalities and maybe triggered by sudden head movement |
|
|
purkinje cells
|
main output of the cerebellum with GABA output (project to dentate, emboliform and globose nuclei which then project to the superior cerebellar peduncle>thalamus>cortex>brainstem |
|
|
medications causing cerebellar toxicity
|
cytarabine and 5-flurouracil |
|
|
friedreichs ataxia |
GAA repeat in the frataxin gene on chrom 9 |
|
|
ataxia telangictasia
|
AR, neuropathy, ataxia and extraocular movement abnormalities characteristically with inability to move the eyes without head thrusting |
|
|
balo's concentric sclerosis
|
form of demyelination with concentric sclerosis may appear as an onion skin lesion on MRI |
|
|
useless hand of oppenheim |
sensory deafferentation makes the hand feel useless with otherwise normal motor function |
|
|
MS mimics
|
B12, lupus, lyme |
|
|
optic neuritis and MS
|
in a 15yr period MS occurs in ~50% of cases (increased risk with MRI lesions)
|
|
|
visual acuity and ON
|
<20/50 did not measurably benefit from treatment with steroids |
|
|
crossed abductors
|
implies spread of the reflex above level L4 into L2/3 indicating disinhibition of the reflex arc |
|
|
CSF with MS
|
may have elevated WBC but usually no more than 50 (usually lymphocytes) |
|
|
hemorrhagic leukoencephalopathy of Weston Hurst
|
immune mediated encephalopathy with areas of hemorrhage often in the temporal lobe (maybe a subform of ADEM)
|
|
|
MS and pregnancy
|
Interferons should be stopped at least one month prior to conception |
|
|
Risk of developing MS with an affected family member
|
3-5% |
|
|
Natalizumab
|
monoclonal antibody against cellular adhesion molecule alpha4-integrin (binds to lymphocytes and prevents adherence to the blood vessels in the brain and gut) |
|
|
PML risk with Tysabri
|
1/1000 |
|
|
Tysabri SE
|
Anaphylaxis occurs in about 1/50 patients often in the 2nd or 4th dose and is an absolute contraindication to restarting natalizumab |
|
|
Fingolimod
|
active modulator of 4/5 sphingosine-1 phosphate receptors (making the cells not have the signal necessary for egress from the lymph nodes an secondary lymphoid tissue) |
|
|
Dalfampridine
|
walking medication, voltage-sensitive potassium channels
|
|
|
Cladribine
|
purine nucleoside analogue that interferes with behavior and proliferation of certain WBCs/lymphocytes (MS Med) |
|
|
glial neoplasm with necrosis and pseudopalisading nuclei
|
glioblastoma multiforme |
|
|
fried egg appearance
|
oligodendrogliomas (fixation artifact) |
|
|
perivascular pseudorosettes
|
ependymomas |
|
|
true rosettes |
ependymoma |
|
|
homer-wright rosettes |
medulloblastoma
|
|
|
Ki67
|
marker of nuclear proliferation |
|
|
glial fibrillary acidic protein
|
marker of glial intermediate filaments |
|
|
Melan-A/HMB-45 |
melanocytes |
|
|
Cytokeratin
|
marker of epithelial intermediate filaments |
|
|
cd3
|
tcells |
|
|
Rosenthal fibers |
pilocytic astrocytoma, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, Alexander's disease, chronic reactive gliosis |
|
|
1p19q deletion
|
good prognostic factor for oligodendrogliomas |
|
|
Tumors presenting with sz
|
oligodendrogliomas, SEGA, DNET, gangliogliomas |
|
|
von Hippel-Lindau |
cerebellar hemangioblastoma, chrom 3; AD |
|
|
Zellballen arrangement of nest of cells |
paraganglioma |
|
|
brain mets
|
lung>breast>melanoma |
|
|
anti-hu (AANA-1)
|
small cell carcinoma; associated with sensory neuropathy and neuronopathy |
|
|
Anti-Ri (ANNA-2)
|
Can see opsoclonus myoclonus with SCLC cancer and in children neuroblastoma->Tx ACTH |
|
|
paraneoplastic retinal degneration
|
SCLC; anti-recoverin Ab |
|
|
limbic encephalitis and testicular germ cell tumor |
anti-ma |
|
|
types of diffuse astrocytomas
|
fibrillary, gemistocytic and protoplasmic |
|
|
Diffuse astrocytomas grade/mri
|
WHO grade II/ T2 hyperintense with no enhancement |
|
|
meningeal carcinomatosis
|
Polyradiculopathies, multiple cranial neuropathies, AMS Tx whole brain radiation and intraventricular methotrexate |
|
|
ependyomoma
|
3rd most common CNS tumor in children, 90% are intracranial typically in the 4th ventricle (can lead to elevated ICP) |
|
|
oligoastrocytomas
|
have a better prognosis than pure astrocytomas but worse than oligodendrogliomas
|
|
|
Astrocytoma grade/survival
|
grade II-no enhancement 5-10yrs grade III-some enhancement 2-3yrs grade IV-ring enhancement 15mnth |
|
|
paraneoplastic optic neuropathy
|
anti-CRMP-5 (associated with lung cancer)
|
|
|
meningiomas |
momomorphic cells with oval nuclei sometimes with psammoma bodies |
|
|
ependymomas |
sheets of cells with round nuclei with perivascular pseudorossettes and true ependymal rosettes |
|
|
p53 mutation |
seen with nearly 1/2 of anaplastic astrocytomas |
|
|
pilocytic astrocytoma |
who grade I, cerebellum most common location, cystic with gad-enhancing mural nodule |
|
|
pleomorphic xanthoaxtrocytoma |
Eosinophilic granular bodies and Rosenthal fibers maybe seen |
|
|
SEGA
|
hamaromatous tumor in the intraventricular region; who grade I; perivascular pseudorosettes, candle gutterings are masses alonge the ventricular surface similar histologically to SEGA |
|
|
Oligodedroglioma staining |
negative for glial fibrillary acidic protein |
|
|
Ganglioglioma
|
glial and neuronal components; common in children in the temporal lobes with sz; cyst with enhancing mural nodule; eosinophilic granular bodies; GFAP and synaptophysin positive |
|
|
synaptophysin
|
marker of neuronal differentiation which detects neuronal vesicle proteins |
|
|
NF2 tumors
|
ependymoma, schwannoma, meningioma (more than 1/2 of meningiomas are associated with loss of chromosome 22) |
|
|
hemangioblastoma
|
most common primary cerebellar neoplasm in adults, ~10% of these tumor secrete an erythropoietin like substance leading to secondary polycythemia); who grade I, 25% associated with von Hipplel Lindau |
|
|
medulloblastoma
|
homer-wright pseudorosettes, invasive tumor which arises from the cerebellum in children (~20% of childhood brain tumors) |
|
|
colloid cysts |
arise near the foramen of monro and can produce HA or drop attacks/acute hydrocephalus; have a thin-walled lining containing thick gelatinous fluid |
|
|
Epidermoid cysts |
arise from ectopic ectodermal tissue usually around the cerebellopontine angle; characteristic restricted diffuseion on DWI (helps distinguish them from arachnoid cysts)
|
|
|
dermoid cysts
|
arise from ectopic ectodermal tissue, tend to occur in the cerebellar vermis, parasellar or parapontine region; can contin hair follicles/sebaceous glands and sweat glands; can rupture and cause a chemical meningitis
|
|
|
arachnoid cysts
|
cystic space bound by arachnoid membranes |
|
|
medulloblastoma genetics
|
defect on chrom 17 is most common; poor prognosis with N-myc transcription factor amplification |
|
|
DNET
|
prominent clear spaces that seem to contain ganglion cells, often in the temporal lobe with an MRI showing cystic lesion that does not enhance; "floating neurons" microscopically |
|
|
PCNSL survival
|
5yr 25-45% |
|
|
craniopharyngioma
|
solid with cystic component frequently filled with cholesterol rick brown "machine oil like" fluid |
|
|
chordomas
|
invasive osseo-destructive tumors that arise from remnant of the primitive notochord (commonly in the clivus and sacrococcygeal region) |
|
|
schwannoma
|
elongated nuclei with palisade configurations called Verocay body; S-100 positive |
|
|
cytokeratin
|
positive with epithelial intermediate filamints |
|
|
CD45
|
lymphocytes |
|
|
GFAP positive with high % of Ki67
|
likely astrocytoma |
|
|
astrocytoma |
neoplasms that originate from the neuroglia |
|
|
acute motor and sensory axonal neuropathy
|
GM1, GM1b, GD1a |
|
|
finger abduction |
dorsal interossei (DAB; dorasal abduct) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Benedictine sign |
median neuropathy, on attempt to make a fist, absent flexion of first digit, partial flexion of second digit complete flexion of 4/5th digits |
|
|
Claw hand
|
ulnar neuropathy, on attempt to make a fist the 4/5th digits hyperextend at he MCP joints and partially flex at the interphalangeal joint |
|
|
Wartenberg sign
|
ulnar neuropathy; fifth digit abduction at rest |
|
|
Froment's sign
|
ulnar neuropathy, during attempted forceful adduction of the thumb (as with attempting to hold a piece of paper) thumb flexion occurs |
|
|
intrinsic hand weakness in a frequent bicycle rider
|
ulnar neuropathy 2/2 compression in Guyons canal |
|
|
wrist drop with strong forearm extension, reduced sensation over lateral arm
|
radial neuropathy at the spiral groove |
|
|
OK sign |
anterior interosseus neuopathy |
|
|
acute sensory neuronopathy |
GD1b |
|
|
sensory neuronopathy |
sensory ataxia, asymmetric sensory loss, areflexia, normal strength, reduced SNAP and nl CMAP |
|
|
wrist drop with weak forearm extensors in an alcoholic |
Saturday night palsy, proximal radial nerve injury prior to the spiral groove |
|
|
bilateral carpal tunnel, family history of carpal tunnel, mild sensory polyneuropathy
|
familial amyloid polyneuropathy type 2; transthyretin |
|
|
corneal dystrophy, multiple cranial neuropathies, peripheral sensorimotor neuropathy
|
familial amyloid polyneuropathy type 4 |
|
|
asymmetric demyelinating neuropathy affecting several motor and sensory nerves
|
multifocal acquired demyelinating sensory and motor neuropathy |
|
|
most common type of CMT
|
CMT1; AD demyelinating |
|
|
Duplication of PMP22
|
CMT1A |
|
|
gene mutated in X-linked CMT
|
connexin 32
|
|
|
demyelinating neuropathy with monoclonal gammopathy
|
anti-mag |
|
|
sensory loss, acral mutilation, autonomic symptoms
|
hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy |
|
|
episodes of painful burning in the hands and feet with heat exposure and exercise
|
primary erythromelalgia (or Fabrys)
|
|
|
|
GM1, GM1b, GD1a, GalNac-GD1a |
|
|
painful sensory polyneuropathy, autonomic involvement, cardac and renal involvement, FHx of the same |
familial amyloid polyneuropathy type 1, transthyretin |
|
|
porphyria I which photosensitivity does not occur
|
AIP |
|
|
enzyme deficiency in Fabry's |
alpha-galactsidase A |
|
|
mode of inheritance of Fabry's
|
X-linked |
|
|
retinitis pigmentosa, neuropathy
|
Refsum's disease, myoneurogastrointestinal encephalopathy, neurogenic muscle weakness, ataxia and retinitis pigmentosa, abetalipoproteinemia |
|
|
retinitis pigmentosa, neuropathy, taxia, low vLDL, acanthocytes on peripheral smear
|
abetalipoproteiemia, Bassen-Kornweig syndrome, AR |
|
|
giant axonal neuropathy |
AR, neuropathy, UMN, optic atrophy, tightly curled hair, large focal axonal swelling
|
|
|
Refsum's
|
AD, peroisomal d/o; retinitis pigmentosa (night blindness and visual field constriction), cardiomyopathy and skin changes; elevated phytanic acid levels |
|
|
abetalipoproteinemia
|
AR, defective triglyceride transport, fat malabsorption results in deficiencies in vit A, E, D and K, peripheral smear with acanthocytes |
|
|
H-reflex
|
equivalent of the ankle reflex, stimulate at the tibial nerve in the popliteal fossa |
|
|
early onset rapid recruitment
|
myopathic processes with loss of muscle fibers in which excessive number of short duration small amplitude MUPs fire during the muscle contraction |
|
|
fibrillation potentials
|
seen three weeks after onset of motor axon loss (3-6 months later you get large polyphasic MUP) |
|
|
LEMS
|
CMP amplitude are usually low to borderline low at rest (b/c many fibers fail to reach threshold after stimulus given inadequate release of acetylcholine vesicles); decremental response with slow stimulation (decline in acetylcholine release with each stimuli) but incremental response with rapid repetitive stimuli (>50% to be diagnostic) |
|
|
muscle fiber types
|
type I: slow oxidative type 2a:fast oxidative glycolytic type 2b:fast glycolytc |
|
|
dorsal scapular nerve/long thoracic nerve
|
arises directly from the nerve roots |
|
|
suprascapular nerve
|
innervates the supraspinatus and infraspinatus; arises from the upper trunk |
|
|
thoracodorsal
|
innervates the latissimus dorsi |
|
|
FAP1 |
3rd-4th decade; loss of pain/temp, autonomic dysfunction, cardiac/renal involvement, transthyretin |
|
|
FAP2
|
4-5th decade, carpal tunnel, slowly progressive polyneuropathy (no autonomic features) |
|
|
FAP3
|
similar to FAP1 but with early renal involvementment, abnl apolipoprotein A1 |
|
|
FAP4
|
3rd decade with corneal dystrophy and later cranial neuropathies and skin changes, abnl amyloid protein gelsolin |
|
|
CMTX
|
second most common type of CMT, demyelinating, mutation in connexin 32 |
|
|
CMT2
|
AD; axonal neuropathies, appear later
|
|
|
CMT3 (Dejerine-Sottas)
|
severe form of demyelinating CMTs, presents in infancy, AR and AD forms |
|
|
median nerve
|
derived from lateral and medial cords, does no innervate any muscles in the upper arm (above the elbow)
|
|
|
APB
|
median nerve, C8/T1, thumb abduction |
|
|
pronator teres
|
forearm protnation, C6/7, median nerve |
|
|
Anterior interosseus nerve
|
off the median nerve, innervates the flexor digitorum profundus to the 2/3rd digits, flexor pollicis longus and pronator quadrtus |
|
|
lumbosacral plexus
|
lumbar and sacral plexus connected via the lumbosacral trunk, T12-L4 |
|
|
superior gluteal nerve
|
gluteus medius, gluteus minimus and tensor fascia latae which contribute to thigh abduction |
|
|
thigh abduction when the hip is extended
|
gluteus medius/minimus
|
|
|
thigh abduction when the hip is flexed
|
tensor fascia latae |
|
|
inferior gluteal nerve
|
innervates the gluteus maximus (thigh extension) |
|
|
tibial nerve |
adductor magnus, semimembranous, semitendinosus, long head of biceps femoris (short head innervated by common peroneal nerve), gastroc, tibialis posterior |
|
|
deep peroneal nerve
|
tibialis anterior, extensor halluces, extensor digiorum lonus and brevis, peroneus teritus (lesion will cause foot drop with inability todorsiflex without impairing eversion of the foot) |
|
|
L5 vs peroneal
|
preserved foot inversion is seen with peroneal(though not L5)
|
|
|
hip flexion
|
femoral nerve, L2/3, iliacus |
|
|
knee extension
|
femoral nerve, L3/4, quads |
|
|
obturator
|
thigh adduction, L2/3/4, adductor brevis |
|
|
femoral nerve injury
|
-weakness on hip flexion suggests an intrapelvic injury |
|
|
Tangiers
|
AR, neuropathy, mutation in adenosine triphosphate transporter protein, low serum cholesterol levels an elevated triglyceride levels, orange tonsils |
|
|
brachioradialis |
radial nerve, forearm flexor |
|
|
radial nerve
|
|
|
|
foot eversion weakness
|
superficial peroneal nerve innervated muscles |
|
|
posterior interosseus nerve palsy
|
pure motor nerve, weakness of wrist extension in an ulnar direction |
|
|
Paraspinal fibrillations
|
radicuopathies but not plexopathies |
|
|
Parsonage-Turner
|
frequently affects suprascapular, long thoracic and median nerve; pain>weakness |
|
|
anterior interosseus
|
pure motor branch of the median nerve, weakness in grasping thumb and index finger on attempt to make an okay sign |
|
|
pronator teres syndrome
|
compression of the median nerve as it passes between the two heads of the pronator teres (usually occurs with repetitive movements), deep ache in the forearm and weakness of median nerve innervated muscles (pronator teres strength is intact) |
|
|
humeral fracture
|
radial nerve injury |
|
|
spinal accessory nerve
|
complication of radical neck dissection |
|
|
Wartenberg syndrome
|
superficial sensory radial neuropathy, dysesthesias and numbness over the dorsolateral aspect of the hand |
|
|
musculocutaneous neuropathy
|
anterior shoulder dislocations, coracobrachialis which assists the deltoid in anterior flexion of the arm |
|
|
axillary neuropathy
|
fractures at the surgical neck of the humerus and anterior shoulder dislocations |
|
|
Fabrys
|
alpha-galactosidase A; angiokeratoms, deposition of globotriaosylceramide |
|
|
long thoracic nerve
|
innervates serratus anterior, injury causes winging o the scapula |
|
|
thoracoabdominal polyradiculopathy
|
seen in pt with diabetes with pain and dysesthesias and motor changes in thoracic and abdominal nerves |
|
|
neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome
|
compression of C8/T1 roots, plexus passes through the scalene triangle (anterior/middle scalene and first rib) an and anomalous fibrous band between the scalenes or elongated C7 transverse process leads to compression; weakness of intrinsic hand muscles |
|
|
HSAN1
|
AD, onset in young adulthood with lancinating pains, hypohydrosis |
|
|
HSAN3 (Riley day syndrome)
|
dysphagia, vomiting and recurrent infection, absence of lacrimation
|
|
|
HSAN2
|
begins in infancy; insensitivity to pain, autonomic symptoms and cognitive dysfunction are not prominent |
|
|
HSAN4
|
|
|
|
causes of mononeuritis multiplex |
diabetes, amyloid, paraneoplatic, leprosy, SLE, RA, lymphoma, sarvoid |
|
|
Primary erythromelalgia gene
|
SCN9A |
|
|
lower trunk lesion
|
stretching as when grabbing onto something when falling; weakness in ulnar and median innervated muscles (intrinsic hand muscles and sensory loss on medial forearm and hand) |
|
|
upper trunk lesion
|
Erb'spalsy, shoulder is forecefully pulled down, waiter's tip position |
|
|
L5 radic
|
sensory impairment with dermatome extending to the big toe, weakness in toe extension and ankle dorsiflexion/inversion and eversion (foot drop) |
|
|
acute onset dysautonomia in a smoker with a lung mass
|
paraneoplastic autonomic ganglionopathy (antibody against ganglionic nicotinic acetylcholine receptor); associated with SCLC |
|
|
horner's syndrome with intact facial sweating
|
lesion distal to carotid bifurcation |
|
|
duchenne muscular dystrophy |
absent dystrophin, XLR |
|
|
throat, tongue, ear pain associated with syncope
|
glossopharyngeal neuralgia |
|
|
tilt table test with raise >30bpm or >120bmp within 10 minutes of tilt up without changes in BP but symptoms of orthostasis
|
POTS |
|
|
Emery-Dreifuss
|
LMNA, AD |
|
|
central core myopathy
|
RYR1, central pale cores in NADH stains from absese of mitochondria, associated with malignant hyperthermia |
|
|
tarui disease
|
phosphofructokinase deficiency |
|
|
cause of Hirschsprung's |
maldevelopment of myenteric plexus (sometimes due to RET proto-oncogene) |
|
|
Becker's MD
|
abnormal or reduced dystrophin, XLR |
|
|
Coris disease |
debranching enzyme deficiency (glycogenosis type III) |
|
|
McArdles |
myophosphorylase deficiency(converts glycogen into glucose-6-phosphate), glycogenosis type V, AR; exercise induced weakness, cramps and contractions, no production of lactic acid |
|
|
dermatomyositis |
perifasicular atrophy |
|
|
gene in myotonic dystrophy
|
CTG repeate, DMPK gene |
|
|
pompe's disease |
acid maltase deficiency |
|
|
emery-dreifuss (protein, inheritance) |
LMNA (encodes laminin A/C), AD |
|
|
Oculopharyngeal dystrophy
|
GCG repeat, PABP2 gene |
|
|
myotonic dystrophy
|
CCTG repeat, zinc finger protein |
|
|
inclusion body myositis
|
rimmed vacuoles
|
|
|
critical illness myopathy (path)
|
myosin loss |
|
|
Andersen's disease |
branching enzyme deficiency |
|
|
hypokalemic periodic paralysis |
No myotonia Triggered by exercise, CHO, EtOH, cold and emotions Tx acetazolamide and K+ sparing diuretics |
|
|
hyperkalemic periodic paralysis
|
Tx glucose or thiazide diuretics |
|
|
Andersen-Tawil syndrome
|
periodic paralysis, ventricular arrhythmias and dysmorphic features |
|
|
steroid myopathy |
atrophy of type II fibers |
|
|
centronuclear myopathy |
XLD or AD or AR |
|
|
anti-striational muscle antibodies
|
MG with thymoma |
|
|
Fukuyama MD
|
AR, mutation in fukutin on chrom 9, weakness/ocular and CNS abnl (MR and sz with white matter changes in the frontal region); joint contractures |
|
|
Laminin-alpha-2
|
merosin deficiency, extraocular and facial muscle are spared, contractures |
|
|
FSHD
|
AD deletion in D4Z4, upper arm more atrophic than forearms, "beevor" sign |
|
|
oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy
|
pts are typically French Canadian; GCG opoly A binding protein 2 |
|
|
DM1
|
AD, CTG expansion on chrom 19; fontal balding, atrophy of masseters and temporalis and weakess and atrophy of small muscles of the hands, forearms and peroneal muscules |
|
|
carotid sinus hypersensitivity
|
syncope with asystole for at least three seconds or fall of >50mmHg in SBP in response to pressure on the carotid sinus |
|
|
thymectomy
|
recommended for patients with MG and symptom onset prior to the age of 60 |
|
|
paramyotonia congenita
|
AD, SCN4A, no "warm-up"; worsened with exercise and exposure to cold |
|
|
Nonaka myopathy
|
AR, foot droop but no bulbar involvement |
|
|
Welander MD
|
AD, onset 40-60yrs, distal myopathy |
|
|
Markesbery-Griggs
|
AD distal myopathy with onset later in life; gene encoding titin |
|
|
Miyosihi myopathy
|
AR presenting in adults with weakness and atrophy in distal leg muscles predominantly in the posterior compartment |
|
|
Dysferlin
|
associated with limb girdle MD type 2B |
|
|
anti-Jo
|
if seen in dertamtomyositis can be associated with ILD |
|
|
pure autonomic failure
|
loss of intermediolateral cell column neurons from deposition of alpha synuclein, orthostatic hypotension, early satiety, urinary hesitancy and neck/shoulder aching (coat hanger distribution) |
|
|
orthostatic hypotension
|
decrease in SBP by >20 or DBP>10 or HR >20 |
|
|
rimmed vacuoles
|
IBM
|
|
|
mutation in SLCO1B
|
predisposition to develop statin-induced myopathy |
|
|
LGMD1 (inheritance) vs LGMD2 |
LGMD2-AR |
|
|
LEMS
|
|
|
|
Tx of LEMS
|
3,4 diaminopyridine (DAP) which inhibits presynaptic potassium channels prolonging depolarization and increasing acetylcholine vesicle exocytosis
|
|
|
Nemaline myopathy
|
variability from severe congenital forms to adult onset forms; proximal weakness, cardiomyopathy and prominent respiratory muscle compromise
|
|
|
Glycogenosis type II
|
-Pompe's infantile form -Childhood form -Adult (2-4th decade) with proximal weakness that typically involves the diaphragm |
|
|
Congenital myasthenia
|
choline acetyltransferase deficiency shows NO prominent extra ocular eye muscle involvement slow channel syndrome-AD inheretance |
|
|
Ulriches congenital MD
|
neonatal weakness/contractures, distal hyperlaxity, protrusion of the calcanei |
|
|
Bethlem myopathy
|
mutations in collagen type VI; weakness and contractures as well as hyperextensible interphalangeal joints |
|
|
parasympathetic gangli
|
ganglia are located close to the target site (preganglionic acetylcholine with nicotinic receptors in the ganglia)
|
|
|
AR distal myopathies |
Moyoshi/Nonaka
|
|
|
Horners syndrome best light to be seen
|
more prominent in dim light
|
|
|
Penile erection |
parasympathetic/ejaculation is sympathetic |
|
|
external uretheral sphincter
|
voluntary control with sympathetic innervation |
|
|
myofibrillar myopathy
|
proximal and distal weakness; cardiac involvement in ~25%
|
|
|
myotonia congenita
|
Thomsen disease: AD Beckers disease: AR Mutation in chloride gene CLCN1; myotonia or impaired relaxation is seen ***have a warm up phenomena (unlike paramyotonia) |
|
|
Survival motor neuron gene 1
|
SMA |
|
|
Only LMN
|
progressive muscular atrophy, SMA and benign focal amyotrophy |
|
|
posterior 1/3 of the cord
|
posterior spinal arteries |
|
|
Brown-Sequard
|
I/l loss of motor and vibration, c/l pain and temp |
|
|
adrenomyeloneuropathy; gene/chrom |
ABCD1 gene; chrom X; impaired ability to oxidize VLCFA |
|
|
epidural lipamatosis
|
chronic steroid use |
|
|
Riluzole
|
inhibitor of glutamate release |
|
|
primary lateral sclerosis
|
UMN signs at 3yrs from symptom onset |
|
|
HTLV-1
|
causes tropical spastic paraparesis; causes chronic progressive myelopathy endemic in equatorial and south Africa |
|
|
Hereditary spastic paraparesis
|
Progressively worsening spasticity in the lower extremities; both pure and complicated forms; SPAST gene
|
|
|
% of familial ALS
|
10%
|
|
|
Radiation myelopathy
|
transient; 3-6 mnths after with dysesthesias in the extremities that resolves delayed; >6mths after |
|
|
Most common intradural intramedullary tumors
|
ependymoma and astrocytoma (children) |
|
|
Causes of atlantoaxial dislocation
|
RA; Klippel-Feil syndrome (decreased number and abnormal fusion of cervical vertebrae), Downs, Morquio syndrom |
|
|
Traumatic spinal cord injury
|
methylpred 30mg/kg with 5.4mg/kg/hr *23hrs |
|
|
superficial siderosis
|
CSF xanthochromia MRI with T2 hypointensity |
|
|
Conus medullaris
|
perineal sensory deficit which is b/l and symmetric; pain is symmetric; sometimes decreased DTRs |
|
|
Cauda equina |
radicular pain and sensory loss with an asymmetric dystribution |
|
|
Kennedy's disease |
CAG repeat on chrom X |
|
|
Posterior longitudinal ligament
|
runs along the posterior surface of the vertebral bodies but ventral to the cord |
|
|
Hirayama disease
|
progressive asymmetric wasting of one or both hands and forearms; high incidence of atopic d/o; MRI with cervical cord thinning
|
|
|
Spinal cord abscess
|
most common organism is staph aureus (CSF Cx is positive in only 25% of pts) Tx: antibiotics for 4-6 wks |
|
|
chrom 1 gene associated with AD
|
Presenilin-2 |
|
|
chrom 14 gene associated with AD
|
presenilin-1 |
|
|
chrom 19 gene associated with AD
|
apoliporoptein E4 |
|
|
chrom 21 gene associated with AD
|
amyloid precursor protein |
|
|
neuritic plaques, amyloid angiopathy, neurofibrillary tangles, granulovacuolar degeneration, Hirano bodies
|
AD |
|
|
synucliopathies
|
Parkinsons MSA Lewy body |
|
|
globose neurofibrillary tangles and tuffed astrocytes
|
PSP |
|
|
spongiform encephalopathy
|
CJD |
|
|
gerstmann's syndrome
|
dominant inferior parietal lobe, angular gyrus |
|
|
where pathway
|
parieto-occipital |
|
|
what pathway
|
parieto-temporal |
|
|
Balint syndrome
|
optic ataxia, oculomotor apraxia, simultagnosia (b/l parieto-occipital cortices) |
|
|
Kluver-Bucy syndrome
|
hyperorality, visual agnosia, hypersexuality, blunted affect, hypotamorphosis (b/l medial temporal lobes involving the amygdala)
|
|
|
dressing apraxia
|
non-dominant parietal cortex |
|
|
neglect
|
non-dominant parietal cortex |
|
|
conjugate gaze deviation c/l to hemiparesis
|
lesion in frontal eye fields |
|
|
MCA-ACA watershed
|
transcortical motor aphasia (disconnecting SMA from Brocas) |
|
|
MCA-PCA watershed |
transcortical sensory aphasia (or thalamic) |
|
|
ideomotor apraxia |
patient understand the movement to be executed but has difficulty with postural and spatial orientation; dominant parietal cortex |
|
|
ideational apraxia |
patient struggles with temporal sequence of events; bifrontal or biparietal cortex
|
|
|
MCI
|
impairments in one or more cognitive domains (amnestic MCI has a 15%/yr conversion rate) |
|
|
Papez circut
|
entorhinal cortex>hippocampus>fornix>mamillary bodies>anterior nucleus of the thalamus>cingulate>entorhinal cortex |
|
|
Immediate memory
|
the amount of information someone can keep in concious awarness without active memorization (forward digit span)
|
|
|
Working memory |
manipulation of information retained in immediate memory (adding two of the digits repeated)
|
|
|
Recent memory
|
ability to recall spicific items after a delay of minutes to hours; requires hippocampus and parahippocampus (imapired first in early AD)
|
|
|
Remote memory
|
asking about hisortical life event and long-known information
|
|
|
Declaritive memory |
facts and events (significantly affected in AD)
|
|
|
episodic memory
|
specific events and contexts (most imparied in early AD) |
|
|
pathophys of AD
|
loss of cholinergic neurons in the nucleus basalis of Meynert and loss of choline acetyltransferease activity
|
|
|
Locus coeruleus
|
NE
|
|
|
median and dorsal raphe nuclei
|
serotonin
|
|
|
nucleus accumbens and ventral tegmental area
|
dopamingergic neurons
|
|
|
substantia nigra pars reticulata
|
GABAergic neurons (as compared to the pars compacta whic hcontian dopaminergic neurons)
|
|
|
dorsolateral frontal lobe lesion
|
planing of motor acitivity, problem solving, personality changes, perseveration, apathy, anhedonia and depression
|
|
|
orbitofrontal cortex lesion
|
OCD, disinhibition, hypersexuality, anxiety, depression, impulsiveness, echoapraxia, utiliation behavior (mimicking of the use of objectS) and antisocial behavior
|
|
|
familial FTD
|
most commonly associate3d with 17q21 (and chrom 3/9) |
|
|
progressive non fluent aphasia
|
anomia, word-finding difficulty, effortful speach>>>>global aphasia
|
|
|
semantic dementia
|
progressive speech disturbance with normal fluency but impaired comprehansion, anomia and semantic paraphasias (may resemble transcortical sensory aphasia) with typical left temporal dysfunciton (and/or face/object recognition dysfunction reflecting right temporal dysfunction) |
|
|
dorsomedial nucleus of thalamus |
projects the the dorsolateral prefronal, orbitofrontal, anterior cingulate gyrus and tempral lobe/amygdala
Lesions cause abulia, anterograde amnesia, social disinhbition and motivation loss
|
|
|
anterior nuclues of the thalamus
|
limbic relay and memory formation (Papez circut)
|
|
|
pulvinar nucleus
|
processing visual information and sensory integration
|
|
|
ventral posterolateral nucleus
|
sensory relay from the body
|
|
|
ventral posteromedial nucleus
|
sensory relay from the face
|
|
|
what interferes with ability to do rehab after TBI the most
|
alterations in personality
|
|
|
Lewy bodies
|
cytoplasmic inclusions iwht anti-ubiquitine and alpha-synuclein
|
|
|
Picks bodies
|
spherical aggregations of tau protein in neurons
|
|
|
PSP
|
globose neurofibrillary angles in neurons of subcortical nuclei and tufted astrocytes
|
|
|
memantine
|
low-to-moderate NMDA receptor antagonist (and some action at 5HT3)
|
|
|
Acetylcholine esterase inhibitors
|
Donepezile: pure acetylcholinesterase inhibitor Rivastigmine: combined acetylcholineesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitor Galantamine: combined acetylcholinesterase inhibitor and allosteric nicotinic modulator |
|
|
Neuroimaging in CJD
|
cortical ribboning, pulvinar sign and increased T2 signal in neocortex, thalamus, caudate and putamen
|
|
|
Prion protein gene
|
PRNP genel locataed on chrom 20
|
|
|
prosopagnosia can be associated with
|
achromatoopsia and visual field defects
|
|
|
Pure word deafness (visual auditory agnosia)
|
impaired auditory comprehension with normal written language comprehension distinguishing it from Wernickes (oftne in bilateral middle portions of the superior temporal gyri disconecting Wernickes from Heschl's gyrus)
|
|
|
nonverbal auditory agnosia
|
agnosia to sounds (such as the sounds that animals make) can be seen with b/l anterior temporal lesions
|
|
|
aphemia
|
pure word mutism; inability to speak fluently, imparied repetition and intact auditory comprehension (retained ability to write and comprehend written language); lesion in dominant frontal operculum anterior to Brocas area
|
|
|
Foix-Chavany-Marie
|
anteiror opercular syndrome; severe dysarthria, b/l volunary paralysis of the lower cranial nerves with preserved involuntary and emotional innervation
|
|
|
conduction aphasia
|
repitition is impaired
|
|
|
amelodia (affective motor aprosodia)
|
nondominant posteroinferior frontal gyrus (nondominant hemispheres analogue to Brocas) with loss of abilty to vary speech according to her emotional state similarilty the inability to perceive and understand emotional contex of others speech localizes to the nondominant posteriorsuperior temporal gyrus (analong of Wernickes area) |
|
|
cause of pseudobulbar affect
|
disconnect of the corticobulbar tracts from the brainstem cranial nerve nuclei Tx: dextromethaorphane-quinide combination |
|
|
conduction apraxia
|
impairment in imitation of movements
|
|
|
disassociation apraxia
|
inability to execute a movment on command but intact abilty to imitate
|
|
|
conceptual apraxia
|
misconceptin of the function of an object in the environment (using a fork to eat soup)
|
|
|
dorsomedial prefrontal cortex
|
involved in motor initiation, goal-directed behavior and motivation; lesions can lead to amotivation, apathy, a reduction of movement (involvement of SMA)
|
|
|
Wisconsin card sorting test
|
arrange cards based on a specific concept ot test frontal lobe function, visual conceptualization and set shifting
|
|
|
Capgras syndrome
|
delusional belief that a member of hte patients family is an identical-looking imposter Reduplicative paramnesia: identical places (rather than just people) |
|
|
Fregolis syndrome
|
belief that the same person exists in several disguises |
|
|
intermetamorphsis
|
belief that individuals have swapped identities while maintainent hte same external appearance
|
|
|
Cotards
|
belief that you are dead or dying
|
|
|
astereognosis
|
inabiliity to recognize shapes manipulated in teh hand (non-dominant parietal)
|
|
|
right hemiparesis with right gaze deviation
|
left pontine lesion; parapontine reticular formation leads to i/l conjugate gaze so a lesion leads to c/l gaze 2/2 unoppesed action of the c/l side not overcome with the oculocephalic maneuver
|
|
|
Nondeclarative memory |
memory of skills and other acquired behaviors; does not have a specific localization |
|
|
alien limb
|
lesion to c/l ACA involving corpus callosum or SMA (or CBD)
|
|
|
duration of symptoms distinugising schizophrenia, schizophreniform d/o and breif psychotic d/o
|
brief psychotic d/o <1mn schizophreniform 1-6mnth schozophrenia >6mnth |
|
|
secondary gain in factitious d/o
|
assumption of hte role of a patient
|
|
|
secondary gain in malingering
|
external incentives such as money
|
|
|
duration of symptoms in acute stress reaction vs PTSD
|
acute stress reactoin <1mnth PTST>1mnth |
|
|
cluster A personality d/o
|
paranoid; schizotypal (weird/odd/eccentric), schizoid (loner)
|
|
|
cluster B personality d/o
|
narcissistic; antisocial; boarderline; histrionic (attention seeking)
|
|
|
cluster C personality d/o
|
avoidant; dependent; obsessive-compulsive
|
|
|
antidepressants that lead to hyponatremia
|
SSRIs
|
|
|
MOA of haldol and other typical antipsychotics
|
D2 antagonist
|
|
|
MOA of risperidone and other atypical antipsychotics
|
D2 and 5HT2A antagnoists
|
|
|
depressive episode vs major depressive d/o
|
depressive episode 2wks; major depressive d/o diganosed after two or more episodes that occured at least two months apart
|
|
|
PET in depression |
dorsolateral prefrontal cortex is hypometabolic and orbitofrontal is hypermetabolic
|
|
|
DBS targets for depression
|
subcallosal cingulate gyrus and ventral poriton of the anterior limb of the internal capsule |
|
|
manic episode duration
|
1wk
|
|
|
hypomanic episodes
|
at least four days with milder symptoms
|
|
|
bipolar I vs bipolar II
|
bipolar I: manic bipolar II: hypomanic |
|
|
cyclothymic d/o
|
clinically attenuated form of bipolar d/o with sympomts spanning at least two years
|
|
|
hypochondriasis time
|
at least six months
|
|
|
Fluvoxamine
|
high protein binding that can interact with anticoagulant medications
|
|
|
conduct d/o
|
pervasive violantion of rules and others rights for at least 12 mnths including aggresion to people or animals, destruction of property, theft (can be given to those under 18yrs) |
|
|
antisocial personalit d/o |
have to be 18yrs of age
|
|
|
oppositional defiant d/o
|
hostile and defiant behavior for at least six months (frequent at 6-8yrs)
|
|
|
dysthymic d/o
|
insidious onset of depression for at least 22mnths over a 2yr period
|
|
|
ADHD
|
some symptoms must occur before the age of 7 Get an EKG prior to starting stimulat medications |
|
|
TCAs
|
have activity at muscarinic, histaminergic and alpha-adrenegic receptors |
|
|
adjustment d/o
|
response to a stressor that occured within three months of symptom onset and do not persist beyond six months of that stressor
|
|
|
BDZ MOA
|
GABA a
|
|
|
buspirone
|
5HT1A agonism and dopaminergic agonism
|
|
|
schizophrenia imaging
|
reduced brain volumes with atrophy in the frontal and temporal lobes, hippocampus and thalamus; PET with hypometabolism in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
|
|
|
serotonin syndrome
|
encephalopathy, autonomic hyperactivity, myoclonus, hyperreflexi and tremor
|
|
|
schizoaffective d/o
|
psychotic d/o with concomitant mood d/o (dilusions or hallucinations for at least two weeks wit absence of prominet mood symptoms make it distinguishe from depression with psychotic features)
|
|
|
antidepressant minimal trial
|
6wks
|
|
|
atypical antipsychotics
|
clozapine, olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidoen, ziprasidoen and aripiprazole; D2 and 5HT2A antagonism
Maybe more effective at treating negative symptoms; less EPS but increase risk of weight gain, diabetes and dyslipidemia |
|
|
olanzapine
|
has the highest antimuscarininc activity (dry mouth, confusion and constipation)
|
|
|
flumazenil
|
antagonist of BDZ and other sedative hypontics such as zolpidemand eszopiclone
|
|
|
Clozapine
|
can cause sz at higher doses (and agranulocytosis)
|
|
|
lithium and sodium
|
can cause hypernatremia from nephroenic DI
|
|
|
PML path |
myelin loss, giant astrocytes and altered oligodendrocytes with enlarged nuclie an dviral inclusions
|
|
|
hypopigmented lesions and enlarged peripheral nerves
|
mycobacterium leprae
|
|
|
oculomasticatory myorrhythmia
|
whipple disease
|
|
|
WNV
|
only 1% have severe neurologic presentation
|
|
|
Tx for crypto
|
amphoteracin plus flucytosin for 2-3 wks (amphotericine is associated with hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia and renal failure) and if doing well can switc hto fluconazole 200mg BID for 8-10wks
|
|
|
toxoplamosis
|
intracellular protozone (seen iwth CD4 less than 100) Tx sulfadiazine plus pyrimethamine (both agents affect folate pathways so add folinic acid to the regimen)
TMPSMX for prophylaxis (with CD4 less than 200) |
|
|
JCV
|
polyomavirus
"spaghetti and meatballs" appearance |
|
|
neonatal meningitis bacteria
|
E. coli, group B strep, gram negative bacilli, Listeria
|
|
|
1-23mnth menigitis bacteria
|
Strep pneumo, Neisseria, Strep agalactiae, H. influ, Ecoli
|
|
|
2-50yr menigitis bacteria
|
strep penumo and neisseria (older adults get listeria)
|
|
|
meningitis with neurosurg pts
|
aerobic gram negative bacili (pseudomanas), staph aureus and coag negative staph (stach epidermidis)
|
|
|
meningitis with CNS instrumentation
|
aerobic gram negative bacili (pseudomanas), staph aureus and coag negative staph (stach epidermidis) and propionibacterium acnes |
|
|
leprosy
|
lepromatous varient: impaired cell-mediated immunity-thickened nerves with multiple neuropathies and poorly demarcated skin lesions
tuberculoid varient: good celular immunity; better localized skin lesions and asymmmetric peripheral neuropathys and thickened nerves |
|
|
Tx of brain abscess
|
third generation cephalosporin, metronidazole and vanc for 6-8wks
|
|
|
TB meningits
|
affects the base of the brain and commonly causes multiple cranial neuropathies and AMS
low glucose in CSF (<40), high protein OP is usually elevate dbut may be nl |
|
|
syphilis testing
|
VDRL and RPR are less specific but more sensitive and become negative after some times
Treponemal antibodies will be positive for life (FTAb) |
|
|
fatal familial insomnia
|
prion d/o wit hintractable insomnia and sympathetic hyperactivity
|
|
|
amebic meningoencephalitis
|
naegleria fowleri, acanthamoeba and balamuthia mandrillaris
|
|
|
recurrent sinusitis, renal disease, multiple cranial neuropathies
|
Wegners granulomatois; cANCA
|
|
|
fever, abdominal pain, HA, mononeritis multiplex in pt with hep B
|
polyarteritis nodosa; pANCA
|
|
|
multiple cranial neuropathies, thick skull and elevated ALP
|
osteopetrosis
|
|
|
pentad of TTP |
microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, renal dysfunciton, fever, neurologic symptoms
|
|
|
Facial palsy involving hte upper and lower face, hilar adenopathy
|
sarcoidosis |
|
|
POEMs
|
plasma cell dyscrasia, polyneuropathy, organometaly, endocrinopathy, monoclonal gammopathy and skin changes
|
|
|
Celiacs |
CNS may be the only features (axonal peripheral neuropathy, inflammatory myopathy, cerebral calcifications, sz and prominent cerebellar involvement)
|
|
|
Tx of whipples
|
sulfonamides
|
|
|
IBD and stroke |
increased risk of both venous and arterial thrombosis
cranial nerve VII palsy with Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome (tongue fissuring and angioedema) |
|
|
hypothyrodism
|
pseudomyotonia (delay in muscle relaxation following elicitation of a DTR)
Restricted upgaze is the most common EOM abnormality |
|
|
Churg strauss
|
asthma, eosinophilia and sinus/pulmonary involvement
|
|
|
Bechets
|
uveitis, orogenital ulcers, positive pathergy skin test
|
|
|
pituitary blood supply
|
superior and inferior hypophyseal arteries which arise from the ICA
|
|
|
posterior pituitary releases
|
ADH and oxytoxcin
|
|
|
Central DI
|
thirst, polydypsia and polyuria (common after neurosurgery)
urine osm is low
Tx allow access to water and administration of vasopressin |
|
|
cerebral salt wasting
|
excessive renal losses of sodium; hyponatremia with hypovolemia; Tx is salt supplementation and isotonic fluids
|
|
|
wet beriberi
|
peripheral edema, cardiomegaly, cardiomyopathy, CHF, arrhythmia and tachycardia
|
|
|
dry beriberi
|
sensorimotor peripheral neurpathy with weakness and distal sensory loss
|
|
|
garlic breath>rapidly ascending sensory loss and weakness mimiking GBS
|
arsenic poisoning ; mees lines on nails
|
|
|
almond odor
|
cyanide
|
|
|
alopecia and painful neuropathy
|
thallium
|
|
|
cherry red skin
|
carbon monoxide and cyanide
|
|
|
wrist and foot drop in a patient with encphalopathy
|
lead poisoning
|
|
|
optic nerve necrosis
|
methanol poisoning
|
|
|
globus pallidus necrosis
|
carbon monoxide
|
|
|
putamen necrosis
|
methanol |
|
|
LSD
|
no w/d
|
|
|
DTRs in opiate vs sedative (EtOH/BDZ) w/d
|
hyperactive in EtOH/sedative but not opiate
|
|
|
reward circuit
|
dopamine from midbrain to forbrain (ventral tegmental area and nucleus accumbens)
|
|
|
amphetamines
|
direct release of dopamine and NE and inhibit their reuptake
|
|
|
MRI findings in Wernickes
|
hemorrhage in mammillary bodies, hypothalamus, medial thalami and periaqueductal gray |
|
|
EtOH w/d
|
minor 6-36hrs sz 6-48hrs hallucinosis 12-48hrs DT 48-96hrs |
|
|
Caffeine |
antagonizes adenosine which normally inhibits release of excitatory neurotransmitters
|
|
|
PCP
|
nystagmus, decreased pain (often causing superhuman appearane of strenght); noncompetative NMDA antagonist
|
|
|
B12 deficiency
|
related to defect in methionine production (B12 is a cofactor for methionin synthase which then helps with methylation of MBP)
|
|
|
mercury toxicity
|
mad hatters disease; tremor, ataxia, salivation, psychiatric symptoms
|
|
|
Botulism
|
irreversibly inhibits acetylcholine relase by cleaving proteins (SNAP-25) involved in neuroexocytosi
|
|
|
organophsphate posoining Tx
|
atropine: competes with actylcholine at muscarinic receptors to help prevent cholinergic activation
pralidoxime: bind wtih both muscarinic and nicotinic receptors to help treat neuromuscular dysfunction |
|
|
cells of origin of the peripheral nervous system
|
ectoderm, derived from neural crest cells
|
|
|
cells of origin of vertebral bodies
|
mesoderm of notochord
|
|
|
ballon cells
|
focal cortical dysplasia (a cortical development d/o of cell proliferation)
|
|
|
holoprosencephaly
|
failure of prosencephalon to divide into cerebral hemisphere and other structures. Problem during 4-8wks gesteation.
|
|
|
reduced visual acuity, panhypopit, absent septum pellucidum
|
septo-optic dysplasia
|
|
|
smooth brain, small chin, thin upper lip, intractable seizure
|
lissencephaly type I, Miller-dieker syndrome, L1S1 gene, chrom 17, d/o of microtubules and dynein |
|
|
DCX gene abnormality, phenotype and mode of inheritance
|
lissencephaly type I, DCX gene, X-linked, gene mutation leads to smooth brain in males, double cortex in females
|
|
|
three disorders associated with lissencephaly type II (cobblestone lissencephaly)
|
Walker-Warburg, Fukuyama muscular dystrophy, and muscle-eye brain of Santavuori
Developmental delay, seizures, muscular dystrophy, eye abnormalities |
|
|
Prader-Willi and Angelman
|
chrom 15q11-q13. Prader-Willi when paternally inherited, Angleman when maternally inherited
|
|
|
mental retardation, low set ears, enlarged testes
|
Fragile X, CGG trinucleotide repeat expansion
|
|
|
developmental regression at approximately 6-18mnths, hand wringing and microcephaly
|
Rett syndrome, MeCP2 gene mutation
|
|
|
Cafe au lait spots
|
NF-1
|
|
|
Shagreen patch
|
TS
|
|
|
cutaneous neurofribroms
|
NF-1
|
|
|
gene in NF2
|
Merlin gene, chrom 22
|
|
|
gene in NF1
|
neurofibromin gene, chrom 17
|
|
|
axillary or inguinal freckling
|
NF1
|
|
|
sphenoid wing dysplasia
|
NF1
|
|
|
ashleaf spots |
hypopigmented, TS
|
|
|
lymphangiomyomatosis
|
TS; females>males Tx tamoxifen |
|
|
treatement of hamartomas
|
rapamycin
|
|
|
multiple inctracranial AVMs
|
hereditatary hemorrhagic telaniectasia or Osler-Wber-Rendu syndrome
|
|
|
dental enamel pits
|
TS
|
|
|
hyperpigmented cutaneous lesions and leptomeningeal melanoma
|
neurocutaneous melanosis
|
|
|
multiple endrochondromas and secondary hemangiomas
|
Mafucci syndrome
|
|
|
retinal, cerebellar, and hemangioblastomas; chromosome and mode of inheritance
|
von Hippel-Lindau disease, chrom 3, AD
|
|
|
XLD d/o with skin lesions and variable neurologic involvement; gene
|
incontinentia pigmenti; NEMO gene
|
|
|
freckles, multiple skin and systemic maligancies, neuropathy, ataxia, cognitive decline; pathophys
|
Xeroderma pigmentosa; due ot defect in DNA repair, leading to sensitivity to UV light
|
|
|
brittle hair, b/l subdurals, developmental delay
|
Menkes disease (kinky hair syndrome); copper deficiency due to copper transporter ATP7A mutation
|
|
|
developmental delay, dysmorphic features, inverted nipples, and prominent fat pads; carbohydrate-deficient transferrin in the CSF
|
Congenital d/o of glycosylation
|
|
|
urine with musty odor fair skin with blond hair |
PKU (deficiency of phenuylalanine hydroxylase which converst phenylalanine to tyrosine; AR)
|
|
|
cystathionine-beta-synthase deficiency
|
homocystinuria
|
|
|
accumulation of branched chain amino acids (leucine, isoleucine and valine)
|
maple syrup urine disease; encephalopathy with opisothotonus and abnormal movements
|
|
|
MR, aggressiveness, self-mutilation, hyperuricemia (gout and nephrolithiasis)
|
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome: hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency
|
|
|
Gaucher cells
|
wrinkled tissue paper cells, gaucher disease, glucocerebrosidease deficiency
|
|
|
globoid cells
|
krabbe disease: glactocerebroside beta-galactosidase deficiency
|
|
|
beta-galactosidase deficiency
|
GM1 gangliosidosis
|
|
|
hexosaminidase A deficiency
|
Tay-Sachs disease |
|
|
Hexosaminidase A and B deficiency
|
Sandhoff disease
|
|
|
Acid sphingomyelinase deficiency
|
Niemann-Pick types A and B Type A involves the CNS (cherry red spot is common) Type B (does not involve the CNS) |
|
|
d/o of cholesterol trafficking in the intracellular domain
|
Niemann-Pick type C
|
|
|
Arylsulfatase A deficiency
|
metachromatic leukodystrophy
|
|
|
Fabry's enzyme
|
alpha-galactosidase deficiency
|
|
|
symmetric white matter involvement predominatly in the posterior regions, sparing the U fibers acumulation of vLCFA and ACTH (2/2 adrenal insufficiency) |
Adrenoleukodystrophy: Acyl coenzyme A synthetase deficiency Tx Lorenzos oil |
|
|
Megalencephaly, symmetric white matter involvement predominantly in the anterior regions, Rosenthal fibers on path
|
Canavan disease; aspartoacylase deficiency (accumulation of N-acetylaspartic acid--can see a peak on MRI)
|
|
|
megalencephaly, symmetric white matter involvement predominantly in the anterior regions, rosenthal fibers on path
|
Alexander disease; mutations in glial fibrillary acidic protein
|
|
|
white matter demyelination with tigroid appearance sparing the U fibers; inttermittent nodding movemnts of the head, pendular nystagmus
|
Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease; gene PLP1-Xlinked
|
|
|
kinky hair
|
Menkes disease
|
|
|
progressive external opthalmoplegia, onset <20yrs, short stature, ataxia, heart block, retinitis pigmentosa, CSF pro >100 |
Kearns-Sayre syndrome; if heart block get a pacer
|
|
|
feeding difficulties, vomiting, diarrhea, jaundice, hepatosplenomagaly, FTT, cataracts, reducing substances in the urine
|
galactosemia (three enzynes can be mutated but only galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase is associated with MR)
|
|
|
hyperammonemia, encephalopathy and respiratory alkalosis No evidence of organic acidemias, normal anion gaps and normal serum glucose level |
urea cycle disorder
|
|
|
newborn with ketoacidosis, anion gap, elevated propionic acid level; bleeding d/o
|
Propinic acidemia; AR
|
|
|
alopecia, skin rash, hypotonia, seizures, optic atrophy, hearing loss and hyperammonemia
|
biotinidase deficiency (normally cleaves biocytin and recycles biotin)
|
|
|
psychomotor retardation, myoclonic seizures, and blindness; intraneuronal deposits seen on electron microscopy (fingerprint bodies, granular osmiophilic deposits, curvilinera bodies and rectinlinera profiles)
|
NCL |
|
|
myoclonic epilepsy and cherry red spot; coarse fasial features
|
sialidosis
|
|
|
notochord
|
layer of mesodermal cells in contact with the ectoderm induces formation of the neural plate (later gives rise to the vertebral column) at 3-6wks
|
|
|
rhombencephalon
|
brain stem
|
|
|
pyruvate dehydrogenase
|
responsible for oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to carbon dioxide; XL is th emost common lactic acidosis (with low lactate/pyruvate ratio); episodic or progressive ataxia/nystagmus, dysarthria, lethargy, wekaness, hypotonia and psychomotor retardation Tx keotgenic diet and thiamine supplementation |
|
|
renal artery stenosis
|
can be assoicated with NF1
|
|
|
GLUT-1 |
AD
|
|
|
Chiari II
|
displacement of the cerebellar vermis and tonsils in association with myelomeningocele
|
|
|
accumulation of what in Fabrys
|
ceramide trihexoside; lysosomal storage of birefringent lipids on path
|
|
|
common in Finland |
infantil form of NCL
|
|
|
foramen of Monroe
|
connects latral ventricle to third ventricle
|
|
|
cerebral aqueduct
|
connects thrid and fourth ventricles
|
|
|
Zellwegers syndrome
|
cerebrohepatorenal sydrome; peroxisomal d/o; PEX gene; increased vLCFA; sometimes pachygyria or polymicrogyria
|
|
|
leigh's disease
|
mitochondrial; hypotonia, myoclonus, atqaxia, opthalmoplegia
|
|
|
Kearns Sayre
|
mitochondrial DNA deletions, opthalmoplegia, short stature, retinitis pigmentosa, ataxia, heart block and increased CSF pro >100
|
|
|
Congenital disorder of glycosylation
|
Type I: abnl synthesis of glycans
Typel II: abnormal processing and modification of gylcans>>profound MR
lipdystorphy with prominent fat pads in the buttocks and suprapubic area; invertited nipples |
|
|
splashed on skin lesions
|
incontinetia pigmenti; XLD (only females); NEMO gene
|
|
|
d/o neuronal migration
|
lissencephaly, periventricular nodular heterotopias
|
|
|
d/o of neuronal proliferation
|
megalencephaly and focal cortical dysplasia
|
|
|
d/o of cortical organization
|
polymicrogyria and schizencephaly
|
|
|
NF1
|
TWO or more of; -six or more cafe au lait macules -two or more cutaneous neurofibromas or one plexiform neuromas -inguinal or axillary freckling -optic nerve gliomas -two or more lisch nodules -NF1 in first degree relative -sphenoid whing dysplasia |
|
|
homocystinuria |
AR; deficiency in cystationine-beta-synthase; produces elevation of blood and urine homocysteine and methionine (two variants one is pyridoxine reponsive and the other is not) Collagen metabolism is affected (ectopia lentis, marfanoid habitus, osteoporosis) |
|
|
heterotopia
|
cluster of abnormally located neurons that are otherwise normal
|
|
|
periventricular nodular heterotopia
|
neurons never begun to migrate but rather remined in the subventricular area (where cortical neurons originate); in more than 1/2 the cases this d/o results from mutations in the FLNA gene
|
|
|
urea cycle d/o
|
most common is orthinine transcarbamylase deficiency (Xlinked) but the others are AR; hyperammonemia, encephalopathy and respiratory alkalosis
|
|
|
porencephaly
|
not lined with grey matter (like schizencephaly) |
|
|
Rett syndrome
|
regression at 6-18mnths; hand wringing and ohter motor stereotypies; MECP2 mutation
|
|
|
facial angiofibromas
|
resemble acne, TS
|
|
|
periungual fibroma
|
TS
|
|
|
methylmalonic acidemia
|
accumulation of propionyl-CoA and methylmal; AR, hematologic d/o leading to bleeding, metabolic acidosis, ketosis, hyperglycinemai and hyperammonemia
|
|
|
Betz cells
|
UMN of thenervous system found in the primary motor cortex |
|
|
corticocortical efferents (projections from one area of the cortex to another) |
mainly area III (external pyramidal layer)
|
|
|
corticostriate projections
|
layer V-internal pyramidal cell layer
|
|
|
corticothalmaic projections
|
layer VI-multiform layer
|
|
|
Gaucher disease
|
AR; glucocerebrosidease deficiency (leads to accumulaitono f glucocerebrosides); Type 1: no CNS involvement Type 2/3 with CNS involvement Gaucher cells with wrinkled tissue paper apperance |
|
|
Tay Sachs |
GM2 gangliosidosis hexominidase A deficiency AR increased startle, cherry-red spot, seizures, optic atrophy |
|
|
Sandhoff disease
|
GM2 gangliosidosis Hexompenidase A and B AR causes hepatosplenomegaly not seen in Tay-Sachs |
|
|
|
gyral calcifications from angiomatosis of the leptomeninges and brain; port wine nevus (some pt have only cutaneous findings without CNS involvement but can see hemiatrophy)
|
|
|
Neurofibromin
|
NF1; GTPase inhibits ras (proto-oncogene)
|
|
|
nonketotic hyperglycinemia
|
partial agenesis of the corpus callosum and high CSF gycine; hiccups
|
|
|
Krabbe disease
|
globoid cell leukodystrophy; AR; demylination of the periventricular white mattersparing hte U fibers; deficiency in galactosylceramidase
|
|
|
GM1 gangliosidosis
|
deficiency of beta-galactosidase; cherry red spot with coarse facial features and HSM
|
|
|
Alexander disease
|
mutation in gene for glial fibrillary acidic protein; diffuse white matter signal hyperintensity in the frontal lobes with involvement of the U fibers; "tadpole sign"; Rosenthal fibers
|
|
|
TS inheritance
|
AD inheritance with variable penetrance or sporadic mutation in TSC1 on chrom 9 encoding tuberin or mutation in TSC2 on on chrom 16 for protein hamartin |
|
|
Hunter syndrome
|
XLinked mucopolysaccharidosis (imparied lysosomal degredation of glycosaminogycanse----all are AR except Hunters which is Xlinked)
have nodular ivory-colored lesions on back/shoulders and upper arms |
|
|
Iduronate sulfatase
|
hunter syndrome (mucopolysaccharidoses); Xlinked; accumulation of dermatan and heparan
|
|
|
alpha-L-iduronidase deficiency
|
Hurler syndrome (mucchopolysaccharidoses); accumulation of dermatan and heparan
|
|
|
Epidermal nevus syndrome
|
epidermal nevi are slightly raised parches of hyperpigmentation that are present at birth; not all patients have neurologic manifestations; can have hemimegalencephay i/l to facial nevus
|
|
|
AIP
|
deficiency of specific enzyme involved in heme biosythetic pathyway; AD fashion; AD; elevated ALA and porphobilinogen
Sz>clonazepam/gabapentin (many AEDs can precpittate attacks) |
|
|
Channelopathies
|
Hypokalemic periodic paraylis: calcium Paramyotonia congenita: sodium Myotoia congenita: chloride Anderson's syndrome: potassium |
|
|
SSEP
|
N14: cervicomedullary junction N9: erbs point |

