![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Functional puripotentiality (current stance) |
The brain can do lots of things, but does this in ‘networks’
|
|
|
Disconnection syndrome |
Have not damaged the part of the brain we want, but the connection center for that function |
|
|
1. Primary: 2. Secondary 3. Tertiary |
1. Areas that receive information 2.Organizes/organizes primary info, brings to tertiary 3. receives processed information from secondary areas and makes associations |
|
|
Caudal (inferior) |
down toward the tail bone |
|
|
Rostral (Anterior) |
toward the nose |
|
|
Ventral (anterior) |
toward the stomach |
|
|
Dorsal (posterior)/(superior)- |
toward the back |
|
|
Lateral |
Away from the center |
|
|
Medial (aka mesial) |
Something toward the midline |
|
|
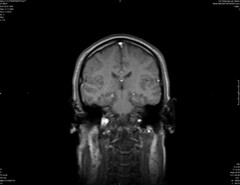
Coronal |
|
|
|
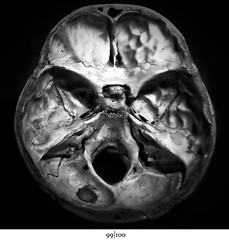
Horizontal |
|
|
|
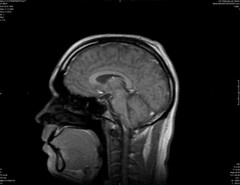
sagittal |
|
|
|
Hindbrain |
Myelencephalon + Metencephalon |
|
|
Myelencephalon |
Medula Oblongata Reticular Formation Cranial Nerves |
|
|
Medula Oblongata |
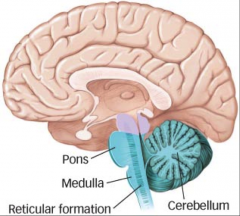
Point where fibers from periphery come up: |
|
|
|
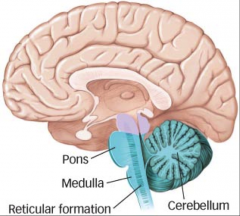
Attentional system: |
|
|
Cranial Nerves |
Nerves that control the face |
|
|
|
Pons, Cerebellum
|
|
|
Pons |
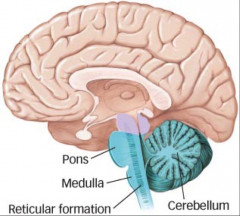
place where peripheral nerve fibers come up |
|
|
|
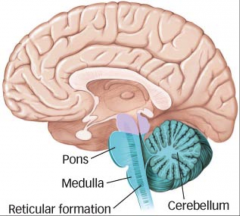
Coordination, movement, balance, (areas of cognition as well) |
|
|
|
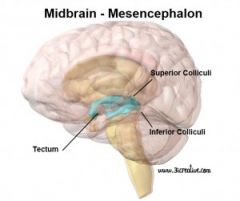
Mesencephalon |
|
|
Mesencephalon |
Tectum + Tegmentum
|
|
|
|
Superior colliculi (vision+motor coordination) |
|
|
|
Periaqueductal grey (produce endogenous opiates) |
|
|
|
Diencephalon (di meaning two – thalamus and hypothalamus ) |
|
|
Diencephalon
|
Thalamus
Hypothalamus |
|
|
Thalamus |
Large structure under corpus collosum
Relay center for sensory information (except smell) c. Phelamic peduncles (thalamic radiation) – projections from thalamus e. Consciousness first emerges. Sleep-wake cycles. And alertness. f. If there is damage, patient might be awake but not exactly present g. Problems: schizophrenia, paying attention to very arbitrary garbage of the environment. 2. Thalamus is made of distinct nuclei a. Different parts project to different parts of the brain. The Dorsal medial projects to the frontal lobes, receives most info from here. Problems here is a disconnection syndrome |
|
|
Parts of the Thalmus |
Inter-thalamic adhesion: Connects the thalami
Phelamic peduncles(thalamic radiation): – projections from thalamus |
|
|
Diencephalon
|
Thalamus
Hypothalamus |
|
|
Thalamus |
Large structure under corpus collosum
Relay center for sensory information (except smell) c. Phelamic peduncles (thalamic radiation) – projections from thalamus e. Consciousness first emerges. Sleep-wake cycles. And alertness. f. If there is damage, patient might be awake but not exactly present g. Problems: schizophrenia, paying attention to very arbitrary garbage of the environment. 2. Thalamus is made of distinct nuclei a. Different parts project to different parts of the brain. The Dorsal medial projects to the frontal lobes, receives most info from here. Problems here is a disconnection syndrome |
|
|
Parts of the Thalmus |
Inter-thalamic adhesion: Connects the thalami
Phelamic peduncles(thalamic radiation): – projections from thalamus |
|
|
Diencephalon
|
Thalamus
Hypothalamus |
|
|
|
Large structure under corpus collosum
Relay center for sensory information (except smell) c. Phelamic peduncles (thalamic radiation) – projections from thalamus e. Consciousness first emerges. Sleep-wake cycles. And alertness. f. If there is damage, patient might be awake but not exactly present g. Problems: schizophrenia, paying attention to very arbitrary garbage of the environment. 2. Thalamus is made of distinct nuclei a. Different parts project to different parts of the brain. The Dorsal medial projects to the frontal lobes, receives most info from here. Problems here is a disconnection syndrome |
|
|
|
Inter-thalamic adhesion: Connects the thalami |
|
|
Glia |
Astrocytes: provide scaffolding. Mesh or web of astrocytes that neurons sit on. This mesh provides the pathways from neuronal migration during development.
Oligodendrocytes: Produces mylon Microglia: Try and kill things that get into the brain |
|
|
Hypothalamus |
1. Also made of distinct nuclei, and must smaller.
2. Optic chasm is right around here 3. Pititary gland (snot gland) Does not actually sit inside the cranium – Hypophesis is the stalk that comes out of the hypothalamus that the pituitary gland sits upon 4. If you lesion a. lateral hypothalamus (makes animal eat) – animal starves to death. Also a reward center. Stops firing when animal starts to become full b. ventral medial hypothalamus (says stop eating)– animals eats till it dies |
|
|
Telencephalon |
Cortical tissues that is connected to other white matter tracts
|
|
|
|
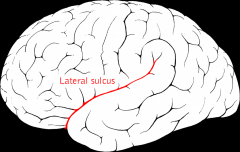
underneath is temporal lobe |
|
|
Central Fissure (Rolando) |
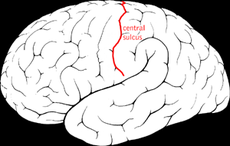
sort of perpendicular to the sylvian |
|
|
|
band of fibers that connects one side of the brain to the other – |
|
|
|
Part of the brain that connects one side to the other |

