![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
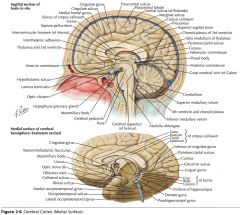
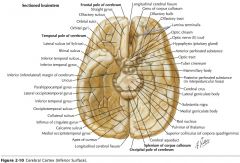
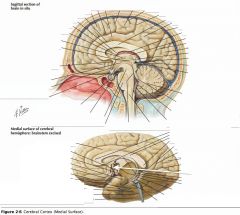
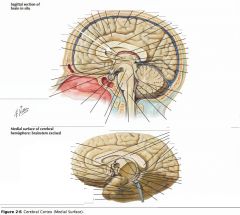
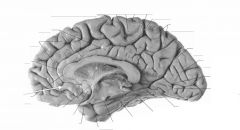
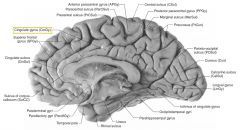
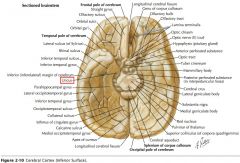
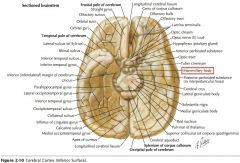
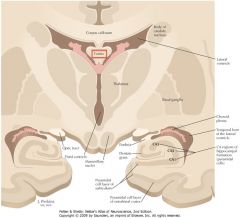
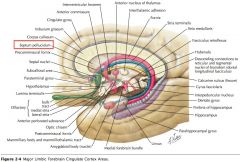
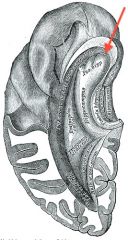
What sulcus is indicated by the white arrow?
|
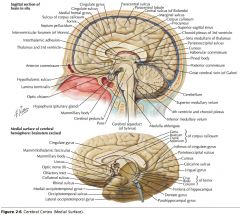
The Cingulate Sulcus.
|
|
|
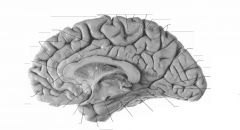
What sulcus is indicated by the white arrow?
|
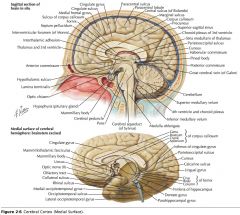
The Sulcus of the Corpus Callosum (Callosal Sulcus)
|
|
|
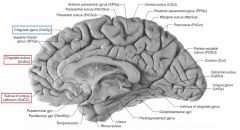
What gyrus is indicated by the white arrow?
|
The Cingulate Gyrus.
|
|
|
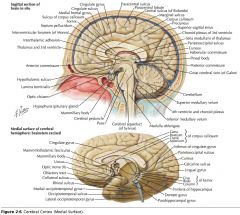
What structure is indicated by the white arrow?
|
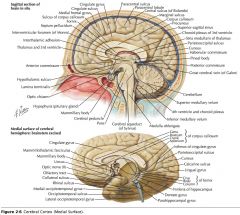
The Uncus
|
|
|
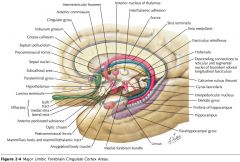
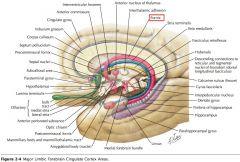
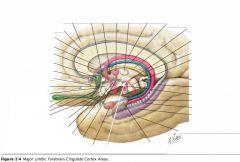
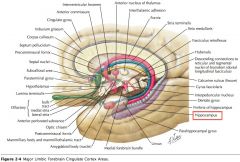
What are the Cingulate Gyrus, the Parahippocampal Gyrus and the Uncus collectively called?
|
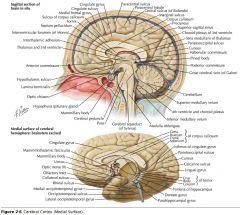
The "Limbic Lobe." (along with some associated structures)
|
|
|
What does the Limbic System do?
|
It is involved with emotion and certain kinds of memory.
|
|
|
What information does the Uncus receive?
|
It receives olfactory input
|
|
|
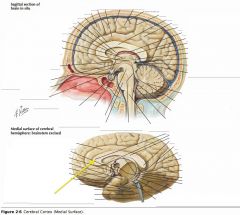
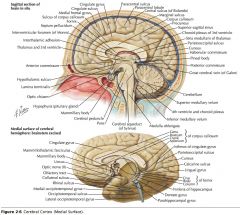
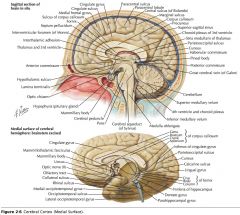
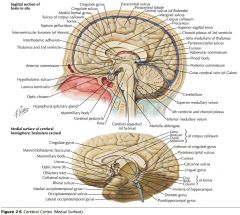
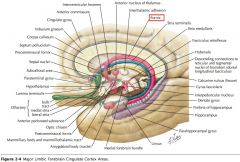
What region of the Corpus Callosum is indicated by the yellow arrow?
|
The Genu
|
|
|
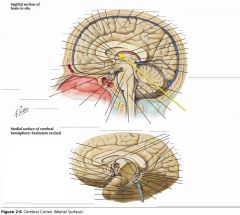
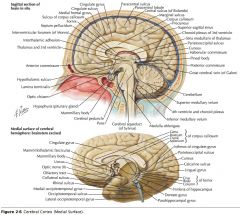
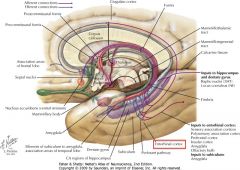
What collection of fibres is indicated by the yellow arrow?
|
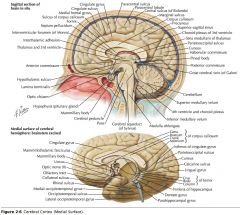
The Fornix.
|
|
|
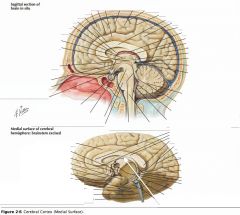
What portion of the Fornix is indicated by the white arrow?
|
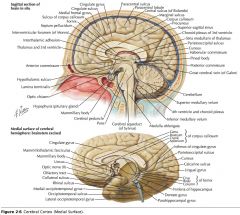
The Body.
|
|
|
What portion of the Fornix is indicated by the white arrow?
|
One of the Columns.
|
|
|
What septum is indicated by the white arrow?
|
The Septum Pellucidum.
|
|
|
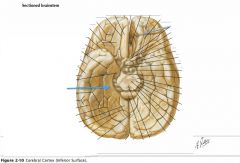
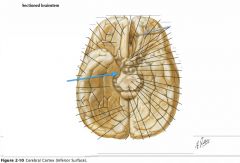
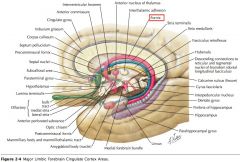
What gyrus is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
The Parahippocampal Gyrus.
|
|
|
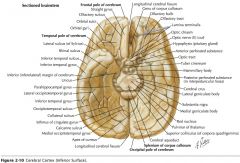
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
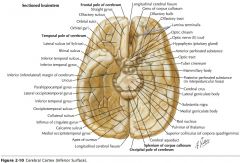
The Uncus
(a prominent bump on the Parahyppocampal Gyrus) |
|
|
What structure is indicated by the blue arrow?
|
A Mamillary Body
|
|
|
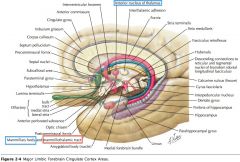
What are the Mamillary Bodies?
|
Two hypothalamic nuclei that receive input from the limbic lobe via the fornix.
|
|
|
What is the region of cortex immediately in front of and below the Rostrum of the Corpus Callosum?
|
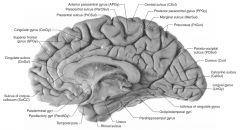
The Septal Area, including the "Parolfactory Gyrus" and the Septal Nuclei.
|
The Septal Area projects to the Hypothalamus and Brainstem.
|
|
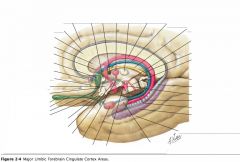
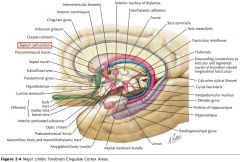
What two sulci bound the Cingulate Gyrus?
|
The Cingulate Sulcus, and
The Callosal Sulcus. |
|
|
What input does the cortex of the Cingulate Gyrus receive?
|
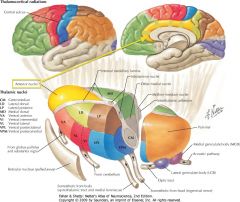
It receives input fro the Anterior Nucleus of the Thalamus.
|
|
|
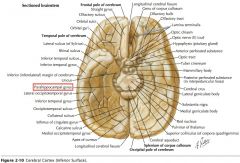
What is the anterior portion of the Parahippocampal Gyrus called?
|
It is the Entorhinal Area.
|
|
|
What is located immediately beneath the Uncus?
|
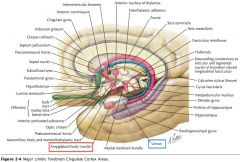
The Amygdaloid Body, or simply the Amygdala.
|
|
|
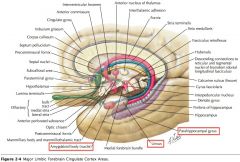
What are the Entorhinal Area, the Uncus, and the Amygdala involved in?
|
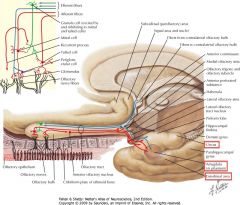
Both olfactory and limbic functions. (Olfactory shown)
|
|
|
Where do the Mammillary Nuclei receive inputs from?
Where do they project to? |
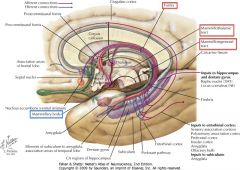
They receive inputs from the Hippocampal Formation through the Fornix.
They project to the Anterior Nucleus of the Thalamus (along the Mammillothalamic Tract) (They also project to the Brainstem along the Mammillotegmental Tract) |
|
|
What is the pathway connecting the Mammillary Bodies and the Anterior Thalamic Nuclei?
|
The Mammillothalamic Tract.
|
|
|
What is the source of fibres for the Fornix?
|
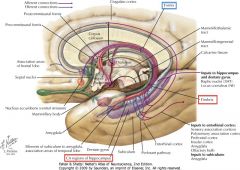
It consists of fibres arising from the Hippocampal Formation.
|
|
|
Does the Septum Pellucidum contain any neurons?
|
Yes, it contains both grey and white matter, including some neurons of the septal nuclei.
|
|
|
|
What is the name of the thin membrane stretching between the Fornix and the Corpus Callosum?
|
The Septum Pellucidum.
|
|
|
What is the posterior portion of the Fornix called?
|
The Crura (legs).
(s. Crus) |
|
|
What is the middle section of the Fornix called?
|
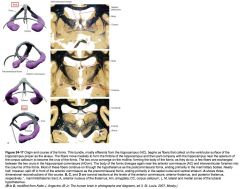
The Body
|
|
|
What is the divergent anterior portion of the Fornix?
|
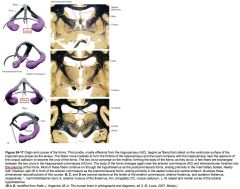
The Columns.
|
|
|
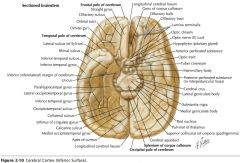
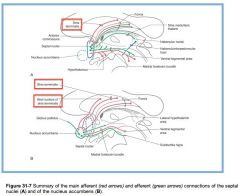
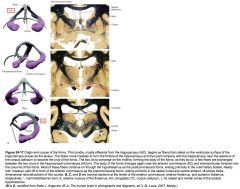
What bundle of axons is indicated by the white arrow?
What does it connect? |
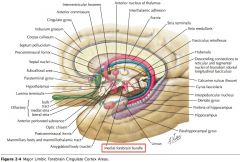
The Medial Forebrain Bundle.
It connects the Septal Area to the Hypothalamus and the Brainstem. |
|
|
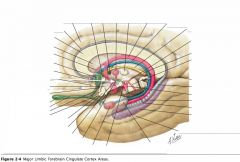
What bundle of axons is indicated by the white arrow?
What do they connect? |
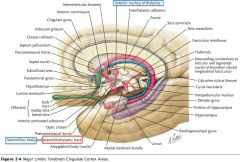
The Mammillothalamic Tract.
It connects the Mammillary bodies and the Anterior Thalamic Nucleus. |
|
|
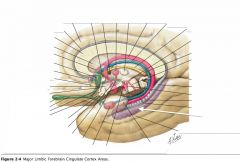
What (purple) structure is indicated by the white arrow?
|
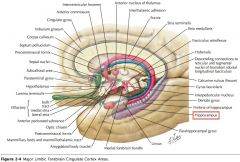
The Hippocampus (Hippocampal Gyrus).
|
|
|
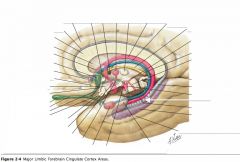
What (blue) structure is indicated by the white arrow?
|
The Dentate Gyrus.
|
|
|
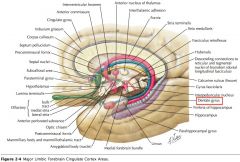
What region is indicated by the white arrow?
|
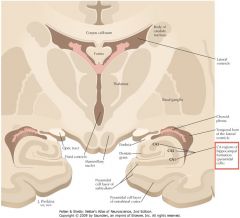
The Hippocampus (Hippocampal Gyrus)
|
|
|
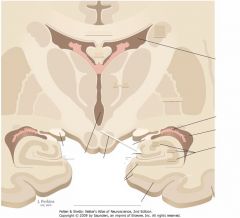
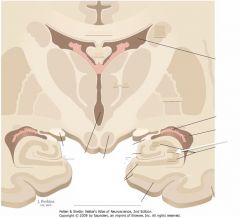
What structure is indicated by the white arrow?
|
The Dentate Gyrus
|
|
|
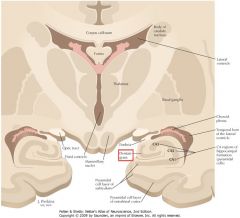
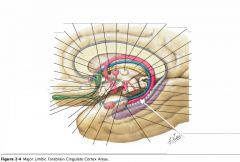
What is the most anterior portion of the Hippocampus called?
|
The Pes Hippocampi, because it looks slightly like a cat's paw.
|
|
|
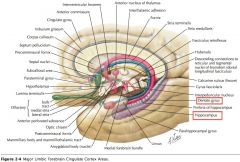
How is the cortex of the Hippocampus and the Dentate Gyrus different from the Neocortex?
|
They consist of only 3 cell layers, instead of the Neocortex's six.
|
|
|
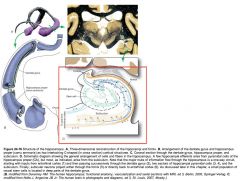
What collection of fibres is indicated by the white arrow?
|
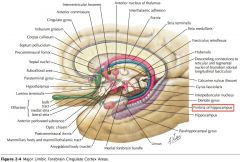
The Fimbria of the Fornix (also of the Hippocampus).
|
|

