![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

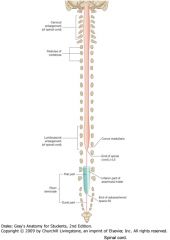
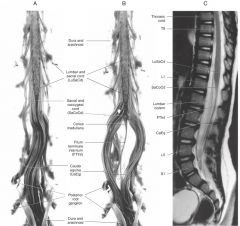
What are the superior and inferior extents of the spinal cord?
|
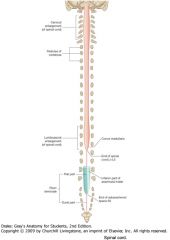
Superior: the Foramen Magnum.
Inferior: Interspace between L-1 and L-2 vertebrae. |
|
|

What are the two locations of the spinal cord where the diameter of the cord is increased?
|
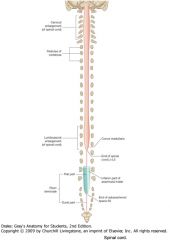
The Cervical Enlargement, between C4 and T1, and
The Lumbo-Sacral Enlargement between the L3 and S3. |
|
|
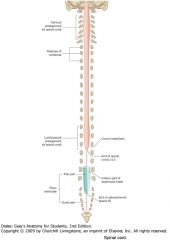
What is the reason for the cervical and lumbosacral enlargements?
|
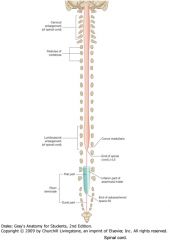
The areas of enlargement correspond to the origins of the spinal nerves that innervate the upper and lower limbs, respectively.
|
|
|
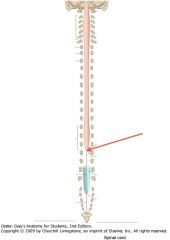
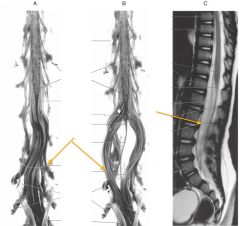
What is the point of the spinal cord indicated by the red arrow?
|
The Conus Medullaris, the point to which the spinal cord tapers.
|
|
|
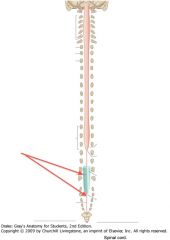
What is the structure indicated by the red arrows?
|
The Filum Terminale
|
|
|
What is the Filum Terminale?
|
It is a connective tissue filament that extends from the tip of the Conus Medullaris to insert on the posterior surface of the coccyx.
|
|
|
What is the collection of nerve fibres indicated by the orange arrows?
|
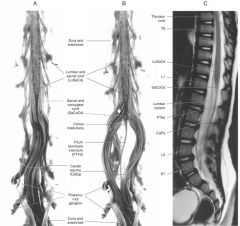
The Cauda Equina.
|
|
|
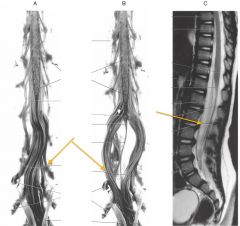
What is contained in the Cauda Equina?
|
The lumbar, sacral and coccygeal spinal nerves that continue down the vertebral canal, inferior to the Conus Medullaris.
|
|
|
|
How many Spinal Nerves are there?
|
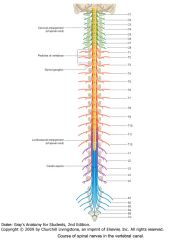
There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves:
C1-C8; T1-T12; L1-L5; S1-S5; Co |
|
|
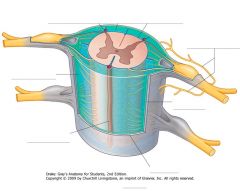
What, generally, wraps around the spinal cord?
|
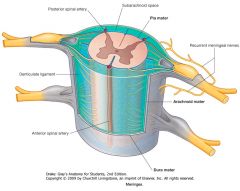
The three meningeal layers:
Pia Mater Arachnoid Outer Dura Mater |
|
|
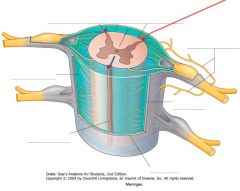
Which meningeal layer is indicated by the red arrow?
|
The inner Pia Mater, which closely invests the surface of the cord.
|
|
|
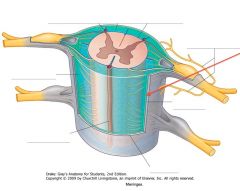
Which meningeal layer is indicated by the red arrow?
Where does it get its name? |
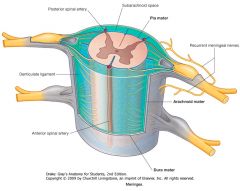
The Arachnoid Mater.
It is so named because of its delicate fibres that look like spider silk. |
|
|
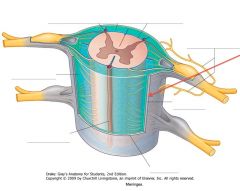
Which meningeal layer is indicated by the red arrow?
|
The Dura Mater
|
|
|
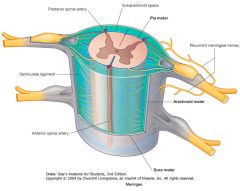
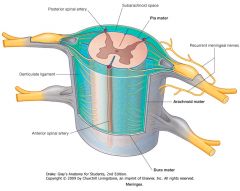
What is found in the space between the Arachnoid Mater and the Pia Mater.
|
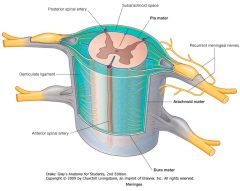
That space, called the Subarachnoid Space, is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
|
|
|
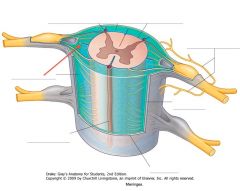
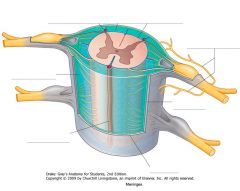
What structure is indicated by the red arrow (the darker blue bit)?
|
A Denticulate Ligament.
21 pairs of these ligaments provide attachment between the inner cord and the outer Dura Mater. |
They form roughly triangular projections of pia mater, with the base on the medial side, and the apex on the lateral side.
|
|
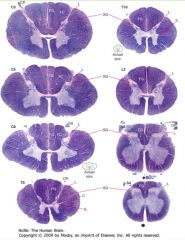
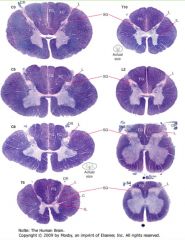
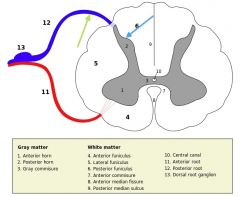
What is contained in the "grey matter" of the spinal cord?
|
It contains collections of neurons and the synapses formed on them.
|
|
|
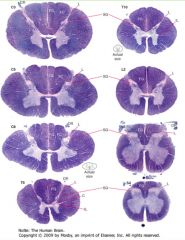
What is the "white matter" of the spinal cord consist of?
How does it appear on slides? |
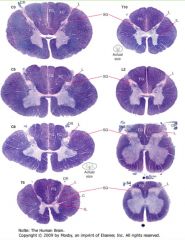
It consists of myelinated axons which ascend and descend the cord.
Because the myelin soaks up the stain, the white matter stains purple. |
|
|
|
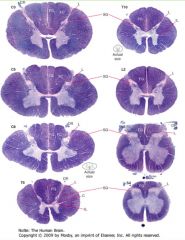
Which spinal levels have more white matter, the sacral or the thoracic?
|
Thoracic
White matter increases the more caudal on the spinal cord. |
|
|
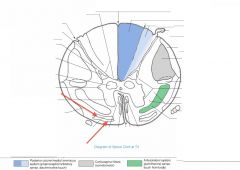
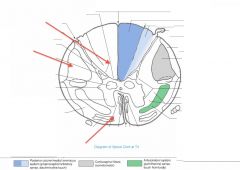
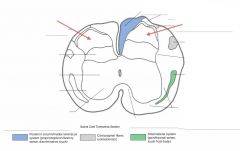
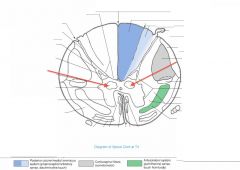
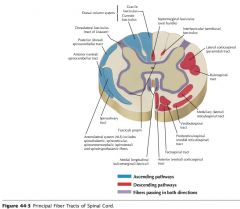
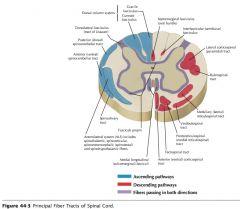
What funiculus are the tracts indicated by the red arrows part of?
|
They're part of the Anterior Funiculus.
|
|
|
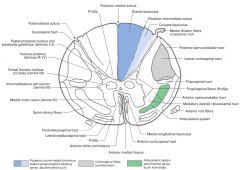
What is a Funiculus composed of?
(Three Funiculi are indicated) |
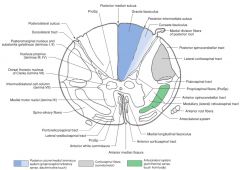
It consists of a group of tracts (bundles of axons), either ascending, descending, or both.
|
|
|
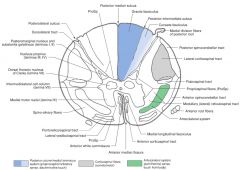
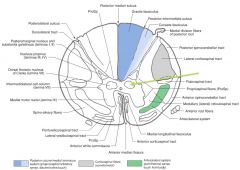
What structure is indicated by the number 2 on the diagram?
|
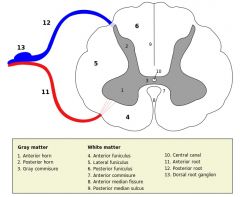
The Posterior (Dorsal) Horn of the grey matter.
|
|
|
What structure is indicated by the number 1 on the diagram?
|
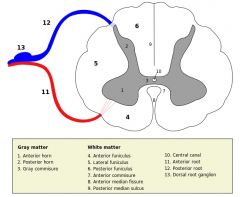
The Anterior (Ventral) Horn of the grey matter.
|
|
|
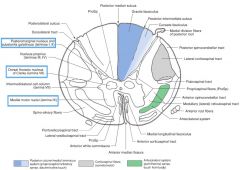
What is contained in the Nuclei (not in the cellular sense) of the grey matter? (e.g. indicated by blue boxes)
|
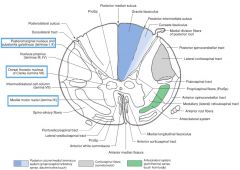
Nuclei consist of nerve cell bodies, the dendrites arising from the cell bodies and the axon terminals that synapse with them.
In 3D, the nuclei are actually columns of neurons that go up over several cord segments. |
|
|
What Nucleus of grey matter is indicated by the red arrow(s)?
What does it do? |
The Substantia Gelatinosa (Rolandi)
The neurons here process incoming pain sensations, but don't give axons conveying the information higher. |
|
|
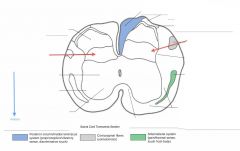
What Nucleus of grey matter is indicated by the red arrow(s)?
What happens here? |
The Nucleus Proprius.
Neurons here give rise to axons which cross the cord in the Ventral White Commissure and ascend contralaterally in the spinothalamic tracts. |
|
|
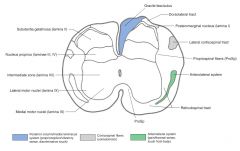
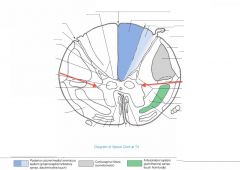
What do the neurons of the Nucleus Dorsalis do?
|
These neurons give off axons that ascend the cord in the Posterior Spinocerebellor Tract (see blue arrow), carrying proprioceptive info from the legs and trunk to the cerebellum (green arrow).
|
|
|
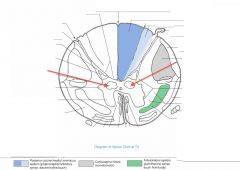
What Nucleus of grey matter is indicated by the red arrow(s)?
What levels have this nucleus? |
Nucleus Dorsalis (Clarke's Column)
It is found throughout the thoracic and upper lumbar regions of the cord. |
|
|
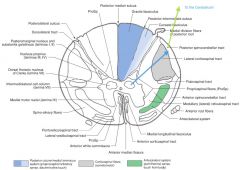
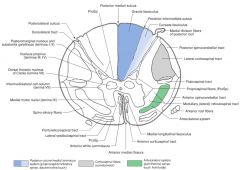
What Nucleus of grey matter is indicated by the red arrow(s)?
Where is it found? |
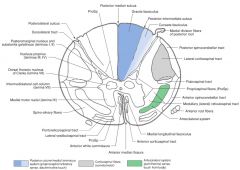
The Intermediolateral Cell Column (Lateral Horn).
It extends from the upper lumbar regions to the thoracic regions of the cord (similar to Nucleus Dorsalis). |
|
|
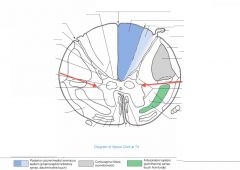
What is contained in the Intermediolateral Cell Column?
|
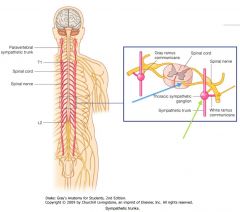
This Nucleus consists of sympathetic preganglionic motor neurons whose axons exit with the Anterior Root (blue arrow), then enter the sympathetic chain of ganglia (green arrow) via the White Ramus Cummunicantes (orange arrow).
|
|
|
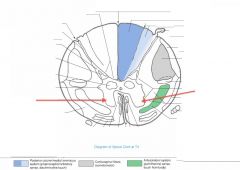
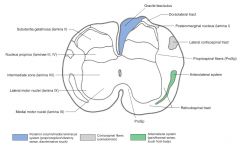
What Nucleus of grey matter is indicated by the red arrow(s)?
|
The Medial Anterior Horn group of motor neurons.
|
|
|
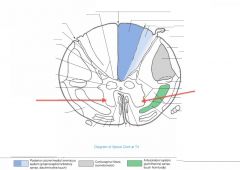
What is the function of the neurons in the Anterior Horn?
|
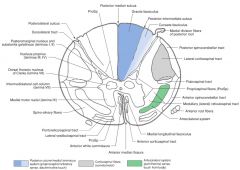
They're the nuclei of somatic motor neurons.
|
|
|
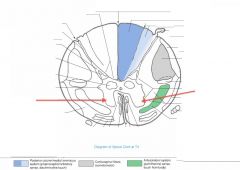
How far up the spinal cord do you find the Anterior Horn Motor Neurons Nucleus?
Where is it bigger? |
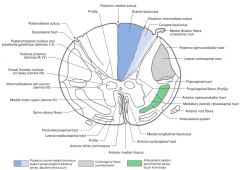
It's all up the spinal cord.
In the cervical swelling, there is both a Medial and Lateral Nucleus. It is also bigger in the area of the lumbo-sacral swelling. |
|
|
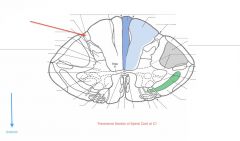
What tract of white matter is indicated by the red arrow?
|
The Dorsolateral Tract (Tract of Lissauer).
|
|
|
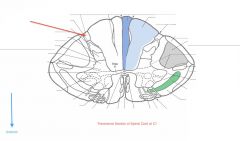
Where does the Dorsolateral Tract receive axons from?
Where do they go? |
Axons of the lateral division of the dorsal root (green arrow) enter the spinal cord and travel up or down the Dorsolateral Tract before entering the grey matter and synapsing in the Dorsal Horn (blue arrow).
|
|
|
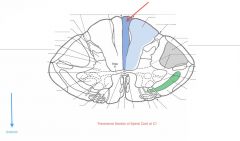
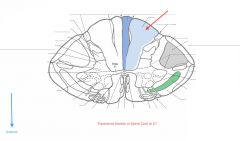
What Tract of white matter is indicated by the red arrow?
What signals does it carry? |
The Fasciculus Gracilis.
It carries sensation of fine touch, proprioception, and vibration from the lower limb. |
|
|
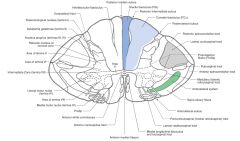
What Tract of white matter is indicated by the red arrow?
What signals does it carry? |
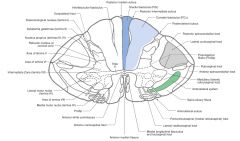
The Fasciculus Cuneatus.
Sensations of fine touch, proprioception, and vibration from upper limb. |
|
|
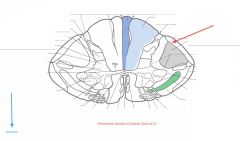
What Tract of white matter is indicated by the red arrow?
What signals does it carry? |
The Dorsal Spinocerebellar Tract.
It carries proprioceptive information from the lower limb to the cerebellum. |
|
|
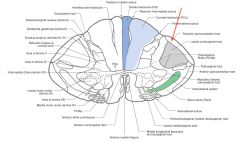
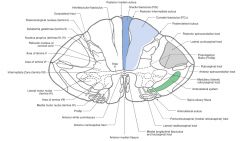
Where do the Dorsal Spinocerebellar Tracts' axons derive?
|
They come from the neuronal cell bodies in the Nucleus Dorsalis (Clarke's Column), on the same side of the spinal cord.
|
Clarke's Column is only located on the upper Lumbar through Thoracic spinal cord.
|
|
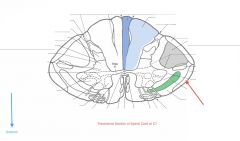
What Tract of white matter is indicated by the red arrow?
What signals does it carry? |
The Anterior Spinocerebellar Tract.
It carries proprioceptive information from the lower limb to the cerebellum. |
|
|
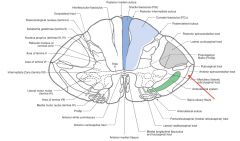
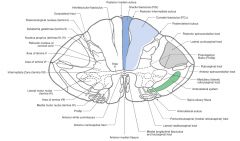
Where does the Anterior Spinocerebellar Tract derive from?
|
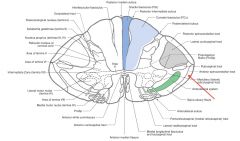
It derives its axons from the cell bodies on the other side of the spinal cord in the dorsal horn.
|
|
|
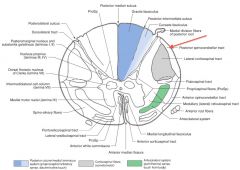
Where does the Posterior Spinocerebellar Tract (red arrow) enter the Cerebellum?
|
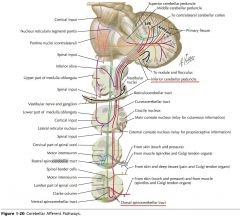
Through the Inferior Cerebellar Peduncle (see red line).
|
|
|
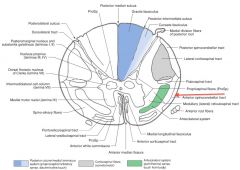
Where does the Anterior Spinocerebellar Tract (red arrow) enter the Cerebellum?
|
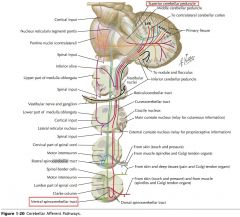
The Superior Cerebellar Peduncle (follow green line).
|
|
|
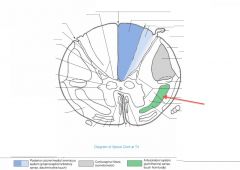
What Tract of white matter is indicated by the red arrow?
What are its divisions? |
The Anterolateral System
It's divided into the Anterior and Lateral Spinothalamic Tracts. |
|
|
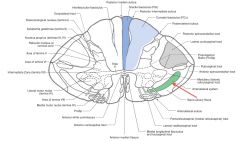
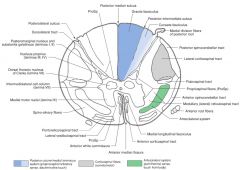
Where do the axons of the Anterolateral system (red arrow) derive from (both Lateral and Anterior Spinothalamic tracts)?
|
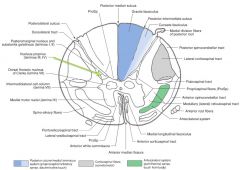
They both derive from the Nucleus Proprius on the opposing side (green arrow).
|
|
|
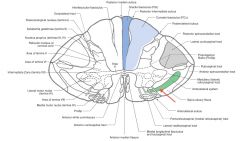
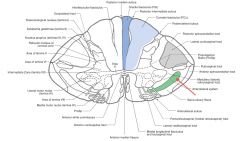
What sensations are carried by the Anterior Spinothalamic Tract (red arrow)?
|
Light touch and pressure.
|
|
|
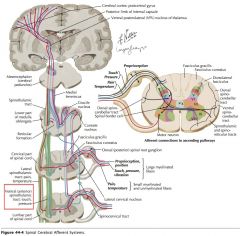
Where do the neurons whose axons form the Lateral Spinothalamic Tract (red arrow) receive their input from?
How is this different from the Anterior Spinothalamic Tract? |
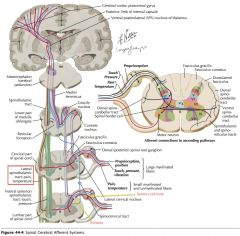
Afferent neurons from the dorsal root ganglion cells within a segment or two of the neurons in question (yellow arrows).
The anterior Spinothalamic Tract's input sensory cell bodies can be located several segments away. |
|
|
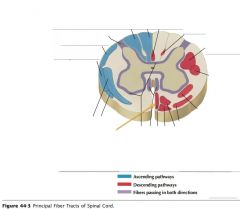
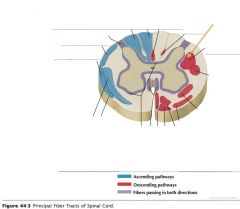
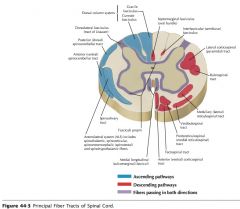
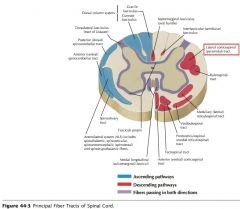
What tract of white matter is indicated by the orange arrow?
|
The Anterior Corticospinal Tract
|
|
|
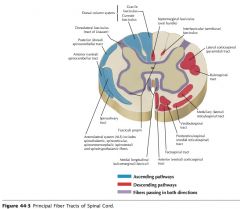
What tract of white matter is indicated by the orange arrow?
|
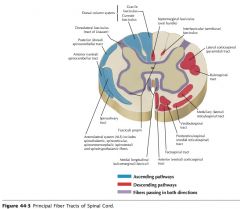
The Lateral Corticospinal Tract.
|
|
|
What types of signals are carried by the Corticospinal Tracts (both Anterior and Lateral)?
|
Motor signals, they are often described as "Upper Motor Neurons."
|
|
|
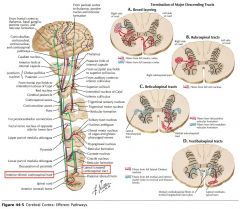
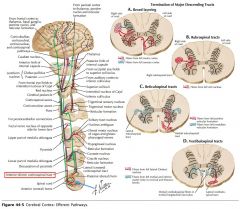
Where do the Lateral Corticospinal Tracts cross?
|
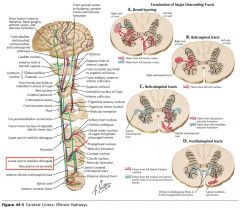
They cross at the Pyramidal Decussation in the Medulla.
|
|
|
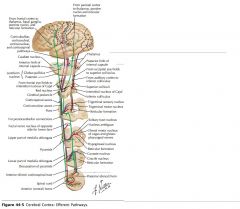
Which white matter tracts contains 75-90% of the pyramidal tract fibres that cross at the pyramidal decussation in the medulla?
|
The Lateral Corticospinal Tracts.
|
|
|
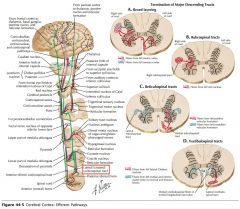
Do the anterior Corticospinal Tracts cross before entering the spinal cord?
|
No, although they may (but not always) cross at the level they terminate, using the Ventral White Commissure (blue arrow).
|
|
|
How low down the spinal cord does the Anterior Corticospinal Tract descend?
The Lateral? |
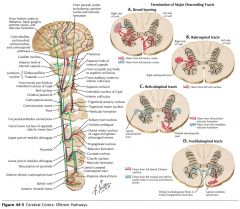
The Anterior Corticospinal Cord only extends as far as the upper thoracic cord.
The Lateral goes down all the way. |
|

