![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Motor Control is the study of what?
|
Motor Control is the study of the nature and cause of movement.
|
Definition listed on lecture 1 outline.
|
|
|
Motor Control is dependent on what three things? Expand and contrast.
|
1. Perception (Senses)
Have to think about moving from point A to point B. 2. Cognition (understanding and reasoning) How do I get from point A to Point B. 3. Motor Capability (action) The muscle have to be able to contract in order to get from A to B. |
|
|
|
What are the two anatomical divisions of the nervous system?
|
CNS & PNS
|
only the names of the divisions
|
|
|
What makes up the CNS?
|
the brain and the spinal cord
|
|
|
|
What makes up the PNS?
|
Cranial and spinal nerves
|
|
|
|
What are the physiological divisions of the nervous system?
|
Somatic and automatic
|
Just list the names
|
|
|
What is the function of the somatic division?
|
The somatic division innervates the body wall, skin, and muscles. Mostly voluntary
|
|
|
|
What is the function of the Autonomic division?
|
The autonomic divsion-
central and peripheral nerves innervate organs, blood vessels. Mostly involuntary |
|
|
|
What are the two parts of the autonomic Nervous system?
|
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic?
|
|
|
|
What is the function of the sympathetic nervous system?
|
The sympathetic arouses the body. If something alarms, enrages, or challenges you (such as a longed-for job interview) the sympathetic system will accelerate your heartbeat , raise your blood pressure, slow digestion, raise blood sugar, and cool you with perspiration, making you alert and ready for action. (Lie-detection machines measure stress responses which sometimes also accompany lies.)
|
"arousing"
|
|
|
What is the difference between a nerve and a neuron.
|
A neuron is one specialized cell that conducts impulses through electrical and chemical processes.
A nerve is a lot of neurons grouped together outside the CNS. |
|
|
|
What is the difference between a nerve and a tract?
|
A tract is a group of nerves with the same information/type of information being transmitted.
|
|
|
|
Do neurons multiply?
|
no
|
|
|
|
Do neurons need oxygen?
|
yes
|
|
|
|
Name the two types of neurons, tell what kind of impulses they send and which direction they go.
|
Efferent neurons send a motor impulse to glands or muscles and are descending.
Afferent send a sensory impulse and are ascending. |
|
|
|
How many neurons are in a typical motor impulse?
|
2- One UMN and one LMN
|
|
|
|
How many neurons are in a typical sensory impulse?
|
Three.
1st order neuron, 2nd order neuron, and 3rd order neuron. |
|
|
|
What is the name of a neuron cell body?
|
Soma
|
|
|
|
What is the name for a bundle/collection/group of cell bodies?
|
ganglia
|
|
|
|
What color are cell bodies?
|
grey
|
|
|
|
Why is white matter white?
|
Myelin on axons
|
|
|
|
What are tracts?
|
bundles of axons belonging to neurons that appear white. They are pathways for information in the CNS (brain and spinal cord) and can be ascending(sensory) or descending (motor).
|
|
|
|
Where does one neuron connect to another?
|
at a synapse
|
|
|
|
What flows across the synapse?
|
Ions flow across the membranes which is an electrical current.
|
|
|
|
What are the 3 main parts of a neuron.
Be able to name them and label them on a picture |
Dendrites
Axon Cell Body |
|
|
|
In what part of the neuron are the following found?
Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Nucleus Nissl granules |
Myelin- axon
Nodes of R.-axon Nucleus- cell body Nissl- cell body |
|
|
|
What is it called when a neuron supplies enough stimulus to another neuron or muscle to allow sodium ions to move into the cell and reverse polarity?
|
Action potential
|
|
|
|
What is it called where a motor neuron comes into close contact with a skeletal muscle cell?
|
Nueromuscular Junction or
Mylonueral junction |
|
|
|
What is the name of the chemical released by neurons to stimulate or inhibit other neurons or effector cells?
|
Neurotransmitter
|
|
|
|
What are the two types of action potentials?
|
Excitatory Presynaptic Potential (PSP)
Inhibitory Presynaptic Potential (PSP) |
|
|
|
How is it determined which action potential will be produced?
|
Whichever one is the strongest
|
|
|
|
How are action potentials measured?
|
Temporal Summation- repetition of the same stimulus in the same place. This builds over time.
Spatial Summation- repetitions of the same stimulus at the same time but in different spaces. Adds up for a stronger muscle contraction. (The cell becomes more negative, depolarization occurs and it's more likely to fire.) |
|
|
|
When axons of a motor neuron branch to adhere to a sarcolema, what is that called?
(site of contact between the axon and a muscle fiber) |
motor endplate
|
|
|
|
What is the name of the auto immune disease when there is no action potential at the neuromuscular junction
|
myasthenia gravis
|
|
|
|
What 2 filaments connect to cause a muscle contraction?
|
actin and myosin
|
|
|
|
Can an axon divide and innervate hundreds of muscle fibers?
|
yes
|
|
|
|
Do peripheral nerves contain sensory, motor, or both?
|
both
|
|
|
|
What is the connective tissue around 1 axon called?
|
Endoneurium
|
|
|
|
Connective tissue around fasicles of axons
|
perineurium
|
|
|
|
Connective tissue around groups of fasicles
|
Epineurium
|
|
|
|
What body chart shows what nerve our skin sensation travels on?
|
Dermatone
|
|
|
|
What body chart shows which nerve causes motor movement in a muscle?
|
myotome
|
|
|
|
Name the vertebral spinal roots are involved in the "slap, slap, slide"
|
C1-T2
|
|
|
|
Where does cervical spine C8 exit?
|
Below c-8?
|
|
|
|
Are cranial nerves part of the CNS?
|
No
|
|
|
|
Are spinal nerves part of the CNS?
|
No
|
|
|
|
Are tracts part of the CNS?
|
yes
|
|
|
|
Where do cranial nerves enter and exit?
|
The brain stem
|
|
|
|
Do cranial nerves carry motor and sensory information?
|
Yes between the head and the ANS
|
|
|
|
What are neurons that send messages from the cortex tot he ventral horn?
|
UMN
|
|
|
|
Neurons that send messages from the ventral horn to a muscle
|
LMN
|
|
|
|
1. Epineurium- connective tissue around groups of fasicles forming a nerve.
2. Perineurium- surrounding bundles of axons called fasicles 3. Endoneurium- connective tissue around one axon |
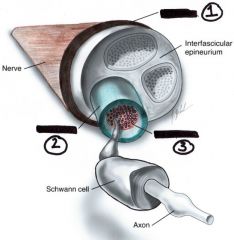
Name these three structures on the peripheral Nerve and define them
|
E.P.E.
|

