![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cranial Nerve I is associated with:
A) Telencephalon B) Diencephalon C) Mesencephalon (ventral) D) Mesencephalon (dorsal) E) Metencephalon (Pons) F) Myelencephalon (Medulla) |
A) Telencephalon
Cranial Nerve I, the olfactory nerve, arises directly from the forebrain. |
|
|
Cranial Nerve II is associated with:
A) Telencephalon B) Diencephalon C) Mesencephalon (ventral) D) Mesencephalon (dorsal) E) Metencephalon (Pons) F) Myelencephalon (Medulla) |
B) Diencephalon
Cranial Nerve II, the optic nerve, arises directly from the forebrain as a tract of the diencephalon.. |
|
|
Cranial Nerve III is associated with:
A) Telencephalon B) Diencephalon C) Mesencephalon (ventral) D) Mesencephalon (dorsal) E) Metencephalon (Pons) F) Myelencephalon (Medulla) |
C) Mesencephalon (ventral)
Cranial Nerve III, the Oculomotor Nerve, exits the brainstem from the interpeduncular fossa. |
|
|
Cranial Nerve IV is associated with:
A) Telencephalon B) Diencephalon C) Mesencephalon (ventral) D) Mesencephalon (dorsal) E) Metencephalon (Pons) F) Myelencephalon (Medulla) |
D) Mesencephalon (dorsal)
Cranial Nerve IV, the trochlear nerve, exits the brainstem on its dorsal surface, caudal to the inferior colliculus. |
|
|
Cranial Nerve V is associated with:
A) Telencephalon B) Diencephalon C) Mesencephalon (ventral) D) Mesencephalon (dorsal) E) Metencephalon (Pons) F) Myelencephalon (Medulla) |
E) Metencephalon (Pons)
Cranial Nerve V, the trigeminal nerve, exits the brainstem from the pons. |
|
|
Cranial Nerve VI is associated with:
A) Telencephalon B) Diencephalon C) Mesencephalon (ventral) D) Mesencephalon (dorsal) E) Metencephalon (Pons) F) Myelencephalon (Medulla) |
E) Metencephalon (Pons)
Cranial Nerve VI, the abducens nerve, exits the brainstem from the pontomedullary junction. |
|
|
Cranial Nerve VII is associated with:
A) Telencephalon B) Diencephalon C) Mesencephalon (ventral) D) Mesencephalon (dorsal) E) Metencephalon (Pons) F) Myelencephalon (Medulla) |
E) Metencephalon (Pons)
Cranial Nerve VII, the facial nerve, exits the brainstem from the cerebellopontine angle. |
|
|
Cranial Nerve VIII is associated with:
A) Telencephalon B) Diencephalon C) Mesencephalon (ventral) D) Mesencephalon (dorsal) E) Metencephalon (Pons) F) Myelencephalon (Medulla) |
E) Metencephalon (Pons)
Cranial Nerve VIII, the vestibulo-cochlear nerve, exits the brainstem from the cerebellopontine angle. |
|
|
Cranial Nerve IX is associated with:
A) Telencephalon B) Diencephalon C) Mesencephalon (ventral) D) Mesencephalon (dorsal) E) Metencephalon (Pons) F) Myelencephalon (Medulla) |
F) Myelencephalon (Medulla)
Cranial Nerve IX, the glossopharyngeal nerve, exits the brainstem from the postolivary sulcus. |
|
|
Cranial Nerve X is associated with:
A) Telencephalon B) Diencephalon C) Mesencephalon (ventral) D) Mesencephalon (dorsal) E) Metencephalon (Pons) F) Myelencephalon (Medulla) |
F) Myelencephalon (Medulla)
Cranial Nerve X, the vagus nerve, exits the brainstem from the postolivary sulcus. |
|
|
Cranial Nerve XI is associated with:
A) Telencephalon B) Diencephalon C) Mesencephalon (ventral) D) Mesencephalon (dorsal) E) Metencephalon (Pons) F) Myelencephalon (Medulla) |
F) Myelencephalon (Medulla)
Cranial Nerve XI, the spinal accessory nerve, exits the brainstem from the postolivary sulcus. |
|
|
Cranial Nerve XII is associated with:
A) Telencephalon B) Diencephalon C) Mesencephalon (ventral) D) Mesencephalon (dorsal) E) Metencephalon (Pons) F) Myelencephalon (Medulla) |
F) Myelencephalon (Medulla)
Cranial Nerve XII, the hypoglossal nerve, exits the brainstem from the preolivary sulcus. |
|
|
Common tumor of the cerebellopontine angle?
|
An acoustic neuroma, correctly called a vestibular schwannoma, is a benign primary intracranial tumor of the myelin-forming cells of the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII).
|
|
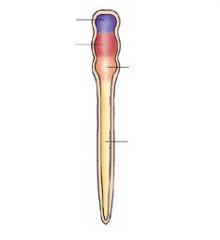
Name the parts.
|
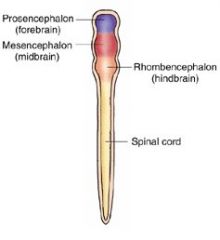
|
|
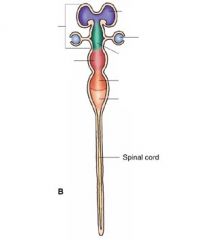
Label the sections.
|
5 vesicle section.
|
|
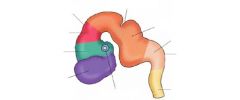
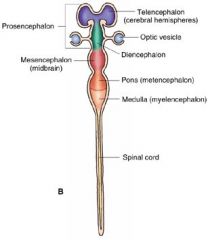
Label the sections.
|
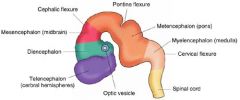
5 vesicle brain, lateral view.
|
|
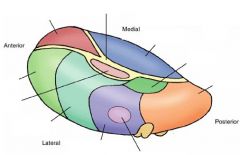
Label the sections.
|
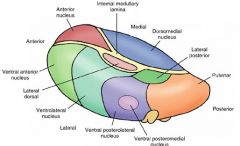
Thalamus.
|
|
|
What is the name of the boundary between the CNS and the PNS?
|
The Redlich-Obersteiner's zone is marked by the transition of myelinating cells from oligodenrocytes to Schwann cells.
|
|
|
Which structures are within the Telencephalon?
|
Cerebral hemispheres
* Cerebral cortex * Basal ganglia * Lateral Ventricles + Foramina of Monro * Closely tied to CN I |

