![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
define Cerebral Palsy
|
A static (permanent, nonprogressive) disorder of movement and posture that results from an insult to or anomaly of the immature nervous system
As the CNS matures, peripheral manifestations of the central lesions change (although the original lesion does not change). Meaning, some children improve, some require bracing or surgery, and others plateau. |
|
|
Data from the perinatal collaborative study suggest abnormal antenatal events yield difficult pregnancies, labors, and deliveries, and that perinatal difficulties are associated with, not the cause of....
|
Cerebral Palsy
|
|
|
Why are VLBW* infants at increased risk of CP?
|
Infants who are born weighing less than 1000g are at high risk of ICH* and very high risk of PVL*
Immature oligodendroglia are vulnerable to oxidative damage (from stress, ischemia, infection, inflammation) *VLBW=very low birth weight ICH=intracranial hemmorhage PVL=periventricular leukomalacia |
|
|
what are the mental abilities like for a cerebral palsy pt?
|
Many persons with CP function at “normal” educational and vocational levels.
|
|
|
Bilateral spasticity of the legs greater than the arms
Brisk LE reflexes, ankle clonus, and bilateral Babinski sign In infants: often scissor their legs when held upright, may “commando*” crawl, and may be difficult to diaper because of hip adduction what is this? how is this pt intellect |
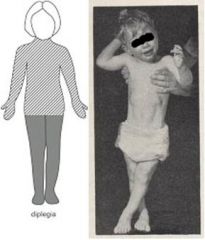
Spastic Diplegia
Intellect is usually unaffected |
|
|
The most severe form of CP
Marked motor impairment of all 4 extremities... what is this? what is their intellect like? |
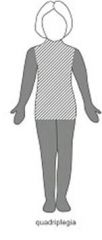
Spastic Quadriplegia
Classically associated with seizures, mental retardation, swallowing dysfunction |
|
|
Classically associated with
seizures, mental retardation, swallowing dysfunction Which Palsy? |
Spastic Quadriplegia
|
|
|
Arm is more affected than the leg with difficulty in hand movement noted in infancy (early handedness before age 3)
Spasticity in the affected extremities (equinovarus* deformity of the foot) and a circumductive gait Weakness of the hand and foot dorsiflexors, may have unilateral ankle clonus and Babinski problem effects half the body...what do they have? intellect? |
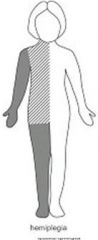
Spastic Hemiplegia
25% have cognitive abnormalities (i.e. 75% do not) |
|
|
Infants are hypotonic with head lag
As they grow older they develop variable tone with rigidity and dystonia Oropharyngeal muscles frequently involved (speech, swallow, drooling, tongue thrust) what is this? intellect? most commonly 2ndary to? |
Extrapyramidal CP
intellect often intact CP most likely secondary to perinatal asphyxia |
|
|
a pt is referred to your office with suspected CP, over time it appears to be gettin worse...what do you say
|
this is not CP
doesnt progress A history of a progressive disorder should lead you to look elsewhere (for example, muscular dystrophy, spinal cord tumor, or neurodegenerative diseases |
|
|
Maryanne is a 12 year old straight A student who walks with her right leg turned in and runs with her right elbow flexed and against her body. Which type of CP does she have?
Spastic diplegia Spastic quadriplegia Spastic hemiplegia Extrapyramidal CP Mixed type CP finding on neural exam? cause? |
Spastic hemiplegia
on neural exam: contralateral ventricular dilitation cause: stroke |
|
|
Sally is a 3 year old with mental retardation, daily seizures, a feeding tube in her abdomen, and flexion contractures in her upper and lower extremities. Which type of CP does she have?
Spastic diplegia Spastic quadriplegia Spastic hemiplegia Extrapyramidal CP Mixed type CP finding on neural exam? |
Spastic quadriplegia
neuro imaging: cysts, brisk reflex, spasticity |
|
|
Sarah turns 16 this year and wants to get her driver’s license. Her parents have her car specially adapted to allow control of the gas and break with her hands because her legs are too spastic. What type of CP does she have?
Spastic diplegia Spastic quadriplegia Spastic hemiplegia Extrapyramidal CP Mixed CP |
Spastic diplegia
|
|
|
Michael is a 5 month old who was born following a very long, difficult labor. You notice considerable head lag when you hold him and excessive drooling. His mother is worried that he doesn’t nurse well. What kind of CP does he have?
Spastic diplegia Spastic quadriplegia Spastic hemiplegia Extrapyramidal CP Mixed CP |
Extrapyramidal CP
|

