![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Explain what is meant by MAC.
Indicate its significance, and the physical characteristic it best correlates with |
**Minimal Alveolar Concentration**
- minimal gas concentration that will block movement in response to incision in 50% of patients **MAC best correlates inversley with lipid solubility** (greater lipid solubility = lower MAC) |
|
|
which of the inhalation anesthetics has significant analgesic properties?
**EXAM** |
Nitrous Oxide
|
|
|
What is the significance of the Blood/Gas partition coefficient (λ)?
What does this mean for induction and recovery? **EXAM** |
Measure of the solubility** of a gas in blood.
Drugs with a higher solubility have slower induction Drugs with lower solubility have faster induction |
|
|
Gaseous anesthetics with high solubility have faster/slower induction and recovery
Gaseous anesthetics with low solubility have faster/slower induction and recovery. |
Gaseous anesthetics with high solubility (high λ) have slower induction and recovery
Gaseous anesthetics with low solubility (low λ) have faster induction and recovery. |
|
|
4. Describe the proposed mechanism(s) of action of inhalation anesthetics
|
Increase GABA activity
-increase chloride conductance to produce hyperpolarization (Ketamine and NO act by binding to glutamate NMDA receptors or central ACh receptors) |
|
|
You want to give a patient a pre-anesthetic agent. You need it to be an anticholinergic drug to inhibit secretions, vomiting and bradycardia. Why would you use glycopyrollate over atropine?
**EXAM** |
Glycopyrollate does not cross BBB!
|
|
|
What is the stage and plane of anesthesia when you can begin surgery?
|
Stage III , Plane 3
(no eye movement, normal pupils, pupillary light reflex, decreased muscle tone, no response to skin incision) |
|
|
What is respiration, pupil size, and muscle tone like in a patient in STAGE IV anesthesia (overdose)?
|
Respiration = apnea
Pupils = dilated Muscle tone = flaccid |
|
|
Which drug has analgesic properties?
A) Etomidate B) Ketamine C) Propofol D) Midazolam |
Ketamine
|
|
|
Which drug has significant anti-emetic effects?
A) Etomidate B) Ketamine C) Propofol D) Midazolam |
propofol
|
|
|
Which drug has its clinical use limited by inhibiting the synthesis of cortisol?
A) Etomidate B) Ketamine C) Propofol D) Midazolam |
Etomidate
|
|
|
Which drug produces significant bronchodilation?
A) Etomidate B) Ketamine C) Propofol D) Midazolam |
Ketamine
|
|
|
Which drug is most likely to produce PONV?
A) Etomidate B) Ketamine C) Propofol D) Midazolam |
Etomidate
|
|
|
Which drug is most likely to produce myoclonic movement on induction or emergence
A) Etomidate B) Ketamine C) Propofol D) Midazolam |
Etomidate
|
|
|
Which drug is likely to cause amnesia?
A) Etomidate B) Ketamine C) Propofol D) Midazolam |
Midazolam
|
|
|
Which drug produces a "dissociative anesthesia'?
|
**Ketamine**
Analgesia, immobility, amnesia - No loss of consciousness but like in a trance with eyes open and cataleptic - Patient may appear to be awake but does not respond to sensory stimuli - Used for minor surgical and diagnostic procedures especially in children |
|
|
Which is most likely to stimulate the CV system?
A) Etomidate B) Ketamine C) Propofol D) Midazolam |
B) Ketamine
|
|
|
If you give a pt. too much Midazolam what can you give as a specific receptor antagonist? (antidote)
|
Flumazenil
(Midazolam is a BDZ) |
|
|
What is the best way to get a "balanced anesthesia"?
|
use a combination of anesthetic drugs!!
- take advantage of their best properties - minimize the undesirable side effects |
|
|
Which has the shortest induction time?
A) isoflurane B) desflurane C) sevoflurane |
desflurane
|
|
|
Which has the longest induction time?
A) isoflurane B) desflurane C) sevoflurane |
isoflurane
|
|
|
Why is the rate of induction slower for desflurane (λ=.42) than N2O (λ=.47)?
|
N20 is given at a much higher concentration! (#1 induction ranking)
|
|
|
Which has the the greatest cardiovascular depression?
A) isoflurane B) desflurane C) sevoflurane |
isoflurane = desflurane = sevoflurane
|
|
|
Which has the fastest recovery time?
A) isoflurane B) desflurane C) sevoflurane |
desflurane
|
|
|
Which is metabolized the most?
A) isoflurane B) desflurane C) sevoflurane |
sevoflurane
|
|
|
Which is metabolized the least?
A) isoflurane B) desflurane C) sevoflurane |
desflurane
|
|
|
Which has no respiratory irritation?
A) isoflurane B) desflurane C) sevoflurane |
sevoflurane
|
|
|
Which two create an increased heart rate?
A) isoflurane B) desflurane C) sevoflurane |
Isoflurane
Desflurane (sevoflurane has a stable heart rate) |
|
|
Which two are more likely to cause "emergence delirium" in children?
A) isoflurane B) desflurane C) sevoflurane |
desflurane and sevoflurane
|
|
|
Know which substance of abuse Ketamine is related to
|
PCP
|
|
|
What is meant by "induction anesthesia?
Name the IV agents primarily used for this procedure. |
Induction anesthesia is when a patient cannot feel or react to a skin incision.
Induction Agents: -propofol is most common (IV) -halothane most common in children (gas) |
|
|
12. Explain the mechanism behind propofol’s brief duration of CNS effects following IV bolus administration
|
Short recovery time attributed to redistribution and rapid
clearance from plasma by metabolism (mainly glucuronidation) |
|
|
13. Explain why in spite of the fact that the general inhalation anesthetics have a low Therapeutic Index they still can be safely used to produce anesthesia.
|
They are given at the MAC (minimal alveolar concentration) and then titrated up if necessary.
The MAC is the minimum concentration level that will knock out 50% of patients! Agents can be combined to reduce the MAC of each. (additive effect) |
|
|
14. Explain what is meant by "incomplete anesthetic", indicate which anesthetic gas is considered an incomplete anesthetic.
|
An Incomplete Anesthetic can't produce all stages of anesthesia without producing hypoxia
***Nitrous Oxide is an incomplete anesthetic*** |
|
|
Which inhaled anesthetic is least likely to cause malignant hyperthermia?
**Exam** |
N2O
|
|
|
Which drug decreases both systemic BP and Heart Rate?
a) Ketamine b) Propofol c) Etomidate |
Propofol
|
|
|
Which drug increases both systemic BP and heart rate?
a) Ketamine b) Propofol c) Etomidate |
ketamine
|
|
|
Which drug does not affect systemic BP or heart rate?
a) Ketamine b) Propofol c) Etomidate |
Etomidate
|
|
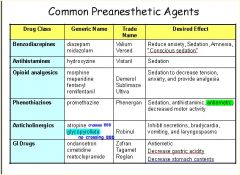
**EXAM**
|
Somewhere in that table is an exam question... have fun... I think it's under Anticholinergics...
|
|
|
You are an anesthesiologist and you just put a patient under using an inhaled anesthetic... Suddenly they have:
-hyperthermia (110+ degrees) -muscle rigidity -metabolic acidosis What's going on? |
Malignant Hyperthermia
|
|
|
Specific drug to treat malignant hyperthermia?
**** |
dantroline
|
|
|
18. Explain what is meant by ‘irregularly descending anesthesia’ and the importance of this concept.
|
Order of sensitivity (most to least) is RAS and cortex →
hippocampus → basal ganglia → cerebellum → spinal cord → medulla (irregularly descending anesthesia) GAs cause an irregularly descending depression of CNS,i.e. the higher functions are lost first and progressively lower areas of the brain are involved, but in the spinal cord lower segments are affected somewhat earlier than the higher segments. The vital centres located in the medulla are paralysedthe last as the depth of anaesthesia increases. This is stage IV anesthesia.. You die... |
|
|
MOA of dexmedetomidine?
** |
Central acting α2 agonist
-Decreases propofol, opioid, inhalation anesthetic dose requirements |
|
|
another objective..
|
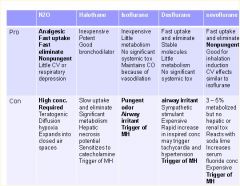
|
|
|
Compared to Propofol and Ketamine, Dexmedetomidine does not stimulate the _______
|
Heart
|
|
|
What neuromuscular blocking agent can cause malignant hyperthermia?
|
Succinylcholine
|
|
|
How does Etomidate decrease Intracranial pressure?
|
causes direct cerebral vasoconstriction
↓ ↓CBF and ↓CMRO2 |
|
|
All of the following IV Anesthetics work by enhancing the GABA receptor except:
A) Propofol B) Ketamine C) Midazolam D) Etomidate ***EXAM*** |
Ketamine
-primarily produces its effects by binding noncompetively to the NMDA receptor site to inhibit the excitatory NT glutamate |
|
|
This IV anesthetic binds to the NMDA receptory to inhibit the excitatory NT glutamate
***EXAM** |
Ketamine
|

