![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
6 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
True or False:
Blunt force injuries to the brain contributes to most to the TBI-related morbidity and mortality via the generation of shear and tensile strains within the brain and its vasculature. |
FALSE!
RAPID ACCELERATION/DECELERATION of the brain contribute to most TBI related morbidity and mortality! |
|
|
What does the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) grade? Along what categories?
|
GCS grades the TBI severity. It is a 15 point scale evaluating best eye, verbal and motor responses.
13-15= Mild TBI, including concussion, usually good prognosis 9-12 = Moderate TBI 8 or less = Severe TBI |
|
|
Mild TBI or concussions can be characterized by:
- Alteration of mental status with or without the loss of consciousness - Impairment of memory and attention - Headaches-can persist for days to weeks - Unsteadiness and dizziness - Nausea and vomiting - Sleep disturbances-also can persist for days or weeks. Which is useful for discerning a veteran with traumatic brain injury versus a veteran with PTSD? |
Headaches.
Individuals with PTSD do not usually complain of headaches but those with TBI nearly always complain of headaches! |
|
|
TBIs can be classified generally into focal and diffuse/generalized. Differentiate between the two.
|
Focal
-Arises due to acceleration/deceleration induced contact between the brain and the inner table of the skull -Defined and localizable pathologic process which impacts the injured region in a relatively homogenous fashion -e.g. Contusion as well as Subdural and Epidural Hematoma formation Diffuse/Generalized -Arises from rapid acceleration-deceleration of the head → shear and tensile loading within the brain -Cells and/or processes within the area of injury are not equally affected -The area of injury or injuries may be poorly localized or spread over large regions of the brain -e.g. Diffuse axonal injury, Neuroexcitation |
|
|
Inflammation typically follows contusion and diffuse necrosis. Which of the following is normally NOT seen for inflammation?
A. IL-1 beta B. TNF alpha C. IL-6 D. IL-4 |
D. IL-4
|
|
|
[ Epidural / Subdural ] hematoma is bleeding between the dura mater and the skull; [ Epidural / Subdural ] hematoma is bleeding between the arachnoid mater and dura mater.
|
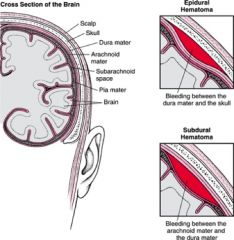
|

