![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
112 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
How many milliliters of CSF are produced per day?
|
500 ml
|
|
|
|
How much CSF is within the ventricles?
|
25 ml
|
|
|
|
Name two degenerative diseases that primarily involve the basal ganglia and mesencephalon?
|
Parkinson's Disease
Huntington Disease |
|
|
|
Where is the obstruction located in noncommunicating hydrocephalus?
|
Within the ventricular system
|
|
|
|
Where is the obstruction located in communicating hydrocephalus?
|
Within the subarachnoid space or arachnoid villi
|
|
|
|
What is the gross pathology of Parkinson's disease?
|
Depigmentation of substantia nigra
|
|
|
|
What is the histopathology of Parkinson's disease? (4)
|
1. Degeneration of neurons in substantia nigra and locus ceruleus
2. Lewy bodies (idiopathic PD) 3. Neurofibrillary tangles (postencephalitic PD) 4. Degeneration of dopaminergic striatonigral pathway |
|
|
|
What is the usual cause of cellular brain edema?
|
Ischemia
|
|
|
|
Where is vasogenic brain edema located? (gray or white matter)
|
White matter
|
|
|
|
Where is cellular (cytotoxic) brain edema located? (gray or white matter)
|
Both, but gray is more significant
|
|
|
|
Periventricular edema is indicative of what condition?
|
Hydrocephalus
|
|
|
|
What is the gross pathology of Huntington Disease?
|
Atrophy of caudate nucleus and putamen
|
|
|
|
What is the histopathology of Huntington disease? (4)
|
1. Loss of major projection neurons in striatum
2. Intranuclear inclusions in neurons 3. Loss of neurons in globus pallidus 4. Mild to moderate cerebral cortical atrophy |
|
|
|
What is the histopathology of ALS? (5)
|
1. Loss of large motor neurons with gliosis
2. Degeneration of cortico-spinal (pyramidal) tracts 3. Bunina bodies and other ubiquitin positive cytoplasmic inclusions in some motor neurons 4. Degeneration of anterior spinal roots 5. Neurogenic atrophy of skeletal muscles |
|
|
|
What is the gross pathology of Alzheimer's disease?
|
Diffuse cerebral cortical atrophy
Hydrocephalus ex vacuo |
|
|
|
What is the gross pathology of dementia with Lewy bodies? (3)
|
1. Some degree of diffuse cerebral atrophy is likely to be present
2. Variable pallor of the substantia nigra is likely to be present 3. Locus ceruleus is usually depigmented |
|
|
|
What is the cause of hydrocephalus in TB meningitis?
|
Meningial fibrosis
|
|
|
|
What type of meningitis has characteristic dilatation of the Virchow-Robin (perivascular) spaces in the basal ganglia?
|
Cryptococcal leptomeningitis
|
|
|
|
What is the histopathology of dementia with Lewy bodies?
|
1. Lewy bodies of both classical and cortical types
2. Alzheimer-type pathology (senile plaques & neurofibrillary tangles) |
|
|
|
What type of pathogen is the most common cause of encephalitis?
|
Viruses
|
|
|
|
What is the pathology of viral encephalitis? (4)
|
1. Necrosis with hemorrhage
2. Perivascular chronic inflammation 3. Microglial nodules 4. Sometimes viral inclusions |
|
|
|
Where does herpes encephalitis typically localize?
|
Temporal and frontal lobes
|
|
|
|
Where does the polio virus localize in the CNS?
|
Anterior horn cells
|
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of coma in the absence of an intracranial hematoma?
|
Diffuse axonal injury
|
|
|
|
What immunohistochemical stain can serve as a sensitive marker to diffuse axonal injury?
|
APP
|
|
|
|
What type of hematoma is found in shaken baby syndrome?
|
Subdural
(often bilateral) |
|
|
|
What is typically the source of bleeding in a subdural hematoma?
|
Bridging veins
|
|
|
|
What is typically the source of bleeding in an epidural hematoma?
|
Meningeal artery (usually middle)
|
|
|
|
What are the typical shapes of subdural and epidural hematomas?
|
Epidural = convex or lens
Subdural = crescent |
|
|
|
In which lobes do brain contusions most commonly occur?
|
Temporal and frontal
|
|
|
|
Where are focal hemorrhages found in the gross pathology of diffuse axonal injury?
|
Parasagittal white matter
Corpus callosum Dorsolateral quadrants of rostral brainstem |
|
|
|
Where do pilocytic astrocytomas commonly occur?
|
Cerebellum
Hypothalamus Optic nerve |
|
|
|
What age group are pilocytic astrocytomas most common in?
|
Young (1-3 decades)
|
|
|
|
What is the histological pattern of pilocytic astrocytoma? (3)
|
Biphasic growth pattern
Solid & microcystic Degenerative astrocytic changes |
|
|
|
What is the radiological finding of diffuse astrocytoma?
|
T2 hyperintensity on non-contrast MRI
|
|
|
|
What is the histological pattern of diffuse astrocytoma?
|
Diffuse infiltration by cytologically atypical cells
|
|
|
|
What is the histological feature that distinguishes anaplastic astrocytoma from diffuse astrocytoma?
|
Mitotic activity
|
|
|
|
What is the radiological finding typical of a glioblastoma?
|
(Ring) enhancement on post-contrast T1 weighted MRI
|
|
|
|
What are histological findings that distinguish glioblastoma from other gliomas?
|
Microvascual proliferation (with leaky blook vessels)
Necrosis (pseupalisading) |
|
|
|
What type of brain tumor is frequently calcified?
|
Oligodendroglioma
|
|
|
|
What are the genetic features that are typical of oligodendrogliomas and how does their presence affect the tumor's prognosis?
|
LOH 1p and 19q
Presence of both is favorable and indicates likely response to chemotherapy |
|
|
|
What are the six most common locations for meningiomas?
|
Parasagittal/flacine
Convexity Sphenoid wing Suprasellar Olfactory groove Posterior fossa |
|
|
|
What is the frequency of metastatic brain tumors as compared to primary tumors?
|
10x more frequent
|
|
|
|
What are the most common sites for ependymomas?
|
Cerebellum and Spinal Cord
|
|
|
|
What grade is the majority of ependymomas?
|
Grade II
|
|
|
|
What is the most common familial cancer syndrome and what are the associated cancers of the syndrome?
|
NF1
Neurofibromas and optic nerve gliomas (pilocytic) |
|
|
|
Meningiomas and Scwannomas are associated with which familial cancer syndrome?
|
NF2
|
|
|
|
What are the two types of peripheral nerve tumors?
|
Neurofibroma
Schwannoma |
|
|
|
Iris hamartomas are typically found in what type of CNS tumor syndrome?
|
NF1
|
|
|
|
A biphasic neoplasm and verocay bodies are found in the histology of what cancer?
|
Schwannoma
|
|
|
|
What is the most common type of embryonal brain tumor?
|
Medulloblastoma
|
|
|
|
What two things can cause the symptoms associated with pituitary adenoma?
|
Hormone production
Mass effects |
|
|
|
What are the four most frequent primary sites of intraparenchymal metastatic tumors?
|
Lung
Breast Skin Kidney |
|
|
|
What is the most common primary brain tumor?
|
Meningioma
|
|
|
|
What percentage of strokes are ischemic?
|
80%
|
|
|
|
Which is more vulnerable to ischemia: neurons or glial cells; white matter or gray matter?
|
Neurons, Gray matter
|
|
|
|
Neurons of which four parts of the brain are most vulnerable to ischemia?
|
1. Cerebral cortex
2. Hippocampus 3. Deep cerebral nuclei 4. Purkinje cells of cerebellum |
|
|
|
What will eventually form in an area of pan-necrosis?
|
A cavity
|
|
|
|
In ischemic strokes, what is focal ischemia due to?
|
Occlusion of a blood vessel
|
|
|
|
In ischemic strokes, what is global ishemia due to? (3)
|
1. Cardiac arrest
2. Systemic hypotension 3. Increased intracranial pressure |
|
|
|
During what time period following a stroke is the mass effect primarily present?
|
The first week
|
|
|
|
Where do lacunar infarcts occur? (3)
|
1. Cerebral white matter and internal capsule
2. Deep cerebral gray mater (basal ganglia, thalamus) 3. Pons |
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of intracerebral hemorrhage?
|
Hypertension
|
|
|
|
What are three brain related diseases associated with small-vessel arteriosclerosis?
|
1. Intracerebral hemorrhage
2. Lacunar infarct 3. Binswanger's disease |
None
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of subarachnoid hemorhage?
|
Ruptured berry aneurysms
|
|
|
|
85% of berry aneurysms are found in what part of the cerebral circulation?
|
Anterior (ICA) circulation
|
|
|
|
What is the most common location for berry aneurysms (40%)?
|
Junction of the anterior cerebral artery and the anterior communicating artery
|
|
|
|
What portion of patients that suffer from aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage die from the event?
|
33%
|
|
|
|
What is seen microscopically on the first day of a stroke?
|
1. Coagulative necrosis of neurons (red neurons)
2. Tissue edema 3. Influx of neutrophils |
|
|
|
What is seen microscopically on the second day of a stroke?
|
Macrophages and maximal edema
|
|
|
|
What is seen microscopically on the third day of a stroke?
|
Proliferation of astrocytes
|
|
|
|
Which is the more common type of hemorrhagic storke?
|
Intraparenchymal hemorrhage
|
|
|
|
What are four consequences of an intercerebral hemorrhage?
|
1. Local brain destruction
2. Mass effect 3. Extension into ventricles (hydrocephelus) 4. Seizures |
|
|
|
What is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage?
|
Arterial vasospasm
|
|
|
|
What is the predominant clinical symptom of degenerative diseases primarily involving the cerebral cortex?
|
Dementia
|
|
|
|
Are metabolic and nutritional diseases among the major causes of dementia?
|
Yes
|
|
|
|
What is a common cause of intracerebral hemorrhage in elderly individuals and Alzheimer disease patients?
|
Amyloid angiopathy
|
|
|
|
What are the neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease composed of?
|
Intraneuronal tau protein aggregates
|
|
|
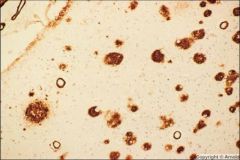
What is seen in this image?
|
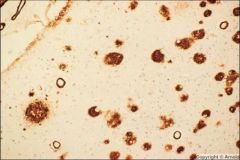
β-amyloid deposit of Alzheimer's disease
|
|
|
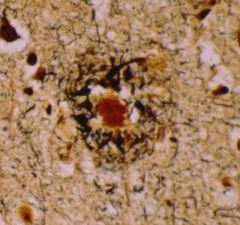
What is seen in this image
|
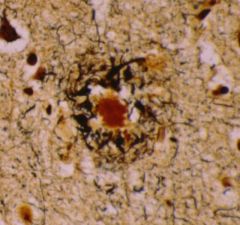
Senile plaque
|
|
|
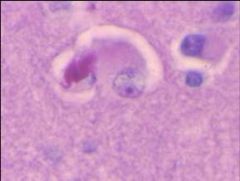
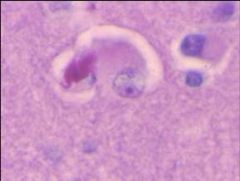
What is seen in this image?
|
Neurofibrillary tangles
|
|
|
What is seen in this image?
|
Cortical Lewy bodies
|
|
|
|
What is the pathology of prion disease? (5)
|
1. Cerebral and/or cerebellar atrophy in some cases
2. PrP amyoid plaque (deposit) 3. Spongy vacuolation of neuropil 4. Neuronal loss 5. Glial hypertrophy and proliferation (gliosis) |
|
|
What disease process is seen in this image?
|
Prion disease
(spongy changes) |
|
|
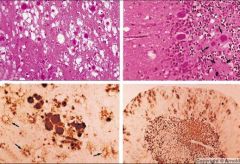
What disease is see in these images?
|
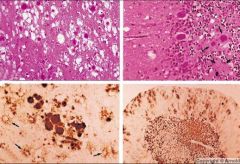
Variant CJD
|
|
|
|
What is the predominant clinical symptom of degenerative diseases primarily involving the basal ganglia and mesencephalon?
|
Movement disorders
|
|
|
|
What is the predominant clinical symptom of degenerative diseases primarily involving the basal ganglia and mesencephalon?
|
Movement disorders
|
|
|
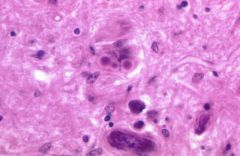
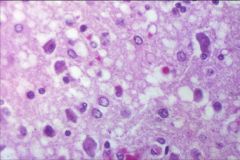
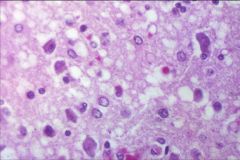
What is the disease process seen in this image?
|
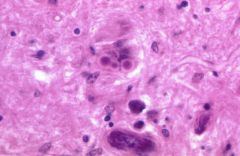
Lewy bodies in Parkinson's disease
|
|
|
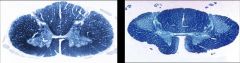
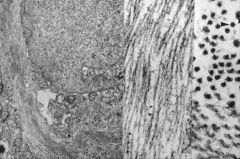
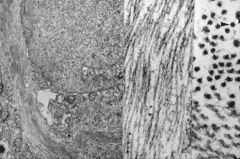
What disease process is seen in the spinal cord of the patient on the right?
(left image is normal) |
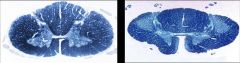
ALS
|
|
|
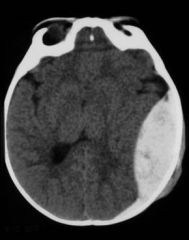
What is seen in this image?
|
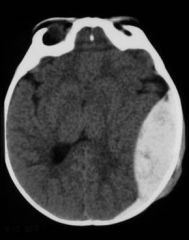
Epidural hematoma
|
|
|
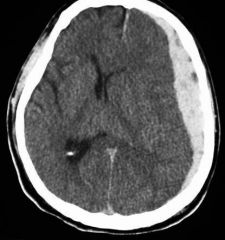
What traumatic brain injury is seen in this image?
|
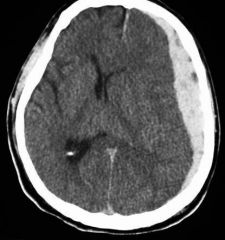
Subdural hematoma
|
|
|
|
What is an early clinical sign of uncal herniation?
|
Ipsilateral pupil dilation
|
|
|
|
What are early clinical signs of central diencephalic herniation (transtentorial) herniation?
|
Drowsiness and small pupils
|
|
|
|
What are the four primary symptoms of hydrocephalus?
|
Headache
Nausea Vomiting Papilledema |
|
|
|
What are five common causes of hydrocephalus?
|
1. Aqueductal stenosis
2. Chiari II malformation 3. Dandy-Walker malformation 4. Post-inflammatory hydrocephalus or post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus 5. Tumors |
|
|
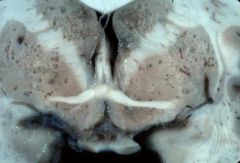
This image of the basal ganglia is characteristic of what infectious disease of the brain?
|
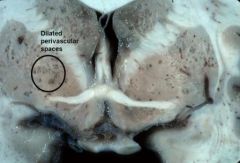
Cryptococcal leptomeningitis
(characteristic dilatation of the Virchow-Robin (perivascular) spaces in the basal ganglia) |
|
|
|
What areas of the brain does HSV-1 infection preferentially involve?
|
Temporal lobes
Inferior frontal lobes |
|
|
|
What parts of the nervous system does poliovirus preferentially infect?
|
Motor neurons of spinal cord
Brain stem |
|
|
|
What cell type does JC virus preferentially infect?
|
Oligodendrocytes
|
|
|
|
What areas of the brain does rabies virus typically infect?
|
Hippocampus
Cerebellum |
|
|
|
What part of the nervous system does varicella-zoster virus typically infect?
|
Dorsal root ganglia
|
|
|
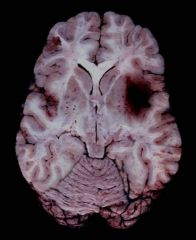
The temporal lobe localization and hemorrhagic necrosis seen in this image is typical of what type of encephalitis?
|
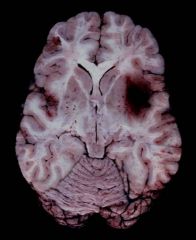
Herpes encephalitis
|
|
|
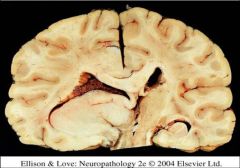
What consequence of the mass effect is seen in this image?
|
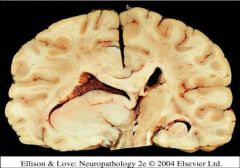
Uncal herniation
|
|
|
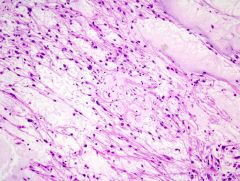
The biphasic growth pattern seen in this image is typical of what brain tumor?
|
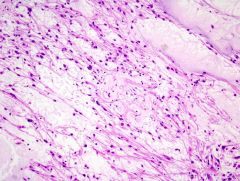
Pilocytic astrocytoma
|
|
|
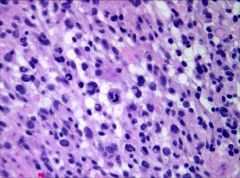
What glioma is seen in this image?
|
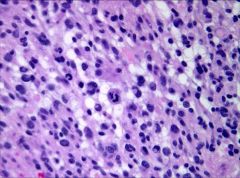
Anaplastic astrocytoma
|
|
|
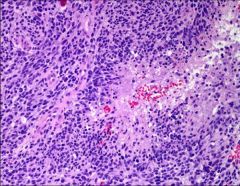
Which type of glioma is seen in this image?
|
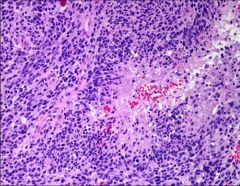
Glioblastoma
|
|
|
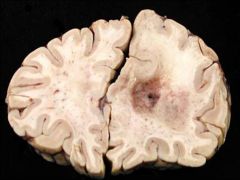
What type of glioma is seen in this image?
|
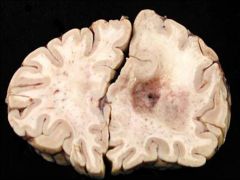
Oligodendroglioma
|
|
|
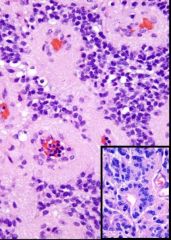
What type of brain tumor is seen in this image?
|
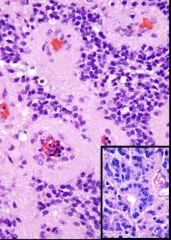
Ependymoma
(rosettes) |
|
|
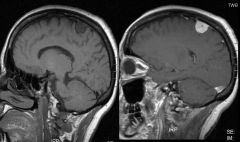
What type of tumor is seen in this image?
|
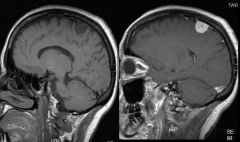
Parafalcine meningioma
|
|
|
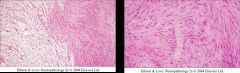
What type of brain tumor is seen in these images?
|
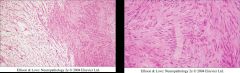
Schwannoma
|
|
|
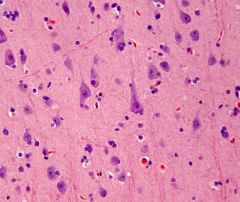
The image above would be expected on what day of a stroke?
|
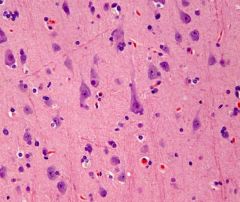
The first
|
|
|
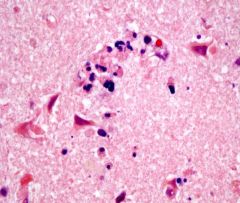
This image would be expected on what day following a stroke?
|
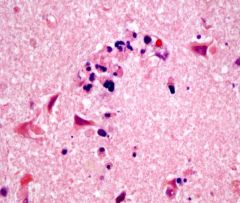
Third
|
|

