![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
88 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What forms do reflex synapses come in?
(sorry poorly worded because I can't think of how else to ask it) |
Monosynaptic
Disynaptic Polysynaptic |
|
|
Where does the coordination of voluntary motor activity take place?
|
Cerebellum (muscle synergy)
|
|
|
Where does modulation of motor activity take place?
|
Basal Nuclei (regulate motor pattern output)
|
|
|
Where is the origin of volitional motor activity?
|
Cerebral (motor) cortex
|
|
|
What type of neuron supplies the Extrafusal Fibers of skeletal muscle?
|
Alpha (α) Motor Neurons
(anterior horn cells, lamina IX cells, final common path) |
|
|
Which motorneurons innervate Skeletal Muscle Fibers directly?
|
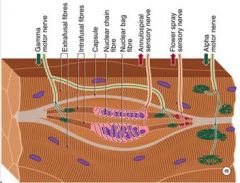
α motor fibers
|
|
|
Which motor nerve type causes the skeletal muscle fiber to contract?
|
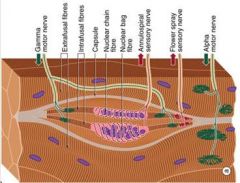
α motor nerve
|
|
|
Which motor cell type is synonymous with lamina IX cells, anterior horn cells, ventral horn cells, lower motor neuron, and final common path?
|
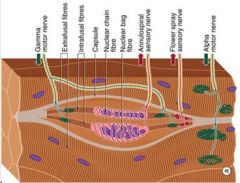
α Motorneurons
|
|
|
Which motor cell type is synonymous with lamina IX cells, anterior horn cells, ventral horn cells, lower motor neuron, and final common path?
|
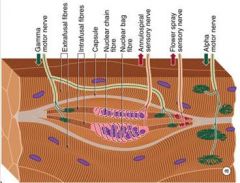
α Motorneurons
|
|
|
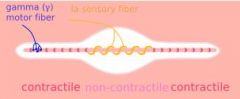
Which motor cell type supplies Intrafusal Fibers of neuromuscular spindles?
|
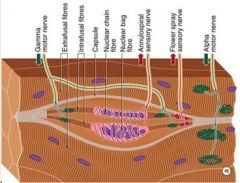
(Gamma) ɣ motor neuron
|
|
|
What motor cell type innervate the Muscle Spindle Fiber directly?
|
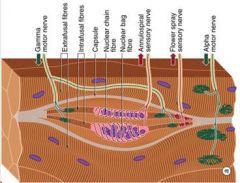
(Gamma) ɣ Motorneurons
|
|
|
What motor cell type regulates spindle sensitivity?
|
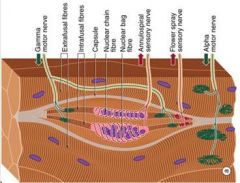
ɣ Motorneurons
|
|
|
What is a receptor that is stimulated by the stretch of a skeletal muscle fiber (extrafusal skeletal muscle)?
|
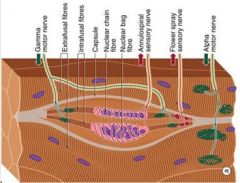
Muscle Spindle (intrafusal skeletal muscle)
|
|
|
What motor cell type is the Dilated portion of the spindle that monitors the velocity of stretch of change in length (dynamic activity)?
|
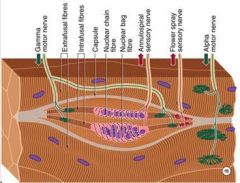
Nuclear Bag
|
|
|
What motor cell type is the elongated portion of the spindle running parallel to the nuclear bag that monitors the change in Length of the muscle fiber?
|
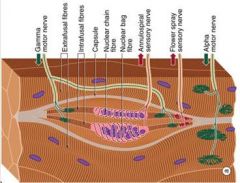
Nuclear Chain
(static activity) |
|
|
What motor cell component is the beginning of the Ia fiber surrounding the nuclear bag and the nuclear chain?
|
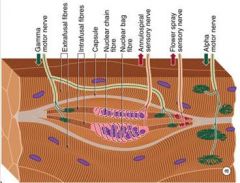
Annulospiral
|
|
|
What fiber type synapses on alpha motor neurons?
|
Ia fiber (or Aalpha)
|
|
|
What are the properties of Ia fibers?
|
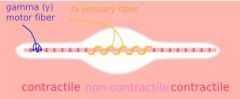
Afferent nerve fibers specifically from annulospiral muscle spindles
Synapse on alpha motor neurons Thick fiber and conducts very fast |
|
|
What are the properties of II fibers?
|
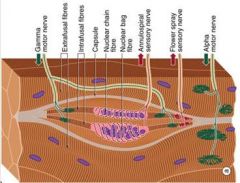
Flower spray endings come together
Afferent fibers from the trailing ends of the muscle spindle Monitor changes in muscle fiber length (static) |
|
|
What glycinergic interneurons are excited by collateral processes of excited alpha-motor neurons?
|
Renshaw Interneurons
|
|
|
How do Renshaw Interneurons act as an off-switch?
|
By inhibiting the alpha-motor neuron which excited them
(Recurrent inhibition) |
|
|
What are the components of reflexes?
|
Afferent Fibers from the stretch receptor, intrafusal muscle fibers(Iα & II)
Efferent Fibers (Aα & Aɣ) |
|
|
What efferent fiber in a reflex is affected by upper motorneurons to regulate tonus & allows us to have Higher Muscle Control?
|
Aɣ - motor neuron to Intrafusal skeletal muscle fiber (ɣ motorneuron)
|
|
|
What fibers in a reflex come back into the nervous system & cause excitation of Agonist alpha motorneurons and inhibition of antagoist alpha motor neurons?
|
Iα - annulospiral ending (dynamic movement)
II - flower spray ending (static activity) (this is what is going to give us movement, excitation of agonist alpha motoneurons and inhibition of antagonist alpha motoneurons.) |
|
|
What are some examples of a monosynaptic (stretch, myotactic) reflex?
|
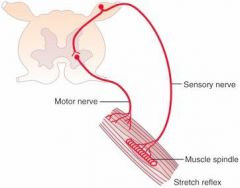
Pateller tendon, Knee Jerk
|
|
|
What is the Receptor, Stimulus, Afferent Fiber,Number of Synapses Efferent Fiber, & effector for the Monosynaptic (stretch, myotatic) reflex?
|
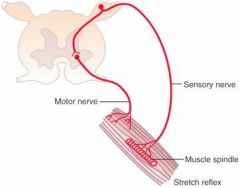
Receptor: Muscle Spindle
Stimulus: Stretch of Muscle, which causes a stretch in the muscle spindle Afferent Fiber: Iα simultaneously excite interneurons which stimulates an agonists alpha motorneuron & exciting interneurons which inhibits the antagonists α motorneuron (reciprocal inhibition) Synapses: 1 Efferent Fiber: Aα (α motorneuron) Effector: Extrafusal muscle fiber of the muscle which was stretched (agonist) |
|
|
What is the term for when afferents simultaneously excite interneurons which stimulates an agonists alpha motorneuron while at the same time exciting interneurons which inhibits the antagonists alpha motorneuron
|
Reciprocal Inhibition (they will have an effect on the antagonist)
|
|
|
What is the purpose of having a Golgi Tendon Reflex?
|
Protective
|
|
|
What are the synapses for the Golgi Tendon Reflex?
|
Inhibitory interneuron to α motorneuron of muscle contracting (agonist)
Excitatory interneuron to alpha motorneuron of opposing muscle (antagonist) |
|
|
What do Iβ fibers do?
|
Simultaneously excite an interneuron that is inhibitory to the alpha motoneuron of the agonist muscle while exciting the alpha motoneuron of the antagonist muscle
|
|
|
Which reflex pertains to reciprocal inhibition?
|
Monosynaptic stretch reflex
(turns itself off) |
|
|
Which reflex pertains to reciprocal excitation?
|
Golgi Tendon Organ
(balance by contracting agonist muscles and inhibiting antagonist muscles) |
|
|
What is the afferent fiber for GTO reflex?
|
Ibeta
|
|
|
What is the afferent fiber for flexor reflex?
|
C or D pain afferents
|
|
|
What is the afferent fiber for myotatic stretch reflex?
|
Ialpha
|
|
|
Which reflex is a flexor crossed extensor?
|
Withdrawal reflex
(stayin alive pose) |
|
|
Which pathway is the primary volitional (conscious) motor pathway?
|
Corticospinal tract
|
|
|
Is the reticulospinal pathway crossed or uncrossed?
|
Primarily uncrossed
(some crossover in the medulla) |
|
|
In the reticulospinal tract, what region has the greatest effect on the FLEXOR muscles?
|
Medulla
|
|
|
In the reticulospinal tract, what region has the greatest effect on the EXTENSOR muscles?
|
Pons
|
|
|
Which pathway is crossed and is involved with Reflexive movements of the head and neck in response to visual and auditory stimuli?
|
Tectospinal tract
|
|
|
Which pathway is involved with Postural adjustments by antigravity musculature in response to the movement or
tilting of the head and has Vestibular nuclei in medulla to interneurons and moto --neurons? |
Vestibulospinal tract
|
|
|
Which pathway coordinates quadripedal movement?
|
Rubrospinal tract
(crossed) |
|
|
Is the vestibulospinal tract crossed or uncrossed?
|
uncrossed
|
|
|
What is An uncrossed pathway which modulates sensory transmission between 1st & 2nd order
neurons in posterior gray horn with respect to painful stimuli. |
Raphe spinal tract
|
|
|
What is the neurotransmitter for the raphespinal tract?
|
seratonin
|
|
|
What lesion would lead to:
1. Paralysis or Paresis 2. Muscle Wasting (atrophy of disuse) 3. Areflexive 4. Fasiculations |
Lower Motor Neuron Lesion
|
|
|
What lesion would lead to:
1. Paralysis (usually hemiplegic) a) Flaccid b) Spastic c) Clasp Knife reflex 2. Hypereflexive 3. Clonus (flexors) 4. Babinski Sign 5. Absence of Abdominal Reflex |
Upper Motor Neuron Lesion
|
|
|
If muscles become inactive through nerve damage, they won't store glycogen or other energy substrates in order to move. So, what happens?
|
The muscles start to shrink & there is no way of completely bringing them back.
Muscle Wasting Atrophy of Disuse |
|
|
What is the term for there is no response to a reflex stimulus?
|
Areflexia
|
|
|
What is the term for oscillations?
|
Fasiculations
|
|
|
What is the term for you can't move?
|
Flaccid
|
|
|
What is the term for limited range of motion, due to limbs or muscles being contracted when injured cells are starting to heal?
|
Spastic
|
|
|
If you can't pull the forearm down pressure will trigger the golgi tendon reflex. What type of reflex is this?
|
Clasp Knife Reflex
|
|
|
What is the term for more exaggerated than usual if you lose upper motor control?
|
Hypereflexia
|
|
|
What is the term for flexor musculature in an extremity starting to oscillate?
|
Clonus (flexors)
(larger than fasiculations) |
|
|
What cerebellar lobe is responsible for:
1. equilibrium 2. communication w/vestibular system 3. developed 1st evolutionarily |
Archicerebellum = Floculonodular Lobe
|
|
|
What cerebellar lobe is responsible for:
1. Propulsive type movements 2. running swimming walking |
Palleocerebellum = Anterior Lobe
|
|
|
What cerebellar lobe is responsible for:
1. *Coordination of fine movement (opposable thumbs) 2. Cerebellum of higher mammals 3. Newest portion evolutionarily |
Neocerebellum = Posterior/Middle Lobe
|
|
|
What lesion affects:
1. loss of muscle tone 2. loss of coordination (ataxia) 3. disorders of equilibrium and gait |
Cerebellar dysfunction
|
|
|
What are the dysinergies associated with cerebellar dysfunction?
|
Ataxia
Dysmetria Dysarthria Dysdiadocokinesia Decomposition of movement Titubation Tremor (intention) |
|
|
What is the condition and area affected by Lack of coordination and Staggered gait?
|
Ataxia
Cerebellar |
|
|
What is the condition and area affected by not being able to touch the tip of nose w/finger & is a misgaging of movement or perception?
|
Dysmetria
Cerebellar |
|
|
What is the condition and area affected by Trouble speaking, slurred speech?
|
Dysarthria
Cerebellar |
|
|
What is the condition and area affected by Inability to do rapily altering movement (pronation/supination)?
|
Dysdiadocokinesia
Cerebellar |
|
|
What is the condition and area affected by appendages all over the place & cannot get a coordinated movement pattern together?
|
Decomposition of movement
Cerebellar |
|
|
What is the condition and area affected by someone who has chronic oscillation of the neck (bobble-head dolls)?
|
Titubation
Cerebellar |
|
|
What is the condition and area affected by beginning to shake when you reach for something?
|
Tremor (cerebellar disease when it is a tremor of intention)
Cerebellar |
|
|
What 3 signs would indicate a chronically drunk individual?
|
Ataxia
Dysmetria Dysarthria The major cause of cerebellar dysfunction is alcohol abuse. |
|
|
What part of the basal ganglia controls Sex & Smell?
|
Amygdala
|
|
|
What part of the basal ganglia controls Behavioral and Cognitive motor control?
|
Caudate
|
|
|
What part of the basal ganglia controls muscles of facial expression?
|
Nucleus Accumbens
|
|
|
What part of the basal ganglia controls Rotational (contratraverse) movement?
|
Globus Pallidus
|
|
|
What part of the basal ganglia controls distal limb operation (hands & feet)
|
Putamen
(use your distal limbs to put-a-man-down) AL gets credit |
|
|
Which part of the basal nucleus influences dopamine?
|
Substantia nigra
|
|
|
What type of lesion leads to dyskinesias (hypo/hyperkinesia)?
|
Basal Nuclei Lesions
|
|
|
What is the most common form of hypokinesia?
|
Parkinsons
Basal nuclei |
|
|
What are bradykinesia, rigidity, and facial mask categorized as?
|
Hypokinesia
Basal Nuclei |
|
|
What are tremors (resting), chorea (tics), ballism, & athetosis categorized as?
|
Hyperkinesia
Basal nuclei |
|
|
What are Reduced or VERY slow movements?
|
Bradykinesia
Basal nuclei |
|
|
What is difficulty in movement?
|
Rigidity
Basal Nuclei |
|
|
What is the term for lack of facial expressions?
|
Facial Mask
basal nuclei (nucleus accumbens) |
|
|
What is the pill rolling referred to as?
|
resting tremor
Basal nuclei |
|
|
What are spontaneous involuntary movements (Toret's syndrome)?
|
Chorea (tics)
Basal Nuclei |
|
|
What is the spontaneously throwing out of a limb?
|
Ballism
Basal Nuclei |
|
|
What is the writhing, snake-like movements?
|
Athetosis
Basal Nuclei |
|
|
What is problems with muscle tone (torticollis)?
|
Dystonia
Basal Nuclei |
|
|
What causes too much bilirubin in your system while your nervous system is developing(Cerebral Palsy)?
|
Kernicterus
Basal Nuclei (We Are Not Retarded!! It is just a motor-system disease) |

