![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which of the following nuclei are NOT part of the anterior region of the hypothalamus?
A. suprachiasmatic nuclei B. arcuate nuclei C. preoprtic nuclei D. paraventricular nuclei E. anterior nuclei F. supraoptic nuclei G. periventricular nuclei |
B. arcuate nuclei
G. periventricular nuclei These are part of the tuberal region! |
|
|
Which of the following nuclei are NOT part of the tuberal region of the hypothalamus?
A. arcuate nucleus B. paraventricular nuclei C. ventromedial nuclei D. dorsomedial nucleu E. lateral hypothalamic nuclei F. periventricular nucleus G. mammillary body |
B. paraventricular nuclei - anterior region
G. mammillary body - posterior region |
|
|
Which of the following are NOT part of the posterior region of the hypothalamus?
A. posterior hypothalamic area B. arcuate nucleus C. mamillary complex D. paraventricular nucleus |
B. arcuate nucleus - tuberal region
D. paraventricular nucleus - anterior region |
|
|
Which region of the hypothalamus is the following located?
Preoptic nuclei |
anterior region (above and rostral to the optic chiasm)
note: makes GnRH, FSH-RH, LH-RH |
|
|
Which region of the hypothalamus is the following located?
Suprachiasmatic and supraoptic n. |
anterior region (above and rostral to the optic chiasm)
note: supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei produce oxytocin and vasopressin which are transported through the axons of the hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract to be stored or released from the posterior lobe of the pituitary (neurohypophysis). |
|
|
Which region of the hypothalamus is the following located?
paraventricular nuclei |
anterior region (above and rostral to the optic chiasm)
note: this produces CRH in response to stress which stimulates the anterior lobe of the pituitary to secrete ACTH |
|
|
Which region of the hypothalamus is the following located?
dorosmedial nucleus |
tuberal region (middle region above tuber cinereum)
|
|
|
Which region of the hypothalamus is the following located?
ventromedial nucleus |
tuberal region (middle region above tuber cinereum)
|
|
|
Which region of the hypothalamus is the following located?
arcuate nucleus |
tuberal region (middle region above tuber cinereum)
note: makes GnRH, GRH, TRH, LH-RH, FSH-RH, STH-RH principal cell group of the median eminence immediately above the infundibulum (pituitary stalk); within this nucleus hypothalamic "releasing factors" are released into the capillaries of the hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system and travel to the anterior lobe of the pituitary. |
|
|
Which region of the hypothalamus is the following located?
lateral hypothalamic area |
tuberal region (middle region above tuber cinereum)
|
|
|
Which region of the hypothalamus is the following located?
posterior hypothalamic area |
posterior region (most caudal)
|
|
|
Which region of the hypothalamus is the following located?
mammillary complex |
posterior region (most caudal)
|
|
|
Neuroendocrine products including regulatory hormones and releasing factors are produced by neurons mainly found where?
|
along the wall of the third ventricle
|
|
|
Which hypothalamic nucleus is described?
principal cell group of the median eminence immediately above the infundibulum (pituitary stalk); within this nucleus hypothalamic "releasing factors" are released into the capillaries of the hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system and travel to the anterior lobe of the pituitary. A. arcuate nucleus B. paraventricular nucleus C. periventricular nucleus D. preoptic nucleus |
A. arcuate nucleus (tuberal region)
GnRH, GRH, TRH, LH-RH, FSH-RH, STH-RH |
|
|
Which hypothalamic nucleus produces CRH in response to stress which stimulates the anterior lobe of the pituitary to secrete ACTH?
A. arcuate nucleus B. paraventricular nucleus C. periventricular nucleus D. preoptic nucleus |
B. paraventricular nucleus (anterior region)
CRH |
|
|
Which hypothalamic nucleus is involved in producing TRH, GHIH?
A. arcuate nucleus B. paraventricular nucleus C. periventricular nucleus D. preoptic nucleus |
C. periventricular nucleus (tuberal region)
TRH, GHIH |
|
|
Which hypothalamic nucleus is involved in producing GnRH, FSH-RH, LH-RH?
A. arcuate nucleus B. paraventricular nucleus C. periventricular nucleus D. preoptic nucleus |
D. preoptic nucleus (anterior region)
GnRH, FSH-RH, LH-RH |
|
|
True or False:
The preoptic areas are the sexually dimorphic areas of the hypothalamus. |
True.
- 2-3 times as large in males as in females - correlated to higher testosterone levels. - lesions of SDN (rodents) disrupts male copulatory behavior - DES treatment increased the SDN-POA volume in females |
|
|
Which two nuclei produce oxytocin and vasopressin which are transported through the axons of the hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract to be stored or released from the posterior lobe of the pituitary (neurohypophysis).
A. supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei B. supraoptic and periventricular nuclei C. suprachiamsmatic and paraventricular nuclei D. suprachiasmatic and periventricular nuclei |
A. supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei
|
|
|
Which nucleus is involved in circadian rhythms?
A. arcuate nuceli B. paraventricular nuclei C. periventricular nuclei D. suprachiasmatic nuclei E. supraoptic nuclei |
D. suprachiasmatic nuclei
|
|
|
True or False:
The hypothalamus is the highest CNS component of the ANS. |
True!
The hypothalamus coordinates autonomic function and integrates it with behavior. |
|
|
Which nuclei are involved in temperature and cardiovascular regulation?
A. anterior and posterior nuclei B. dorsomedial, ventromedial and lateral nuclei C. anterior and lateral nuclei |
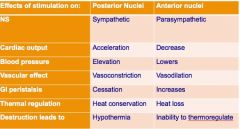
A. anterior and posterior nuclei
Anterior nucleus has parasympathetic functions while posterior nucleus has sympathetic functions. |
|
|
Which nuclei regulate food intake?
A. anterior and posterior nuclei B. ventromedial nucleus, lateral nucleus, dorsomedial nucleus |
B. ventromedial nucleus (satiety center), lateral nucleus (appetite center), dorsomedial nucleus (feeding, drinking and body weight regulation)
|
|
|
This nucleus is inovlved in food intake regulation. Specifically, its neurons have glucoreceptors when its constituent neurons are excited it turns off appetite. Lesions result in hypothalamic obesity and savage behavior.
A. dorsomedial nucleus B. lateral nucleus C. ventromedial nucleus |
C. ventromedial nucleus
|
|
|
This nucleus is inovlved in food intake regulation. Specifically, it is the "appetite center" and its stimulation induces eating. Lesions can lead to anorexia and starvation.
A. dorsomedial nucleus B. lateral nucleus C. ventromedial nucleus |
B. lateral nucleus
|
|
|
This nucleus is inovlved in food intake regulation. Specifically, it is involved in feeding, drinking, and body weight regulation. Stimulation results in savage behavior.
A. dorsomedial nucleus B. lateral nucleus C. ventromedial nucleus |
A. dorsomedial nucleus
|
|
|
Leptin is a hormone produced by adipose tissue that acts on the hypothalamus to [ increase / reduce ] appetite.
|
Leptin reduces appetite.
Thus, leptin receptor deficiency leads to the lateral nuclei not being stimulated. Leptin actually stimulates the lateral nucleus and determines when you stop eating or if you want to eat more. Some individuals have a receptor deficiency and the lateral nuclei is not stimulated and appetite is not curbed. Leptin receptor deficiency leads to an intense drive to eat which can never be satisfied and results in rapid weight gain. |
|
|
True or False:
The mammillary complex is the doorway between the hypothalamus and the hippocampus. |
True
The mamillary complex receives input from the hippocampus via the fornix, and gives rise to the mammillothalamic tract; (part of the classic Papez circuit), and is therefore thought to play some role in memory The hypothalamus receives input from the amygdala which plays a role in the expression of emotions and fear which may influence functions such as feeding and reproduction. |
|
|
Lesions in the mammillary complex leads to what disease that is prevalent in chronic alcoholics and whose symptoms include anterograde amnesia and confabulation.
|
Korsakoff’s and Wernicke’s amnesia
|
|
|
Where are the afferents "ansa peduncularis" and "stria terminalis" coming from?
A. hippocampus B. hypothalamus C. amygdala |
C. amygdala
|
|
|
Which of the following are afferents from the brainstem?
A. ansa peduncularis and stria terminalis B. ventral NE bundle C. mammillary peduncle |
B. ventral NE bundle
|
|
|
Which of the following are afferents from the medulla?
A. ansa peduncularis and stria terminalis B. ventral NE bundle C. mammillary peduncle |
C. mammillary peduncle
|
|
|
Regarding hypothalamus' efferents to the pituitary, the Hypothalamo-Hypophyseal tract goes to the [ anterior / posterior ] lobe. Hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system to the goes to the [ anterior / posterior ] lobe.
|
tract = posterior lobe
system = anterior lobe |
|
|
Regarding hypothalamus' efferents to the pituitary, the Hypothalamo-Hypophyseal tract goes to the [ anterior / posterior ] lobe. Hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system to the goes to the [ anterior / posterior ] lobe.
|
tract = posterior lobe
system = anterior lobe |
|
|
Overproduction of ACTH leads to...
|
Cushing's disease
|
|
|
Overproduction of growth hormone leads to....
|
gigantism, acromegaly
|

