![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
215 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
primary motor cortex is where?
|
precentral gyrus
|
|
|
primary sensory cortex is where?
|
postcentral gyrus
|
|
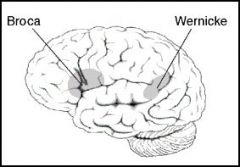
Broca and Wernicke's areas supplied by what vessel?
|
Middle Cerebral artery
|
|
|
What blood vessel supplies the choroid plexus of the 4th ventricle?
|
PICA (Posterior Inferior Cerebellar artery)
|
|
|
What blood vessel supplies most of the dura?
|
Middle Meningeal artery
|
|
|
Name the 5 vessels that make up the Circle of Willis?
|
-anterior communicating
-anterior cerebral - internal carotid - posterior communicating - posterior cerebral |
|
|
Great vein of Galen- in and out?
|
blood in from internal cerebral veins
blood out to straight sinus |
|
|
Superior sagittal sinus recieves blood from?
|
- superficial cerebral veins
- diploic veins - parietal emissary veins |
|
|
Straight sinus is formed by?
|
Great cerebral vein
Inferior sagittal sinus |
|
|
Straight sinus drains?
|
superior cerebellum
|
|
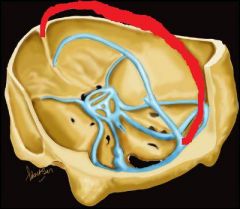
The sinus in red is the?
|
Superior Sagittal sinus
|
|
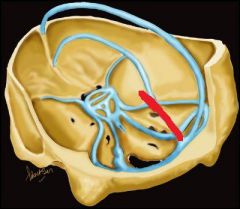
The sinus in red is the?
|
Straight sinus
|
|
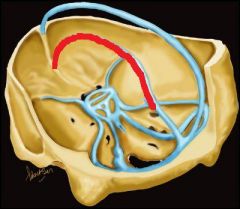
The sinus in red is the?
|
Inferior Sagittal sinus
|
|
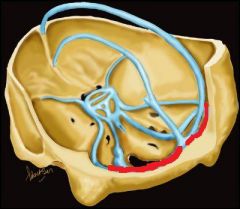
The sinus in red is the?
|
Transverse sinus
|
|
|
Obstruction of right carotid artery causes?
|
Contralateral weakness and loss of sensation (on L side)
|
|
|
Vertebral artery obstruction causes?
|
visual loss (occipital lobe)
dizziness (cerebellum/ brainstem) |
|
|
Obstruction of anterior cerebral artery causes?
|
loss of strength and sensation in lower body
|
|
|
Obstruction of middle cerebral artery causes?
|
loss of strength and sensation in upper body
|
|
|
Person is totally blind. What artery could be blocked?
|
Basilar artery at junction of 2 posterior cerebral arteries
|
|
|
Occlusion of vertebral artery causes?
|
No problem! the other vertebral artery will compensate
|
|
|
What sinus does spinal fluid drain into?
|
Superior Sagittal sinus
(through arachnoid granulations) |
|
|
Cavernous sinus gets blood from?
|
superior and inferior opthalmic veins
|
|
|
Protruding eye with dilated blood vessels could be?
|
Broken carotid artery spills into cavernous sinus
|
|
|
Berry aneurysms usually found where?
|
Anterior Communicating artery in Circle of Willis
|
|
|
Rupture of Berry aneurysm causes?
|
nontraumatic subaracnoid hemorrhage
|
|
|
Aneurysm of Posterior Communicating artery causes?
|
3rd nerve palsy
|
|
|
3rd nerve palsy symptoms?
|
"down n out" eye position
mydrasis (pupil dilation) ptosis (eyelid drooping) |
|
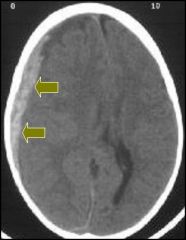
Type of hemorrhage?
|
Subdural hemorrhage
|
|
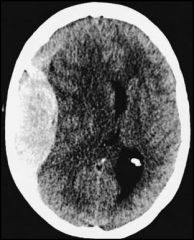
Type of hemorrhage?
|
Epidural hemorrhage
(note white crescent shape) |
|
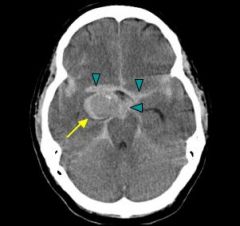
Type of hemorrhage?
|
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
|
|
|
Where is CSF secreted from?
|
choroid plexus
|
|
|
Track the CSF flow from the choroid plexus (10 steps)
|
1. Choroid plexus
2. Lateral ventricles 3. IV foramen 4. 3rd ventricle 5. Aqueduct of Sylvius 6. 4th ventricle 7. Middle foramen of Magendie 8. Lateral foramina of Luschka 9. Subarachnoid space 10. Superior Sagittal sinus |
|
|
Obstruction of CSF pathway leads to?
|
hydrocephalus (swollen lateral ventricles)
|
|
|
Subarachnoid hemorrhage feels like?
|
severe neck/backache, due to blood leakage to spinal cord
|
|
|
Subdural hemorrhage caused by?
|
tearing of bridging veins
|
|
|
Epidural hemorrhage caused by?
|
Middle Meningeal artery tear
|
|
|
Internal capsule is?
|
funnel of motor and sensory fibers from cerebral cortex to brain stem
|
|
|
What supplies the internal capsule?
|
Anterior Choroidal artery
Striate arteries |
|
|
Occlusion of which area of the Circle of Willis causes unilateral blindness?
|
Opthalmic artery...branch of the Internal Carotid
|
|
|
You inject dye into the R carotid. How will you simultaneously fill the L anterior and middle cerebral arteries?
|
Compress L carotid, forcing blood to pass to the L side through the Anterior Communicating artery
|
|
|
Grey matter in brain contains?
|
neuronal cell bodies and synapses
|
|
|
White matter in brain contains?
|
ascending and descending fiber pathways
|
|
|
Ia sensory fibers?
|
supply the sensory receptors in muscle
|
|
|
Fine touch is conveyed by what fibers?
|
Aβ afferent fibers
|
|
|
Pain and temperature conveyed by what fibers?
|
Aδ afferent fibers
|
|
|
What sensory functions are associated with free nerve endings?
|
pain, temperature, itch
|
|
|
What receptor types are associated with touch?
|
Merkel
Meissner Pacinian Ruffini |
|
|
Free nerve endings are found in what tissue?
|
epidermis, dermo-epidermal layer
|
|
|
Loss of free nerve endings results in?
|
no pain sensation
|
|
|
Light touch on fingertips, eyelids, nipples, lips, genitalia involves?
|
Meissner's corpuscles
|
|
|
Course touch or pressure receptors found in deep layers of skin?
|
Pacinian corpuscles
|
|
|
Receptor endings that appear onion-like?
|
Pacinian corpuscles
|
|
|
Spindle-shaped fibers in deep skin, ligaments, and tendons?
|
Ruffini corpuscles
|
|
|
Delicate receptors found in oropharynx and eye conjunctiva?
|
Krause end bulbs
|
|
|
Two-point discrimination is what?
|
minimum distance required to perceive 2 simultaneously applied stimuli as distinct
|
|
|
Two point discrimination is lowest where?
|
fingers, lips, face
|
|
|
Two point discrimination is highest where?
|
legs, arms, back
|
|
|
Thumb innervated by?
|
C6
|
|
|
Index and middle fingers innervated by?
|
C7
|
|
|
Ring and little fingers?
|
C8
|
|
|
Nipples innervated by?
|
T4
|
|
|
Umbilicus innervated by?
|
T10
|
|
|
Patella and large toe innervated by?
|
L4
|
|
|
Middle 3 toes and sole of foot innervated by?
|
L5
|
|
|
Little toe and lateral aspect of food innervated by?
|
S1
|
|
|
Haptics means?
|
Active touching
|
|
|
Being able to identify an object by manipulating it with your hand is called?
|
stereognosis
|
|
|
Merkel cell afferents are sensitive to what?
|
points, edges, curves
|
|
|
Which afferent fibers would be most active when reading Braille?
|
Merkel and Meissner
|
|
|
Which afferent fibers would be most active when writing, using a knife, using a wrench?
|
Pacinian
|
|
|
What do proprioceptors do?
|
Give information about position of body in space
|
|
|
2 types of endings supply the muscle spindle, called?
|
Primary and secondary endings
|
|
|
Primary endings (group Ia afferents) in muscle spindle?
|
highly myelinated
quickly adapt to muscle length changes |
|
|
Secondary endings (group II afferents) in muscle spindle?
|
sustained responses to constant muscle lengths
|
|
|
Intrafusal muscles in muscle are controlled by what motor neurons?
|
γ motor neurons
|
|
|
γ motor neuron cell bodies are located where?
|
ventral horn of spinal cord
|
|
|
What receptors inform the CNS about changes in muscle tension?
|
Golgi tendon organs
|
|
|
Golgi tendon organs are formed by what?
|
Group Ib afferents
|
|
|
Where are Golgi tendon organs found?
|
Around collagen fibers that form the tendons
|
|
|
Cuneus is separated from lingual gyrus by what?
|
calcarine sulcus
|
|
|
What nerve is sensory to the dura mater?
|
trigeminal nerve
|
|
|
A man has:
R side flushing R side papillary constriction ptosis does not sweat Diagnosis? |
Horner's Syndrome
|
|
|
Pt has LOC, draws clock with all numbers on 1 side. Where is lesion?
|
Parietal lobe
|
|
|
Brodmann's Area 4?
|
primary motor cortex
|
|
|
Brodmann's Area 1, 2, 3?
|
primary somatosensory cortex
|
|
|
Brodmann's Area 17?
|
primary visual cortex
|
|
|
Brodmann's Area 41 & 42?
|
primary auditory cortex
|
|
|
A lesion in the ________ would result in loss of sensation to touch and pressure in IPSILATERAL side of body?
|
Dorsal root
|
|
|
Substantia nigra associated with what NT?
|
Dopamine
|
|
|
Raphe nucleus associated with what NT?
|
Serotonin
|
|
|
Locus ceruleus associated with what NT?
|
Norepinephrine
|
|
|
Child born stillborn with enlarged posterior fossa?
|
Dandy-Walker
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of congenital hydrocephaly?
|
Stenosis of aqueduct of sylvius
|
|
|
What blood vessel supplies Broca's and Wernicke's areas?
|
Middle cerebral artery
|
|
|
What is EDTA mainly used for?
|
Tx of severe lead poisoning
|
|
|
Unique symptoms of arsenic poisoning (6)?
|
severe N/V
garlic breath heart problems raindrop hyperpigmentation stocking-glove dysenthesia hemoglobinuria |
|
|
Unique symptoms of mercury poisoning (3)?
|
gingivostomatitis (cold sores in mouth)
hand tremors renal damage |
|
|
Common sources of mercury?
|
thermometers, swordfish, dental fillings, lamps
|
|
|
Treatment of mercury poisoning?
|
dimercaprol, trientine
|
|
|
Unique symptoms of lead poisoning (5)?
|
anemia
vomiting abdominal pain muscle weakness dark deposits on gum line |
|
|
Treatment of lead poisoning?
|
penicillamine, succimer for kids
EDTA for severe cases |
|
|
Where do first order neurons in the DC-ML pathway start? where do they end?
|
Start: DRG
End: facilis cuneatus above T6 facilis gracilis below T6 |
|
|
Where do second order neurons in the DC-ML pathway start? where do they end?
|
Start: facilis cuneate/gracilis
crosses over- called medial lemniscus End: VPL nucleus in thalamus |
|
|
Where do third order neurons in the DC-ML pathway start? where do they end?
|
Start in VPL
end in somatosensory center of cerebrum (post-central gyrus) |
|
|
Ciliary body?
|
Circular band of muscle surrounding lens
contraction makes lens round |
|
|
Fovea?
|
Area of retina specialized for high acuity, many cones
|
|
|
Lens?
|
Thickens/flattens allowing light to focus on the retina
|
|
|
Sclera?
|
External connective tissue coat of eyeball
|
|
|
Function of α1- Gq1?
|
Vasoconstriction
Mydriasis increase HR Contract bladder and sphincter |
|
|
Function of α2- Gi?
|
inhibit NT release
inhibit insulin platelet aggregation decrease lipolysis |
|
|
Function of β1- Gs?
|
increase HR and heart contraction
|
|
|
Function of β2- Gs?
|
relax bronchial airways
relax uterine muscle Vasodilation |
|
|
Function of DA1 & 5- Gs?
|
dilate renal blood vessels
|
|
|
Function of DA2- Gi?
|
modulates NT release
|
|
|
Alpha 1 agonists have what effects?
|
Vasoconstriction
Mydriasis Decrease GI motility Contract bladder |
|
|
Name a direct acting cholinergic agonist used to treat open-angle glaucoma?
|
Pilocarpine
|
|
|
Name 2 α2 agonists used to treat glaucoma?
|
Aproclonidine
Brimonidine |
|
|
Name 2 β2 agonists used to treat glaucoma?
|
Epinephrine
Dipivefrin |
|
|
Name 2 carbonic anhydrase inhibitors?
|
Acetazolamide
Dorzolamide |
|
|
Name 2 β2 antagonists used to treat glaucoma?
|
Timolol
Betaxolol |
|
|
H1 histamine receptor found where?
|
smooth muscle
endothelium CNS tissue |
|
|
H1 histamine receptor causes?
|
vasodilation
bronchoconstriction separates endothelial cells pain, itching |
|
|
H1 histamine receptor activated with what injuries/conditions?
|
allergies
insect stings motion sickness hives |
|
|
H2 histamine receptor causes?
|
gastric acid secretion
|
|
|
H3 histamine receptor causes decrease in what NT release (4)?
|
histamine
acetylcholine norepinephrine serotonin |
|
|
Dendrites do what?
|
receive signals
|
|
|
Fibers that conduct action potentials?
|
axons
|
|
|
Are dendrites afferent or efferent?
|
afferent
|
|
|
Are axons afferent or efferent?
|
efferent
|
|
|
What forms the myelin in the PNS?
|
Schwann cells wrapped around the axons
|
|
|
Gap between myelinated segments?
|
node of Ranvier
|
|
|
Glial cells that store NT and buffer [K+] called?
|
oligodendrocytes
|
|
|
Phagocytic cells in CNS are called?
|
microglia
|
|
|
Glial cells in PNS called?
|
Schwann cells
|
|
|
2 types of motor/efferent fibers called?
|
somatic and autonomic fibers
|
|
|
Somatic fibers terminate in what tissue?
|
skeletal muscle
|
|
|
Autonomic fibers innervate what 4 tissues?
|
cardiac muscle
smooth muscle glands fat |
|
|
What NT is released at the motor end plate/ NMJ?
|
acetylcholine
|
|
|
Are sensory fibers afferent or efferent?
|
afferent
|
|
|
Somatic sensory fibers are found where?
|
skin, muscle, bone
|
|
|
Autonomic sensory fibers are found where?
|
internal organs
blood vessel walls |
|
|
What tissue in ventricles makes CSF?
|
choroid plexus
|
|
|
Dorsal root composed of?
|
sensory/afferent fibers
|
|
|
Ventral root composed of?
|
motor/efferent fibers
|
|
|
Sensory neuron cell bodies found where?
|
dorsal root ganglia
|
|
|
At the intervertebral foramen, dorsal and ventral roots fuse to form what?
|
spinal nerve
|
|
|
More white matter is found in what region of the spinal cord?
|
cervical region
|
|
|
Lateral horn grey found in what region of spinal cord?
|
thoracic and upper lumbar
|
|
|
Ventral horns are larger in what region of the spinal cord?
|
cervical and lumbosacral enlargement
|
|
|
Why is the lumbosacral enlargement so large?
|
contains cell bodies to innervate lower limb muscles
|
|
|
What are laminae?
|
layers of grey matter extending length of cord
|
|
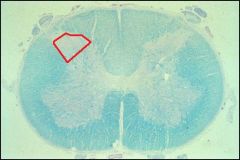
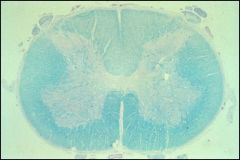
Red area in spinal cord picture is?
|
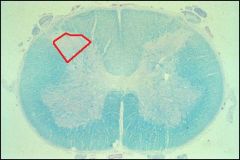
Substancia gelatinosa
|
|
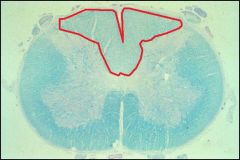
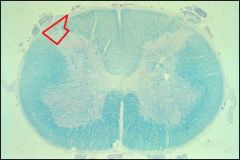
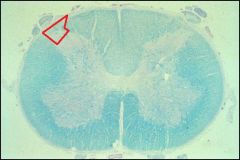
Area outlined in red is?
|
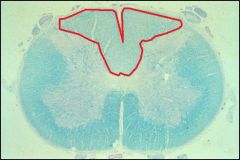
Dorsal funiculus
|
|
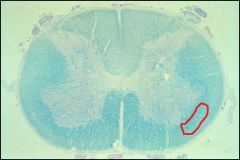
Area in red is the?
|
Spinothalamic tract
|
|
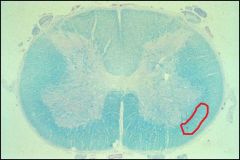
Area in red is the?
|
Dorsothalamic tract of Lissauer
|
|
This section is from what level of the spinal cord?
|
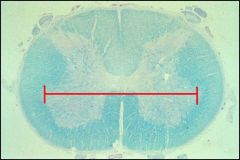
Lumbar
(large ventral horns) |
|
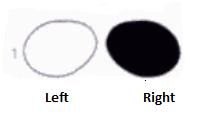
What lesion causes this visual field?
|
Right optic nerve lesion
|
|
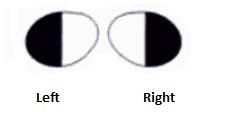
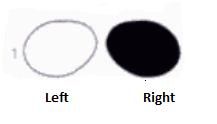
What lesions causes this visual field?
|
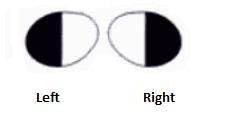
Lesion through optic chiasm
(bitemporal hemianopsia) |
|
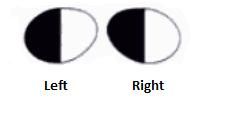
What lesion causes this visual field?
|
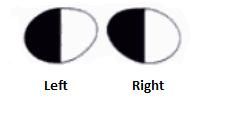
A lesion in the right optic tract
(contralateral hemianopsia) |
|
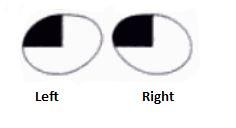
What lesion causes this visual field?
|
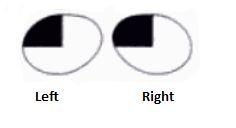
Lesion of optic radiation fibers curving into Meyer's loop
(upper contralateral quadrantic anopsia) |
|
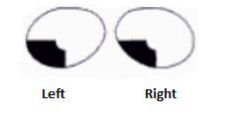
What lesion causes this visual field?
|
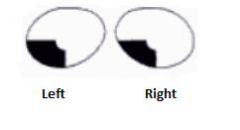
Lesion is in upper bank of calcarine sulcus
|
|
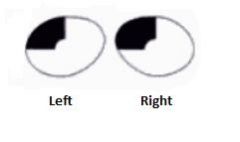
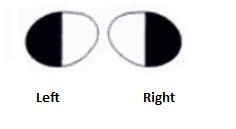
What lesion causes this visual field?
|
Lesion is in lower bank of calcarine sulcus
|
|
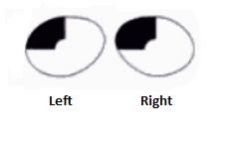
This visual field, together, results in what kind of vision?
|
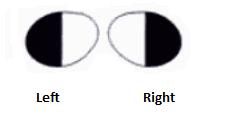
Tunnel vision
|
|
|
At the optic chiasm, what fibers cross?
|
NASAL fibers cross
TEMPORAL fibers do not cross |
|
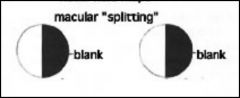
Macular splitting can occur where?
|
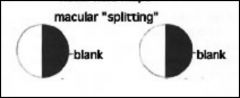
before or after the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN)
|
|
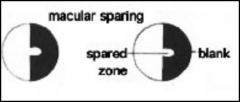
Macular sparing is commonly found where?
|
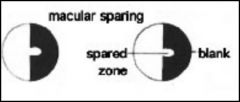
Lesions beyond the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN)
|
|
|
What is the lamina in the most dorsal part of the dorsal horn?
|
Lamina I
|
|
|
Lamina II corresponds to what?
|
substantia gelatinosa
|
|
|
Substantia gelatinosa receives what information?
|
pain and temperature afferents
|
|
|
Failure of posterior neural tube closure?
|
spina bifida
|
|
|
Failure of anterior neural tube closure?
|
anencephaly
|
|
|
What is the location of resting membrane potentials?
|
positive (+) charges outside of cell
negative (-) charges inside cell |
|
|
An increase in resting membrane potential, causing more negative charge?
|
hyperpolarization
|
|
|
A decrease in resting membrane potential causing more positive charge?
|
depolarization
|
|
|
Why is resting membrane potential negative?
|
outside of cell = 0, so inside is negative in comparison
|
|
|
The neuron lipid bilayer stores charges, acting as a ________?
|
capacitor
|
|
|
Depolarization followed by repolarization is called?
|
action potential
|
|
|
Depolarization causes?
|
Opening of voltage-gated K+ channels, becomes more permeable to Na+
|
|
|
Small depolarization after stimulation of presynaptic exitatory neuron?
|
Excitatory post-synaptic potential (EPSP)
|
|
|
Transient hyperpolarization of postsynaptic membrane after stimulation of presynaptic inhibitory neuron?
|
Inhibitory post-synaptic potential (IPSP)
|
|
|
NT binding causes depolarization and hyperpolarization of what receptors?
|
ionotropic
|
|
|
General somatic afferent (GSA) fibers carry?
|
pain, temperature, touch, proprioception from skin, muscle, joints
|
|
|
General visceral afferent (GVA) fibers carry?
|
pain, temperature, touch, proprioception from organs
|
|
|
General somatic efferent (GSE) fibers carry?
|
motor fibers to skeletal muscle
|
|
|
General visceral efferent (GVE) fibers carry?
|
pre- and post-ganglionic autonomic fibers
|
|
|
Preganglionic sympathetic cell bodies found?
|
intermediolateral column in lamina VII from T1-L2,3
|
|
|
Preganglionic parasympathetic cell bodies found?
|
Lamina VII in sacral spinal cord
|
|
|
Flaccid paralysis, weak/absent deep tendon reflexes, hypotonia are typical of lesions where?
|
lower motor neuron lesions
|
|
|
6 symptoms of lower motor neuron cell damage?
|
1. flaccid paralysis or paresis (weakness)
2. areflexia 3. hypotonia 4. atrophy 5. fibrillation 6. fasciculation |
|
|
Muscle contraction is normally an effective stimulus for this receptor?
|
Golgi tendon organ
|
|
|
What forms the Golgi tendon organ?
|
terminals of Ib primary afferent fibers wrapped around muscle tendon
|
|
|
What activates the Golgi tendon organ?
|
muscle stretch and muscle contraction
|
|
|
Viral disease that attacks lower motor neurons in the ventral horn of spinal cord?
|
Poliomyelitis (Polio)
|
|
|
Symptoms of polio?
|
flu-like symptoms followed by flaccid paralysis
|
|
|
Patient complains of sudden muscle weakness and sensory loss. Increases in intensity and frequency, then suddenly disappears. Diagnosis?
|
Multiple sclerosis
|
|
|
Signs of multiple sclerosis?
|
sudden attacks of paresis, vision loss, that partially clear
|
|
|
Bilateral loss of pain and temperature
ipsilateral flaccid paralysis leading to spastic paralysis? |
Brown-Sequard Syndrome
|
|
|
What is the Babinski sign?
|
Dorsiflexion of the big toe when the bottom of the foot is stroked
|
|
|
Upper motor neuron damage associated with what symptoms?
|
initial flaccid paralysis that changes to spastic paralysis or paresis over time
|
|
|
Spastic paralysis?
|
hypertonia
hyperreflexia Babinkski sign + Clonus |
|
|
Clonus is ?
|
involuntary contraction and relaxation of skeletal muscle
|
|
|
Patient has right lower facial muscle weakness...where is the lesion?
|
upper motor neuron
|
|
|
Afferent pupil defect, seen in swinging flashlight test, is caused by what lesion?
|
Optic nerve before optic chiasm
|
|
|
Symptoms of Bell's Palsy?
|
no tears, no saliva
ipsilateral paralysis of facial muscles hyperacusis- sensitive to noise |
|
|
What causes Bell's palsy?
|
CN VII (Trigeminal nerve) damage
|
|
|
Retinal detachment is most common between what layers (Boxer) ?
|
between pigment and photoreceptor layer
|
|
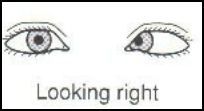
This eye defect is caused by?
|
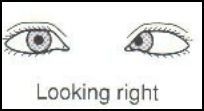
6th nerve (abducens) palsy in right eye
|
|
|
Cones mediate what?
|
color vision
high visual acuity |
|
|
Rods mediate what?
|
nocturnal vision
low visual acuity |
|
|
What part of the retina contains only cones?
|
macula
|
|
|
Miosis?
|
constriction of pupil
|
|
|
Mydriasis?
|
dilation of pupil
|
|
|
What nerve innervates the lateral rectus muscle?
|
abducens (CN VI)
|
|
|
What eye muscle does the trochlear nerve supply?
|
superior oblique
|
|
|
3 characteristics of damage to CN III?
|
down and out gaze
ptosis (droopy eyelid) pupillary dilation |

